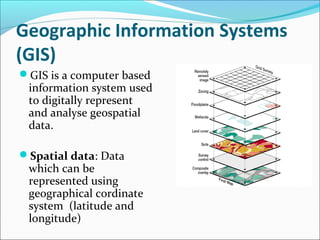
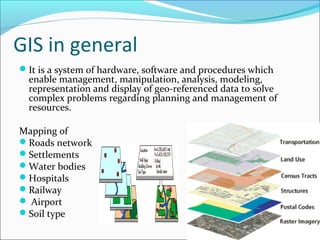
This document defines and describes the key concepts in geoinformatics. It begins by defining geoinformatics as the science and technology dealing with the acquisition, storage, processing, and dissemination of geographic information. The main branches of geoinformatics discussed are remote sensing, geographic information systems, cartography, global navigation satellite systems, photogrammetry, and database management systems. Remote sensing is defined as acquiring information about objects without physical contact, using sensors on platforms like aircraft and satellites. Geographic information systems are computer systems for storing, analyzing, and displaying geographic data. Cartography is the art, science, and technology of mapmaking.