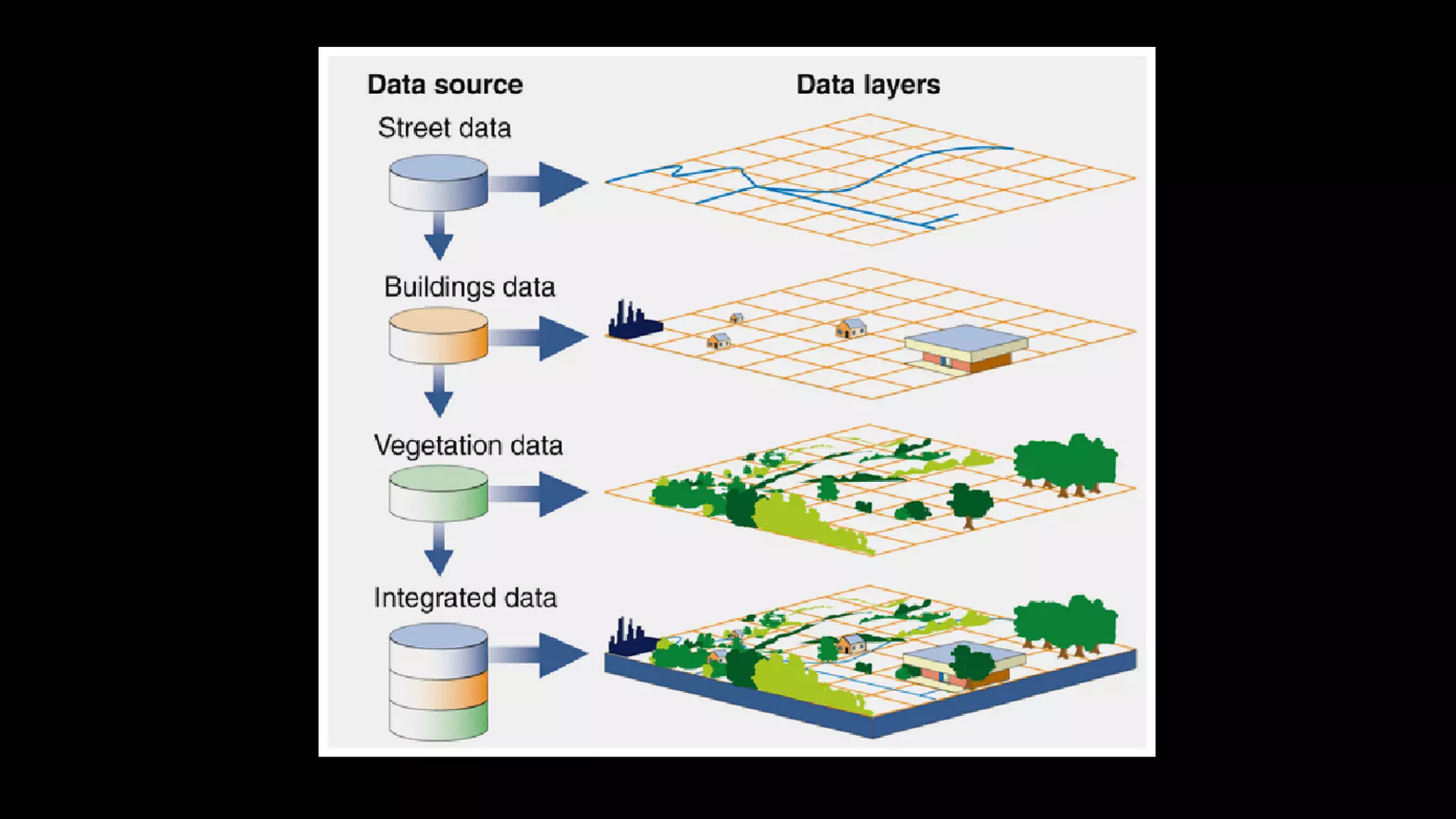
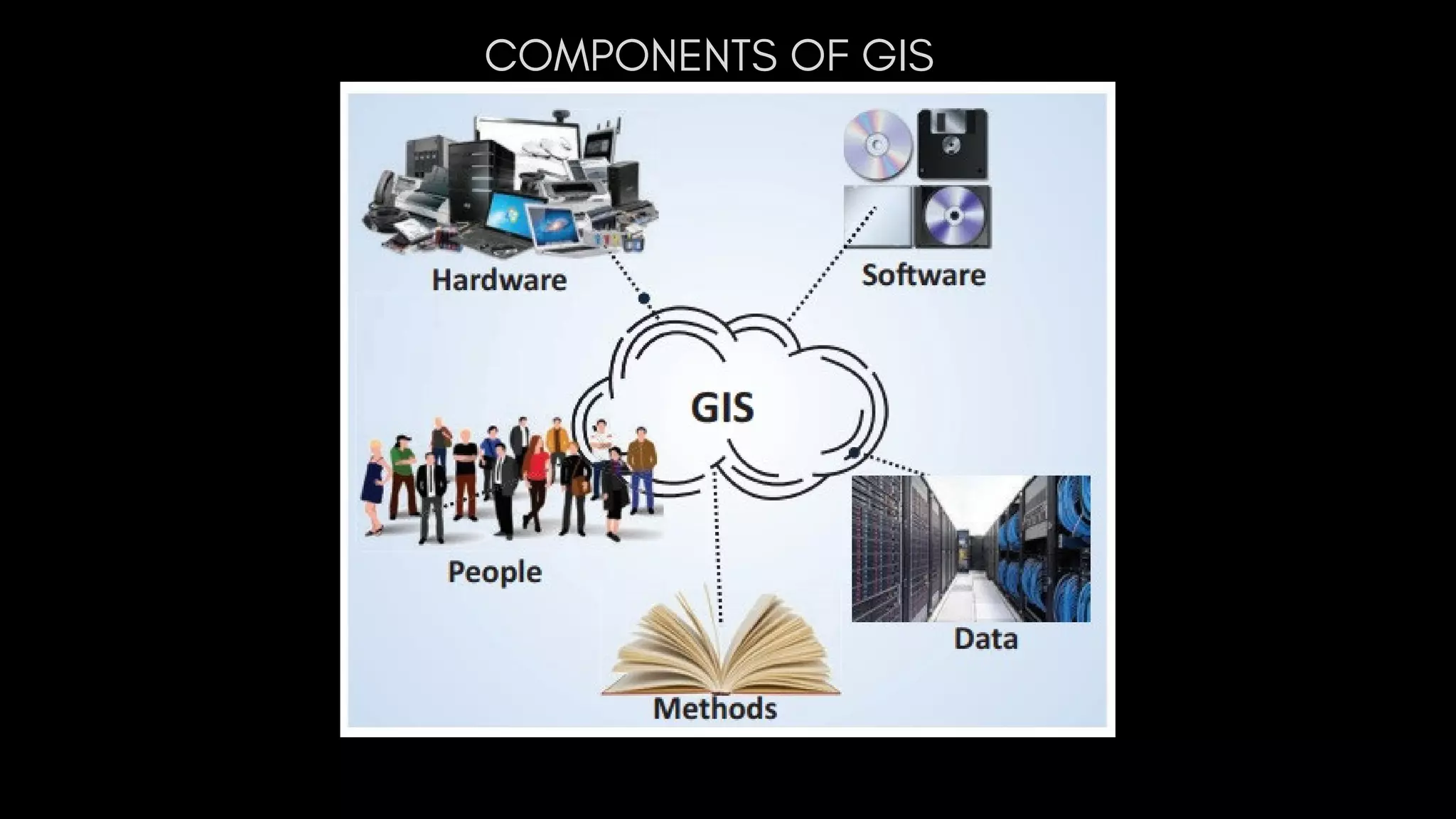
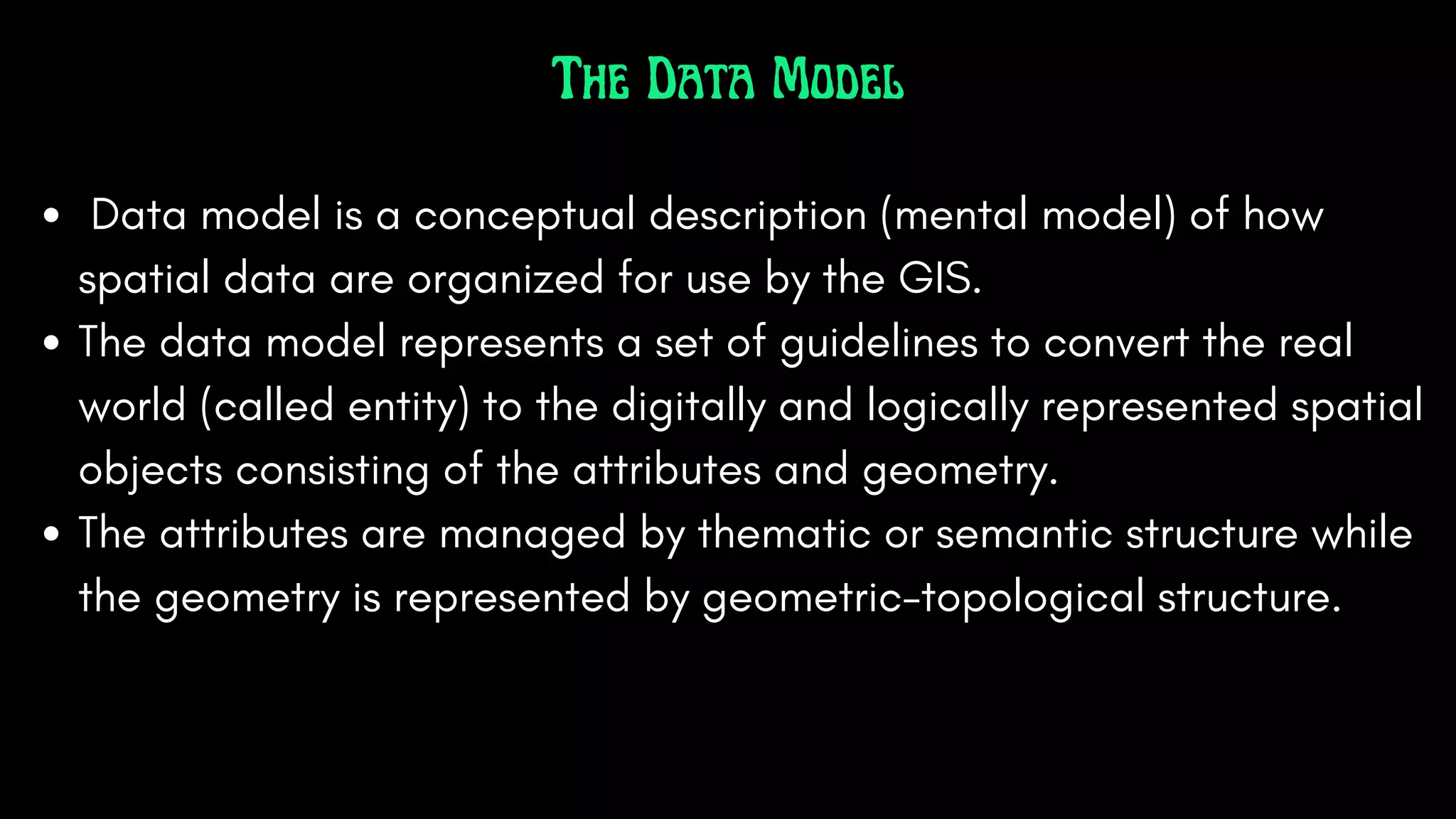
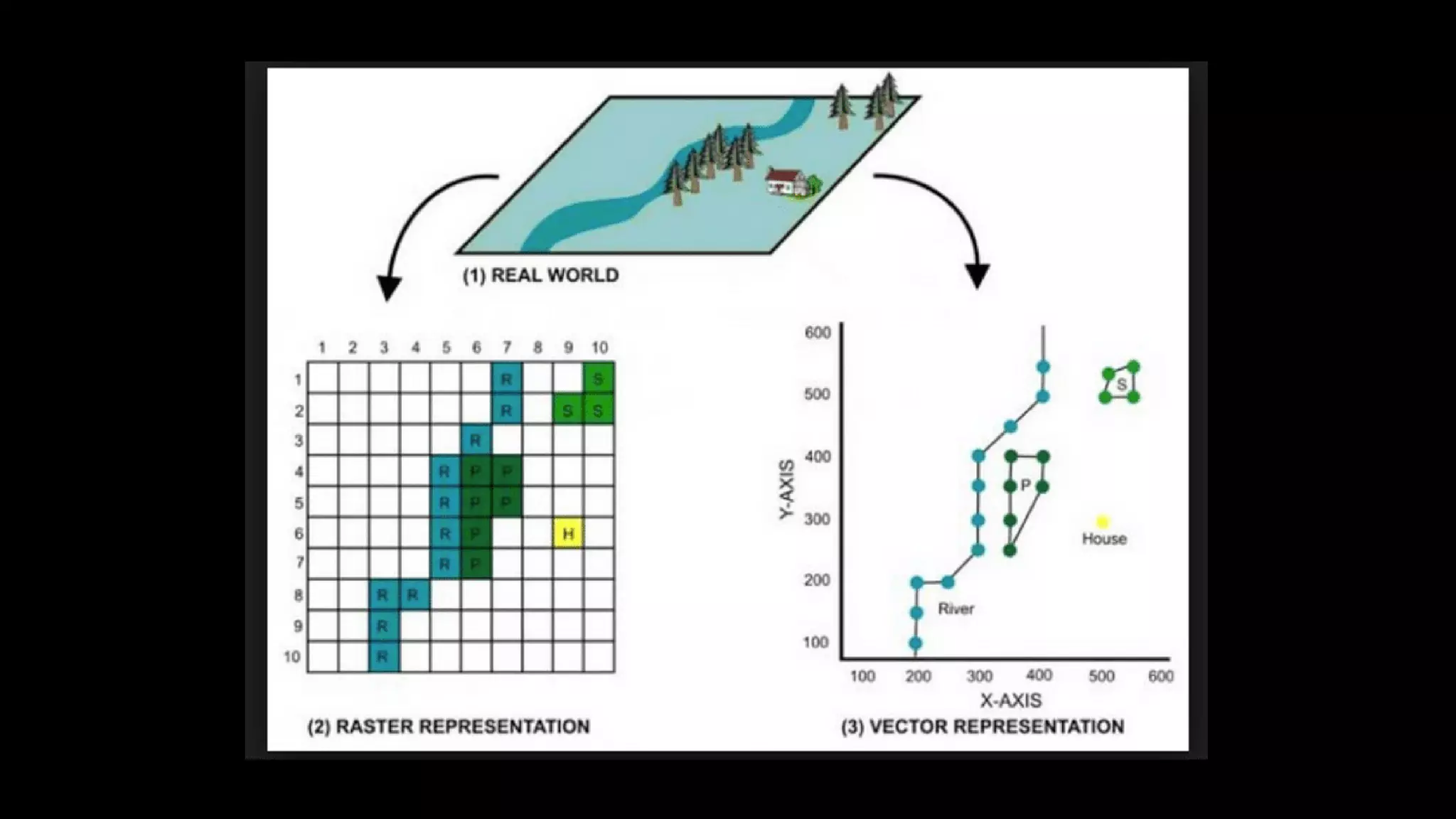
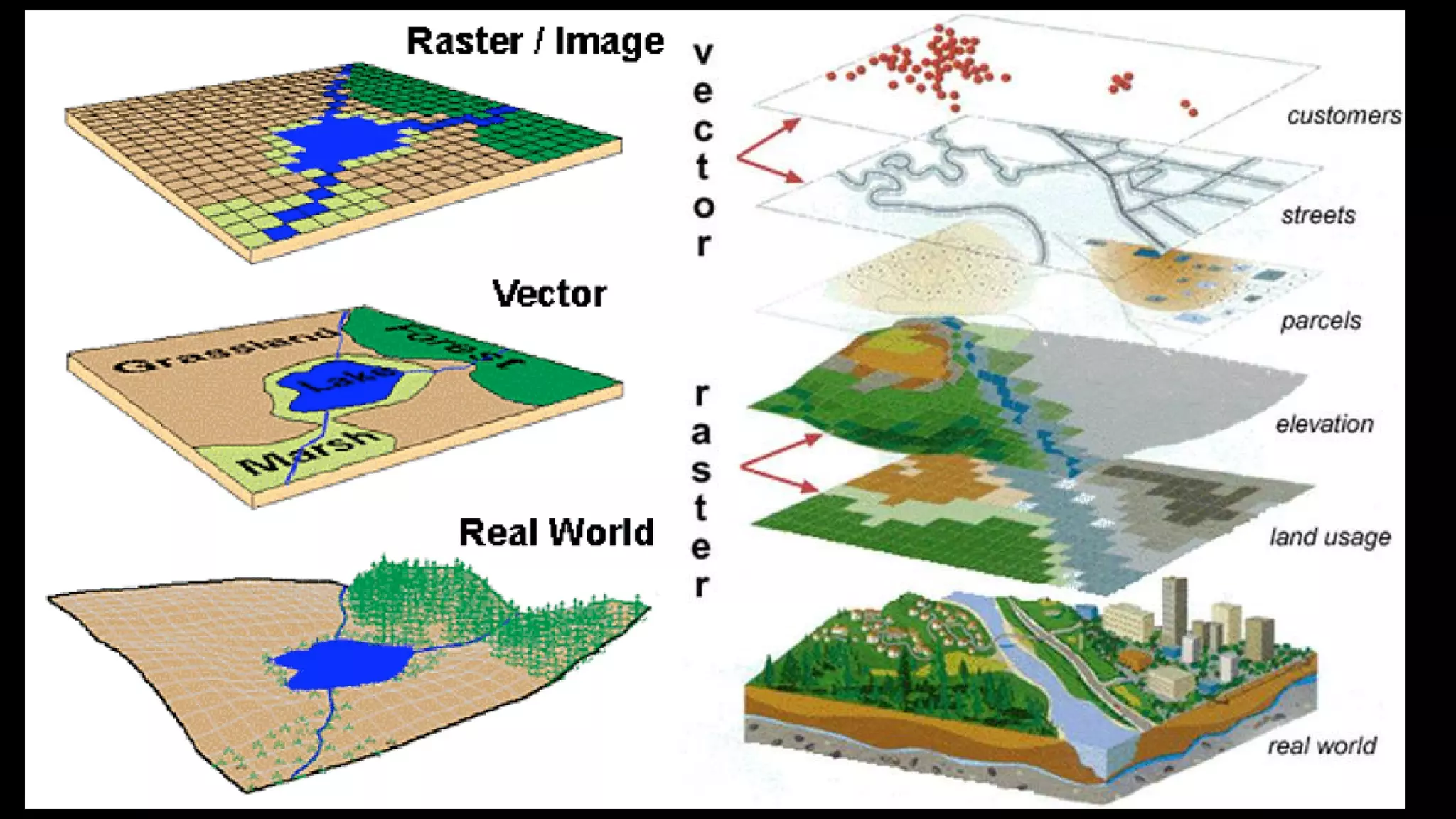
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) integrate hardware, software, data, people, and methods to capture, analyze, and visualize spatial data, supporting improved decision-making. GIS uniquely handles spatial information, allowing for precise geographic analysis and mapping that surpasses traditional methods. Various industries, including supply chain management, insurance, forestry, urban planning, banking, and public health, benefit from GIS technology for tasks such as risk assessment, resource management, and urban development.