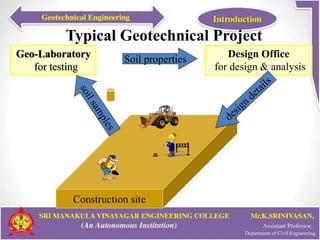
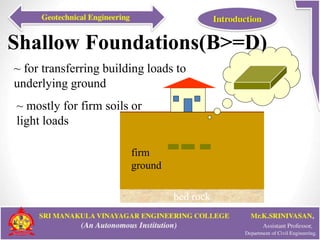
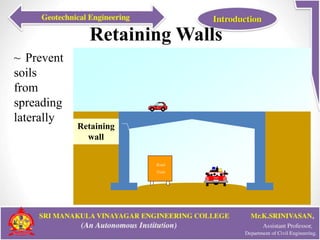
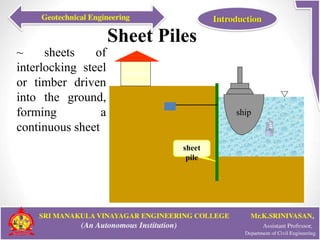
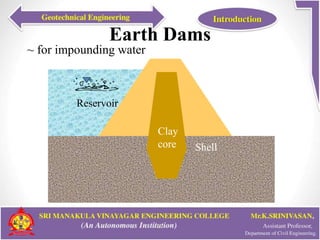
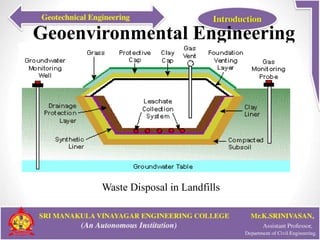
This document provides an introduction to geotechnical engineering. It defines soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering. It describes typical geotechnical projects which include investigating subsurface conditions, testing soil properties, and designing earthworks and foundations. It discusses shallow and deep foundation systems used to transfer building loads to the ground. It also describes retaining walls, excavation support systems, sheet piles, cofferdams, tunnels, earth dams, landslides, and mechanically stabilized earth walls. The document outlines geoenvironmental engineering topics and various soil testing and instrumentation methods. It discusses geotechnical engineering problems related to groundwater, excavations, earth slopes, and earthquakes. Finally, it presents various ground improvement techniques.