This presentation demystifies Genetic Algorithms (GAs), a cornerstone of evolutionary computation, by breaking down their principles, processes, and practical uses. Structured for students, AI enthusiasts, and engineers, it systematically explains how GAs mimic natural selection to solve optimization problems efficiently.
Key Sections Covered:
1. Introduction to Genetic Algorithm:
- Definition: Formal explanation of GAs as search heuristics inspired by Darwinian evolution.
- Search Space: How GAs navigate problem landscapes to find optimal solutions.
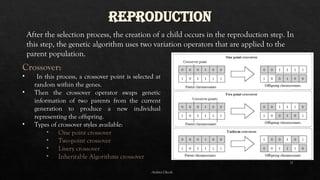
2. Genetic Algorithm Terminologies: Chromosomes, genes, populations, fitness functions, and other core concepts.
3. How Genetic Algorithms Work
4. Advantages & Disadvantages
Pros: Handles non-linear problems, parallelism, global optimization.
Cons: Computationally intensive, parameter sensitivity.
5. Applications:
- Real-world uses in machine learning, robotics, finance, logistics, and engineering design.
Summary of key takeaways and cited resources for further learning.
Why This PPT Stands Out?
✅ Beginner-Friendly: Simplifies complex ideas with clear definitions and examples.
✅ Visual Learning: Uses diagrams and flowcharts to illustrate workflows.
✅ Practical Focus: Highlights applications across industries.
✅ Structured Flow: Logical progression from theory to implementation.