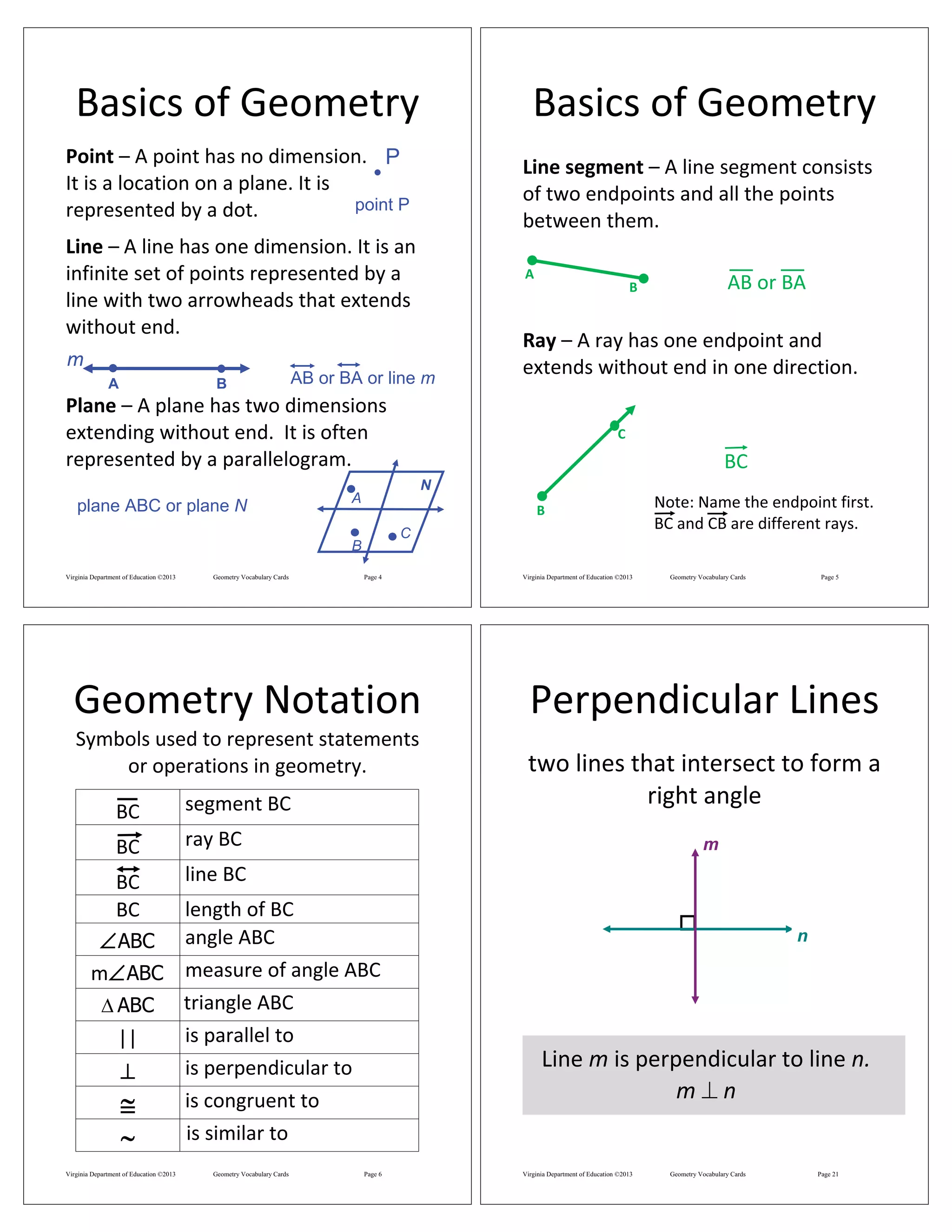
This document defines and illustrates key geometry terms including:
- Points, lines, planes, line segments, rays and their properties
- Notation used in geometry
- Relationships between parallel and perpendicular lines cut by a transversal
- Transformations including rotations, reflections, translations and dilations
- Properties of triangles such as angle sums, exterior angles, similarity, and key segments like altitudes and medians.