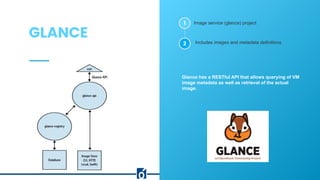
OpenStack is a cloud operating system that manages compute, storage, and networking resources in data centers through a user-friendly dashboard. Created in 2010 by Rackspace and NASA, it offers benefits like scalability, security, and open-source collaboration, while providing core services such as Nova for compute, Cinder for storage, and Neutron for networking. The architecture includes components like Keystone for authentication and Horizon for the user interface, making it a robust solution for cloud management.