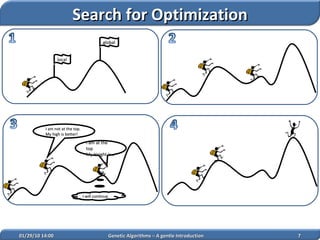
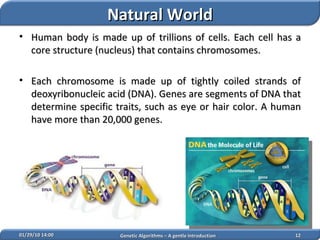
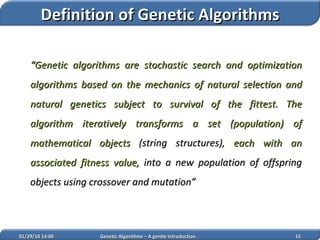
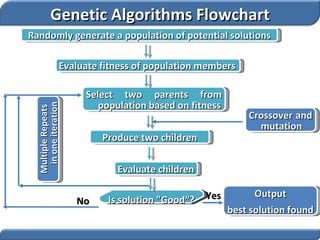
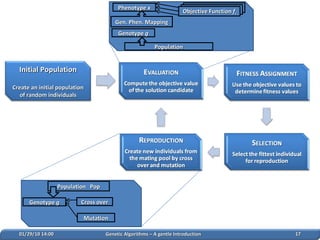
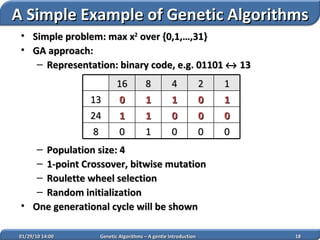
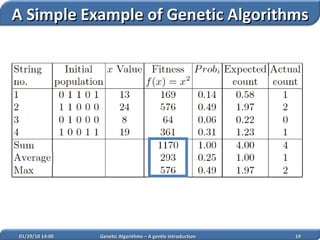
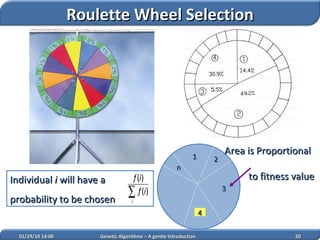
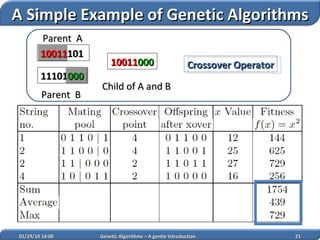
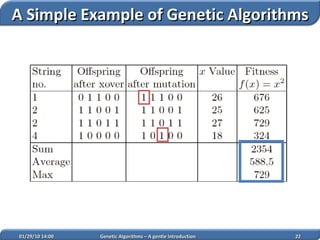
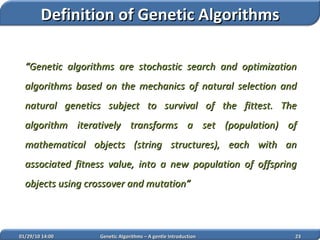
1. Genetic algorithms are stochastic optimization algorithms inspired by natural evolution that use operations like selection, crossover and mutation to evolve solutions to problems.
2. They work on a population of potential solutions, evaluating their fitness to survive and reproduce, with reproduction combining traits of parents to form new potential solutions over generations.
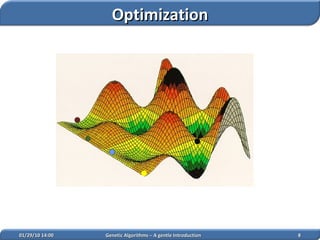
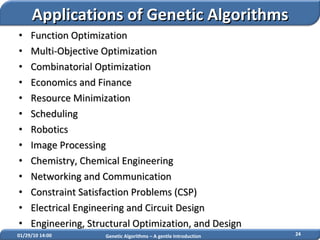
3. Genetic algorithms find wide applications in function optimization, multi-objective optimization, scheduling, image processing, engineering design and other domains requiring search and optimization.