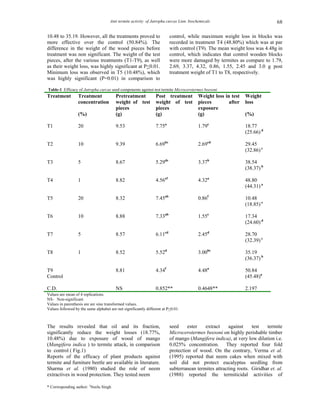
The study evaluated the anti-termite activity of Jatropha curcas oil and its toxic fraction against Microcerotermes beesoni termites. Wood blocks were treated with different concentrations (1%, 5%, 10%, 20%) of the oil and toxic fraction. Both treatments showed the highest protection at 20% concentration. Weight loss ranged from 18.77-48.80% for the oil and 10.48-35.19% for the toxic fraction. All treatments proved more effective than the control, with minimum weight loss of 10.48% for the toxic fraction at 20% concentration. The oil and toxic fraction demonstrated potential as natural termite control agents.