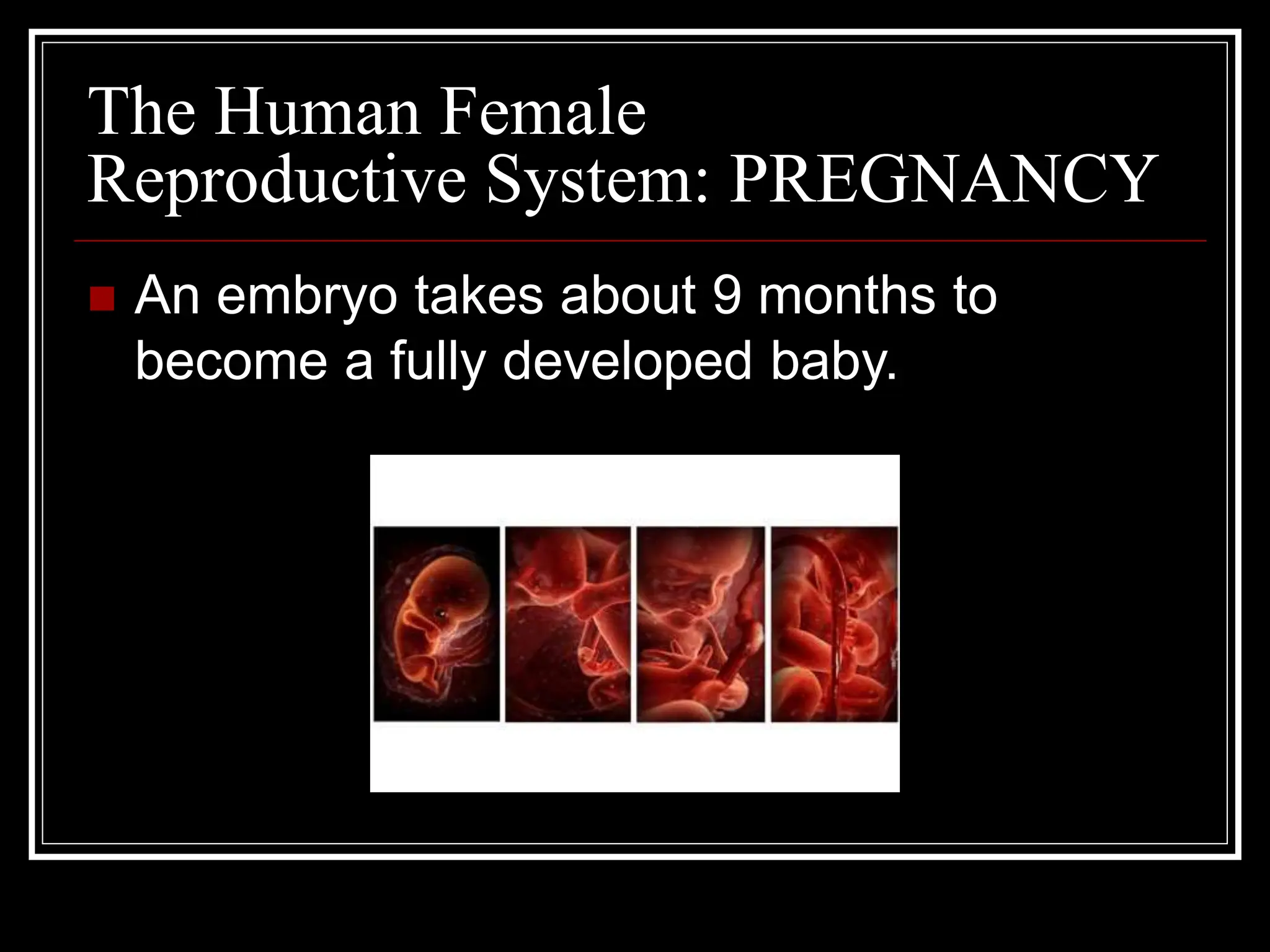
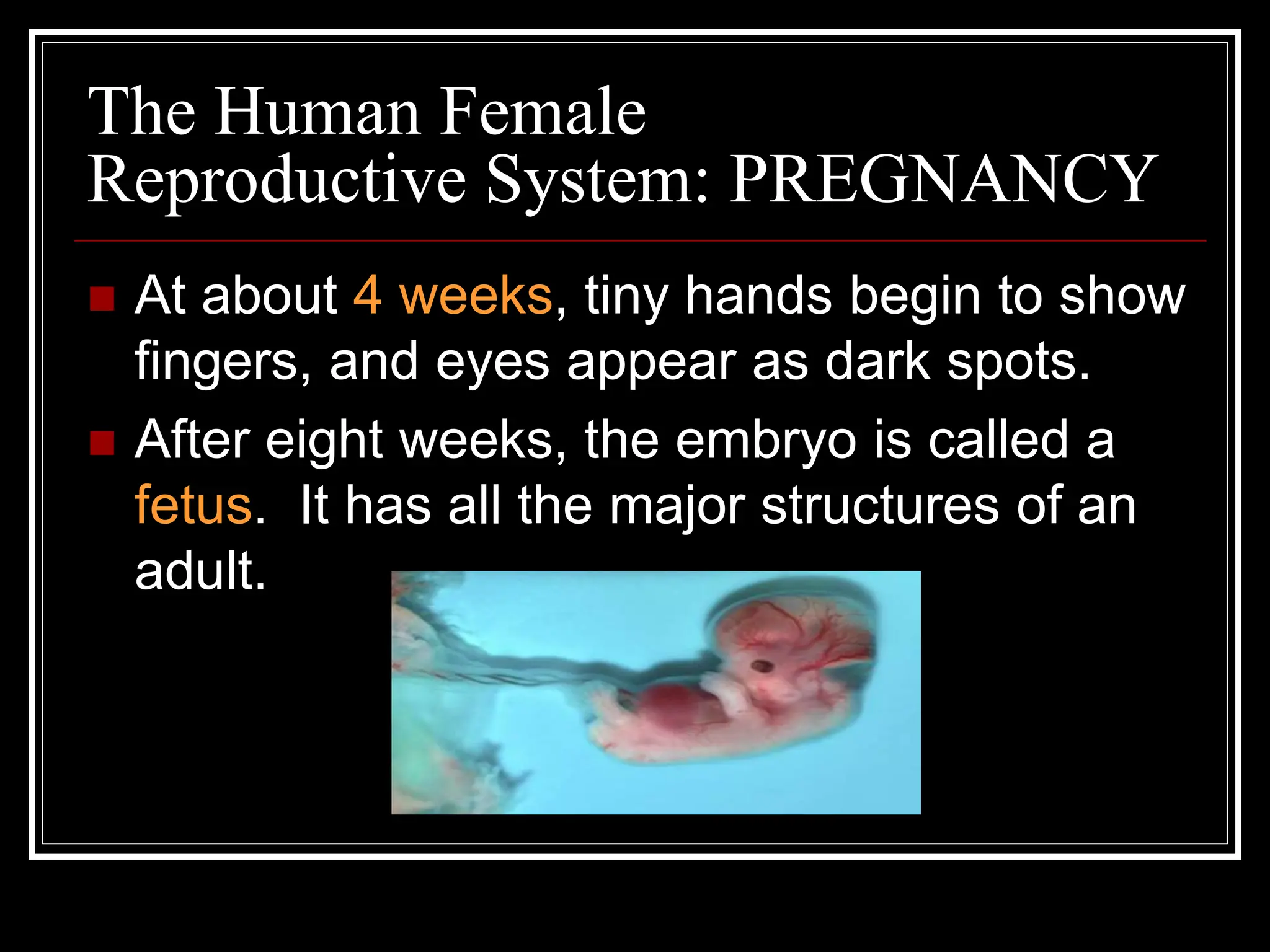
The document summarizes the human reproductive system and process of development from conception through birth. It describes that humans reproduce sexually through the fertilization of a female egg by male sperm. The fertilized egg then develops inside the female body over approximately 9 months until birth. Both male and female reproductive systems are described, including the production and release of eggs and sperm and the changes that occur during pregnancy, birth, and development of the offspring.