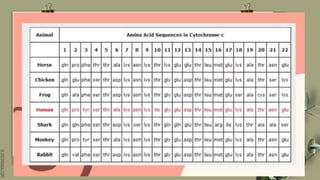
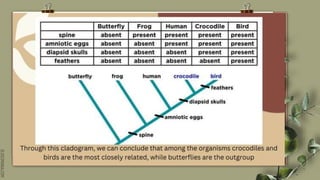
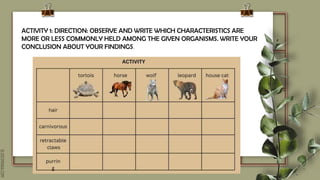
This document discusses using molecular evidence like amino acid sequences to infer evolutionary relationships between organisms. It focuses on cytochrome c, an important protein found in most organisms. Comparisons of cytochrome c amino acid sequences between species can reveal evolutionary relationships, as more similar sequences indicate more closely related species. Specifically, 37 of the 104 amino acids in human cytochrome c are found in the same positions as in other organisms, suggesting descent from a common microbial ancestor over two billion years ago. Phylogenetic trees and cladograms are also discussed as tools to visualize hypothetical evolutionary relationships between groups of organisms based on multiple lines of evidence.