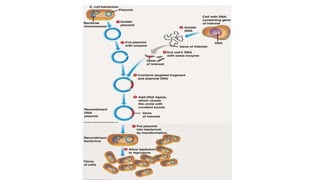
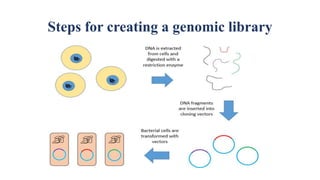
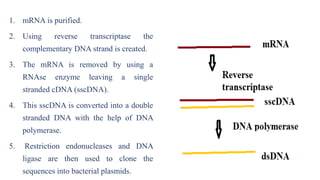
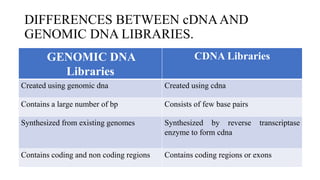
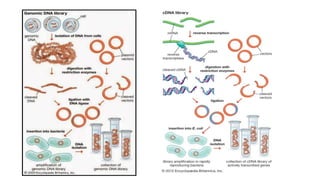
Gene cloning involves producing multiple copies of a gene using genetic engineering techniques. The main steps are: isolating the donor DNA fragment, inserting it into a vector, transforming host cells, and selecting recombinant cells containing the desired DNA insert. Gene cloning strategies include creating genomic DNA libraries, which contain all DNA from an organism's genome, and cDNA libraries, which contain only coding regions created from mRNA. Genomic libraries contain both coding and non-coding regions from genomes, while cDNA libraries contain only coding exons synthesized from mRNA using reverse transcriptase.