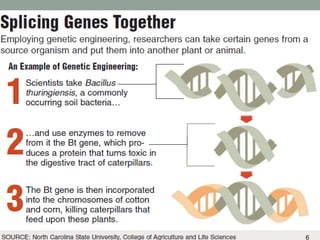
Genetically modified foods are created by altering the DNA of food crops. The top three reasons for genetic modification are to make crops resistant to herbicides, improve nutritional content, and increase crop yields. Potential benefits include lower costs for farmers and more durable, nutritious foods. However, critics argue that GM foods could lead to antibiotic resistance, new diseases, and harm the environment through gene transfer to weeds and loss of biodiversity. There is ongoing debate around labeling and regulation of genetically modified organisms in food.