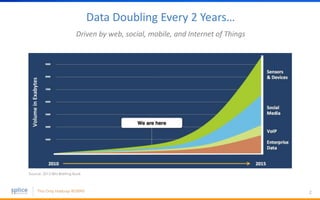
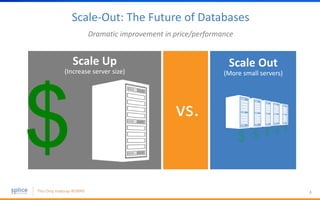
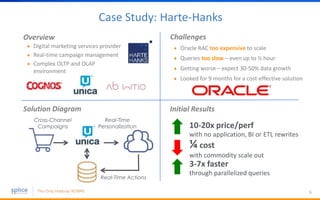
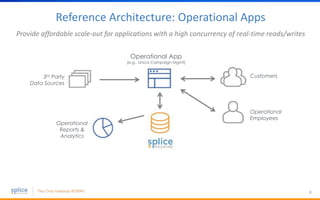
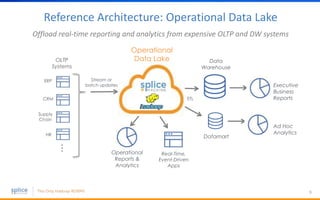
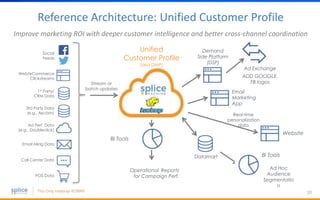
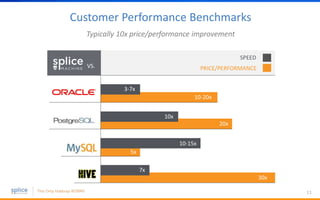
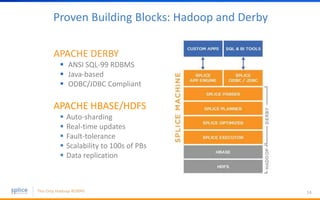
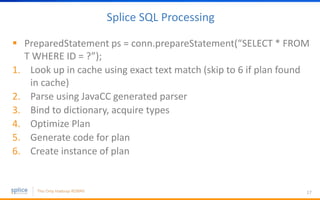
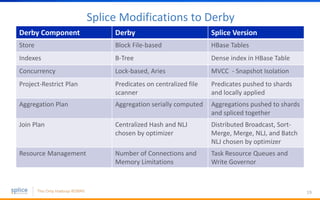
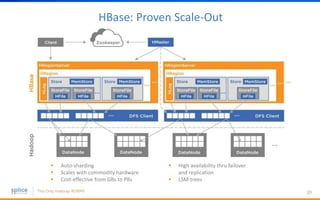
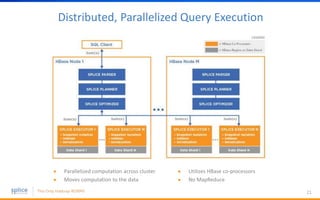
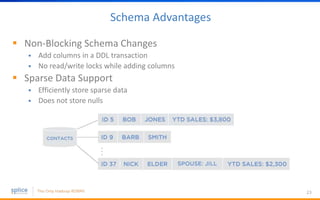
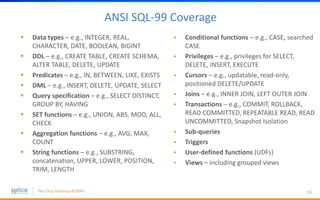
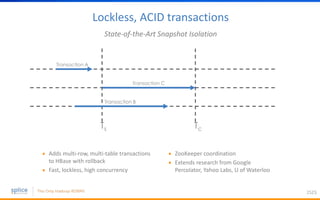
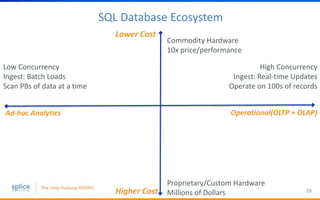
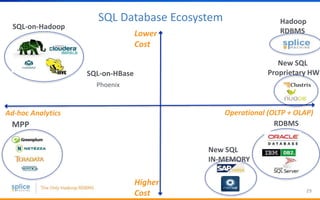
The document discusses the advantages of replacing traditional relational databases, like Oracle, with Hadoop-based scale-out SQL databases, emphasizing significant cost savings and performance improvements. It highlights successful case studies, particularly in digital marketing, where companies experienced 10-20x improvements in price/performance without the need for application rewrites. The document also details the underlying technology, features of the Hadoop RDBMS, and its operational benefits across various use cases.