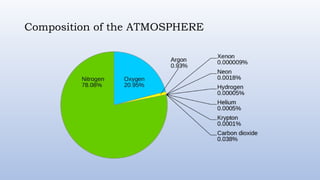
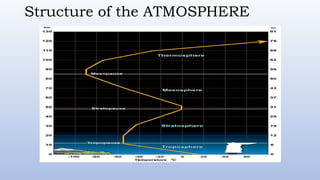
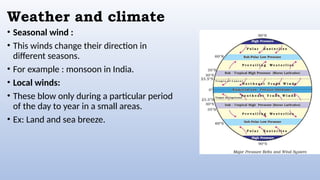
The document discusses the composition and structure of the atmosphere, highlighting gases like nitrogen and oxygen, as well as atmospheric layers such as the troposphere and stratosphere. It addresses weather and climate, detailing factors like temperature, air pressure, winds, humidity, and types of rainfall. The importance of rainfall for ecosystems and its role in maintaining balance in nature is also emphasized.