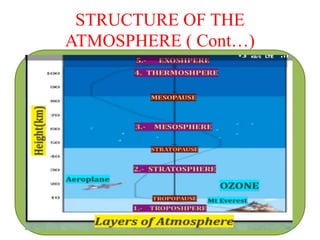
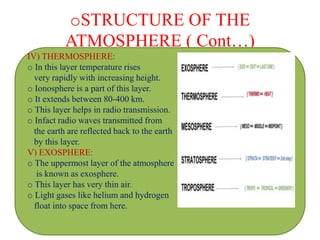
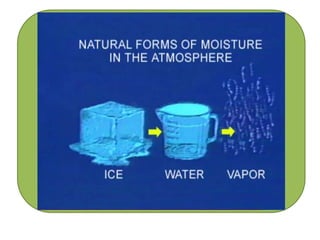
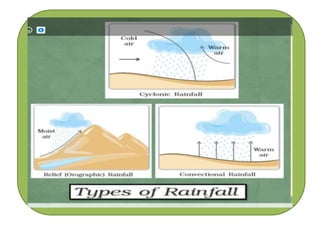
Air is a mixture of gases that makes up the Earth's atmosphere, which is essential for life as it regulates temperature and provides oxygen and protection from solar radiation. The atmosphere is composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen as well as smaller amounts of gases like carbon dioxide, and it is divided into layers with differing properties based on temperature and composition from the Earth's surface to outer space. Weather results from short-term changes in atmospheric conditions while climate describes average weather patterns over a longer period of time in a particular region.