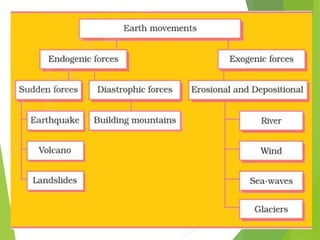
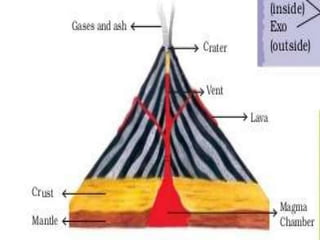
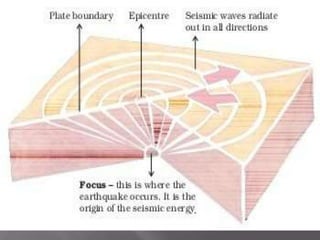
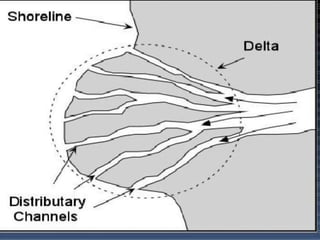
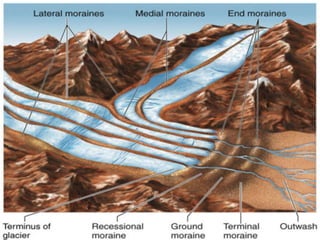
The document discusses different landforms created by geological processes. It describes exogenic and endogenic forces that shape the Earth's surface, including weathering, erosion, and the work of rivers, seas, ice, and wind. Specifically, it explains how rivers form meanders, ox-bow lakes, floodplains, and deltas, and how sea waves create sea cliffs, arches, and stacks by eroding coastal rocks. It also discusses how glaciers transport debris in moraines and how wind forms sand dunes and deposits loess in deserts.