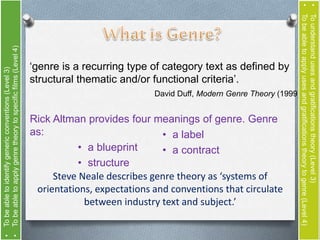
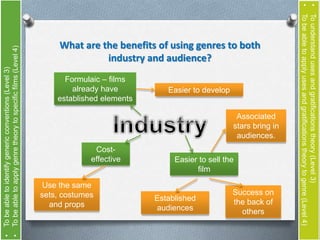
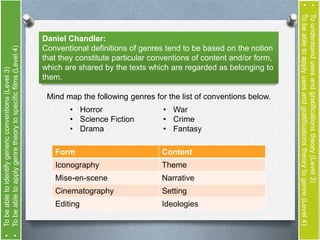
The document discusses genre theory and uses and gratifications theory in relation to film. It provides definitions of genre from theorists like David Duff and Rick Altman. Genre is described as providing benefits to both the film industry and audiences. Uses and gratifications theory holds that audiences engage with different genres to fulfill needs like information, social interaction, entertainment and more. The document examines genres like action, comedy and horror and asks the reader to analyze how audiences might benefit from engaging with different genres.