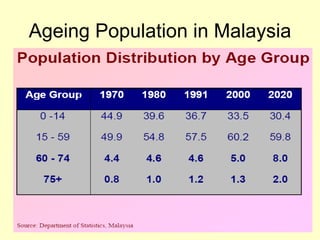
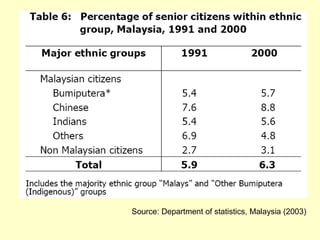
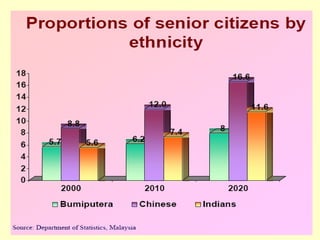
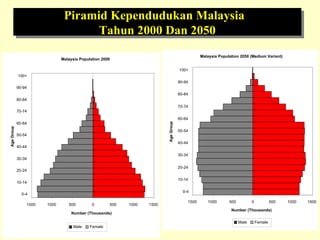
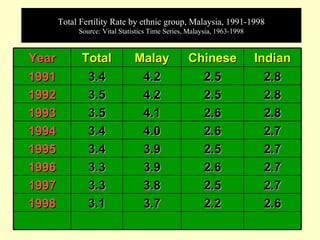
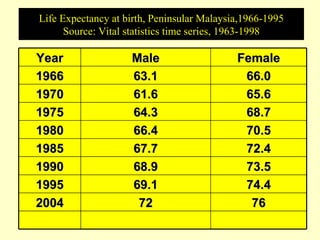
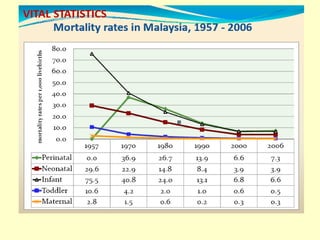
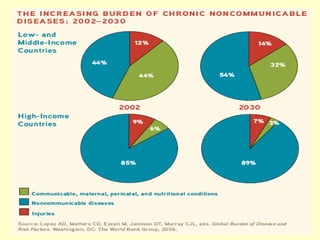
This document outlines geriatric health and aging issues in Malaysia. It defines key terms like geriatrics and gerontology. It then discusses Malaysia's aging population trends like increasing life expectancy and decreasing fertility rates. Common health problems among the elderly are also covered, such as multiple chronic illnesses, functional decline, and increased healthcare costs. The national policy for older persons aims to ensure their dignity, well-being, and access to opportunities as valued members of society.