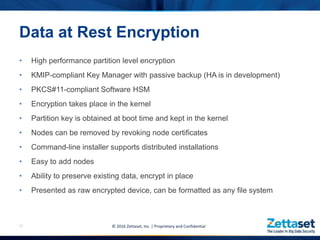
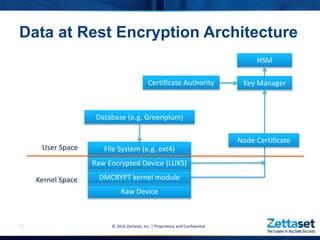
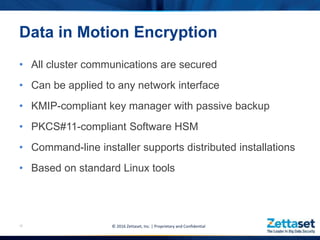
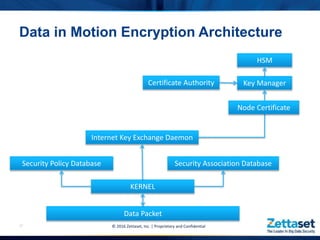
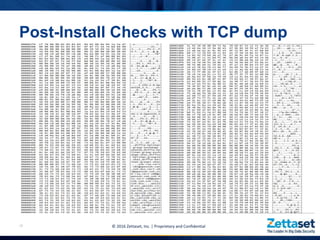
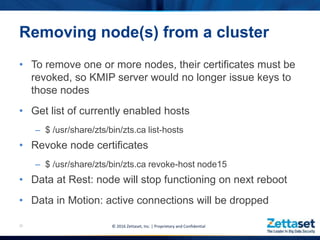
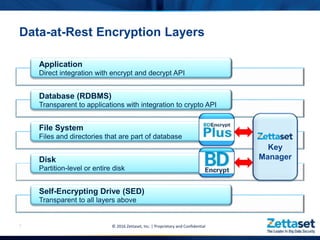
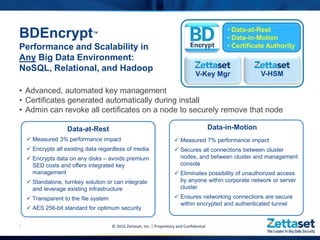
This document provides a comprehensive overview of Zettaset's big data encryption solutions, emphasizing their proprietary and confidential nature. It details the challenges addressed by Zettaset, including adapting to elastic cloud environments and enhancing key management processes. The encryption suite is designed for optimized performance, scalability, and security of data both at rest and in motion within distributed systems.






![11
Installer Architecture
Installer Host
node01 node02 node03
Inventory File
[hosts]
node01
node02
node03
SSH Trust
Package Deployment Configuration Deployment
© 2016 Zettaset, Inc. | Proprietary and Confidential](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bdepreso-161031011555/85/Zettaset-Elastic-Big-Data-Security-for-Greenplum-Database-11-320.jpg)