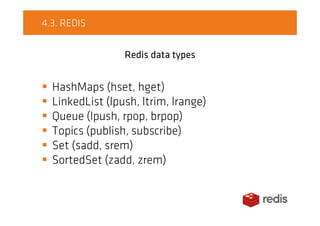
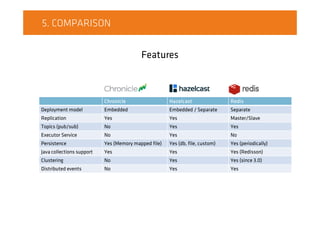
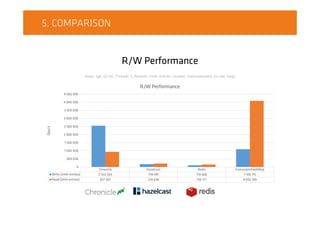
The document compares on-heap and off-heap caching options. It discusses using heap memory within the JVM versus off-heap memory outside the JVM using memory-mapped files, ByteBuffers, and Unsafe. Popular caching libraries like Chronicle, Hazelcast, and Redis are also summarized. Chronicle uses memory-mapped files for off-heap caching while Hazelcast supports on and off-heap and Redis is separate from the JVM process. Performance tests show Chronicle generally outperforming ConcurrentHashMap and Redis for write and read throughput.



![Objects on heap
Source: http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/j-codetoheap/
Integer (64-bit JVM): 7:1 (28 bytes)
9:1 (36 bytes)
Integer (32-bit JVM):
3:1 overhead ratio
16 bytes
String (32-bit JVM):
3.75:1
60 bytes
int[1]
2. HEAP MEMORY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/on-heapcachevsoff-heapcache-151021093203-lva1-app6892/85/JDD2015-On-heap-cache-vs-Off-heap-cache-Radek-Grebski-5-320.jpg)
![3. OFF-HEAP MEMORY
Off-heap (native) memoryJVM Process
OS memory
Other processes /
unallocated
byte[]
byte[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/on-heapcachevsoff-heapcache-151021093203-lva1-app6892/85/JDD2015-On-heap-cache-vs-Off-heap-cache-Radek-Grebski-6-320.jpg)
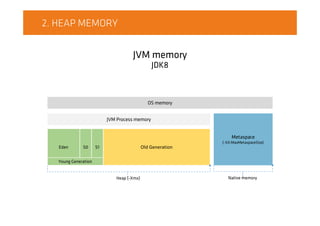
![3.1. MEMORY MAPPED FILE
Off-heap memoryJVM Process
OS memory
JVM Process
/tmp/myFile.dat
byte[]
byte[] byte[]
byte[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/on-heapcachevsoff-heapcache-151021093203-lva1-app6892/85/JDD2015-On-heap-cache-vs-Off-heap-cache-Radek-Grebski-7-320.jpg)

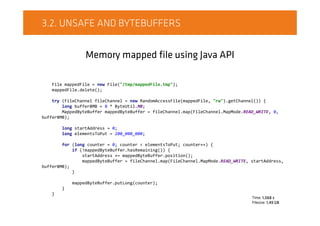
![3.2. UNSAFE AND BYTEBUFFERS
ByteBuffer.allocate ( <2GB )
JvmUtils.verifyJvmArgumentsPresent("-Xmx2g");
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) ByteUtil.GB);
byteBuffer.putChar('a') //2bytes, position =0
.putInt(123) //4bytes, position = 2(0 + 2(char))
.put("test".getBytes("UTF-8")); //6 => 2(char) + 4(integer)
byte[] bytesToBeReadInto = new byte["test".getBytes("UTF-8").length];
char charA = byteBuffer.getChar(/*address*/ 0); // 'a'
int int123 = byteBuffer.getInt(/*address*/ 2); //123
byteBuffer.position(6); //set cursor position
byteBuffer.get(bytesToBeReadInto); //"test" as byte[] read into "bytesToBeReadIntoRead"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/on-heapcachevsoff-heapcache-151021093203-lva1-app6892/85/JDD2015-On-heap-cache-vs-Off-heap-cache-Radek-Grebski-9-320.jpg)









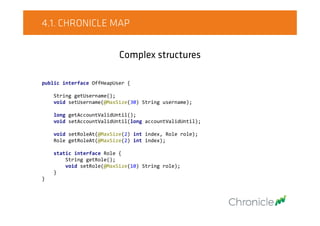

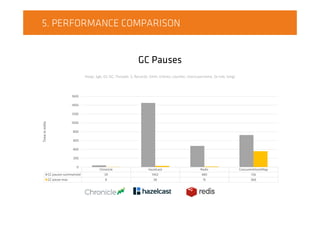
![4.1. CHRONICLE MAP
GC pauses
0,0
5,0
10,0
15,0
20,0
25,0
30,0
35,0
40,0
45,0
50,0
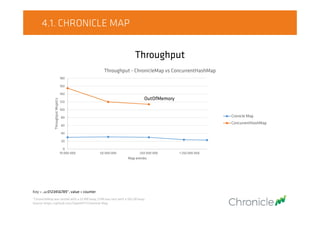
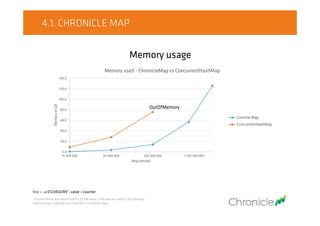
10 000 000 50 000 000 250 000 000 1 250 000 000
WorstGCpauseinseconds
Map entries
Worst GC pause [s] - ChronicleMap vs ConcurrentHashMap
Cronicle Map
ConcurrentHashMap
OutOfMemory
Key = „u:0123456789”, value = counter
*ChronicleMap was tested with a 32 MB heap, CHM was test with a 100 GB heap.
Source: https://github.com/OpenHFT/Chronicle-Map](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/on-heapcachevsoff-heapcache-151021093203-lva1-app6892/85/JDD2015-On-heap-cache-vs-Off-heap-cache-Radek-Grebski-26-320.jpg)
![Objects on heap
Source: http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/j-codetoheap/
Integer (64-bit JVM): 7:1 (28 bytes)
9:1 (36 bytes)
Integer (32-bit JVM):
3:1 overhead ratio
16 bytes
String (32-bit JVM):
3.75:1
60 bytes
int[1]
2. HEAP MEMORY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/on-heapcachevsoff-heapcache-151021093203-lva1-app6892/85/JDD2015-On-heap-cache-vs-Off-heap-cache-Radek-Grebski-27-320.jpg)

![4.2. HAZELCAST
Example
@Test
public void hazelcastClusterTest(){
Config hazelcastConfig = new Config();
HazelcastInstance hazelcastInstance1 = Hazelcast.newHazelcastInstance(hazelcastConfig);
HazelcastInstance hazelcastInstance2 = Hazelcast.newHazelcastInstance(hazelcastConfig);
Map<String, String> node1Map = hazelcastInstance1.getMap("someMapName");
Map<String, String> node2Map = hazelcastInstance2.getMap("someMapName");
node1Map.put("key", "value");
Assertions.assertThat(node2Map.get("key")).isEqualTo("value");
}
Output:
Members [2] {
Member [192.168.1.23]:5701 this
Member [192.168.1.23]:5702
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/on-heapcachevsoff-heapcache-151021093203-lva1-app6892/85/JDD2015-On-heap-cache-vs-Off-heap-cache-Radek-Grebski-29-320.jpg)





![3. OFF-HEAP MEMORY
Off-heap (native) memoryJVM Process
OS memory
Other processes /
unallocated
byte[]
byte[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/on-heapcachevsoff-heapcache-151021093203-lva1-app6892/85/JDD2015-On-heap-cache-vs-Off-heap-cache-Radek-Grebski-39-320.jpg)