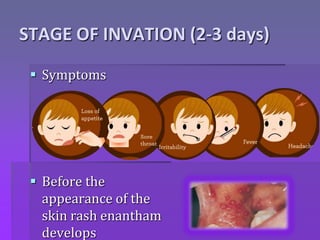
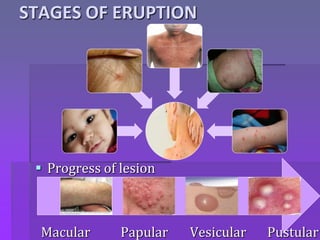
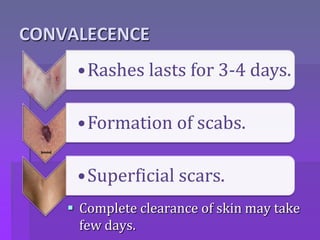
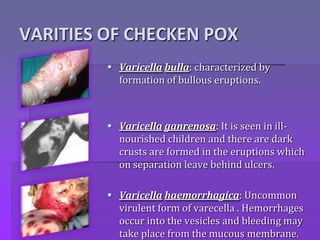
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella zoster virus and results in a primary infection called varicella (chickenpox) and recurrent infection called herpes zoster (shingles). The incubation period is 10-21 days. The virus spreads one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted, which is 5-7 days. The clinical presentation involves an invasion stage with symptoms, followed by a rash that progresses from macular to papular to vesicular to pustular lesions. Complications can involve the skin, respiratory system, kidneys, or be systemic. Diagnosis is usually based on the characteristic rash, but tests like PCR or antibody titers can also