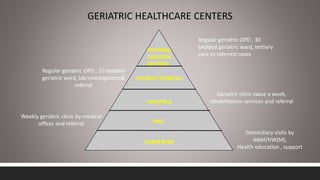
Geriatric health problems and programs in India
In 3 sentences:
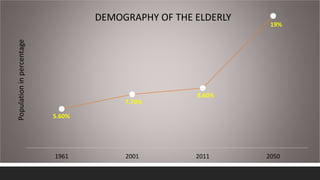
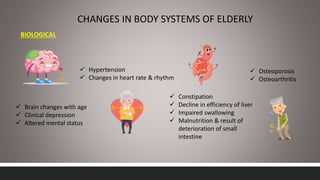
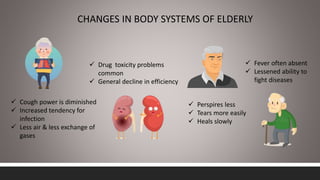
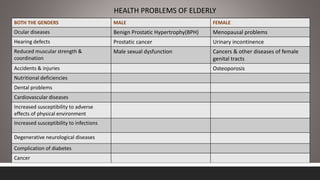
India has experienced rapid growth in its elderly population, projected to reach 19% of the total by 2050, bringing increased focus on geriatric health issues. Common health problems faced by the elderly include diseases of various body systems associated with aging as well as psychological and social issues. The government of India has established several policies and programs to promote healthcare, financial security, and welfare of the growing elderly population, including the National Policy on Older Persons, Maintenance and Welfare of Parents Act, and National Program for Health Care of Elderly.