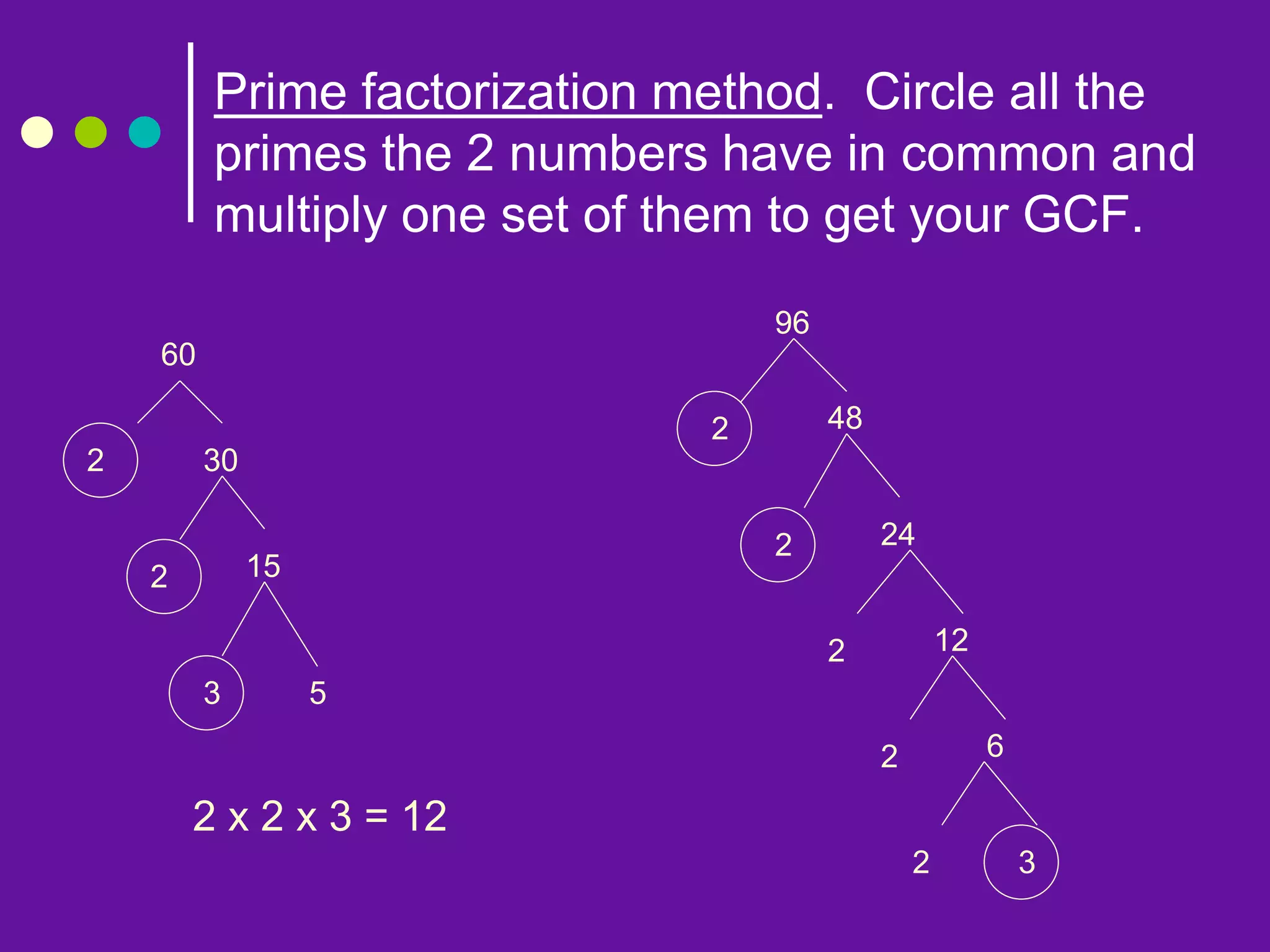
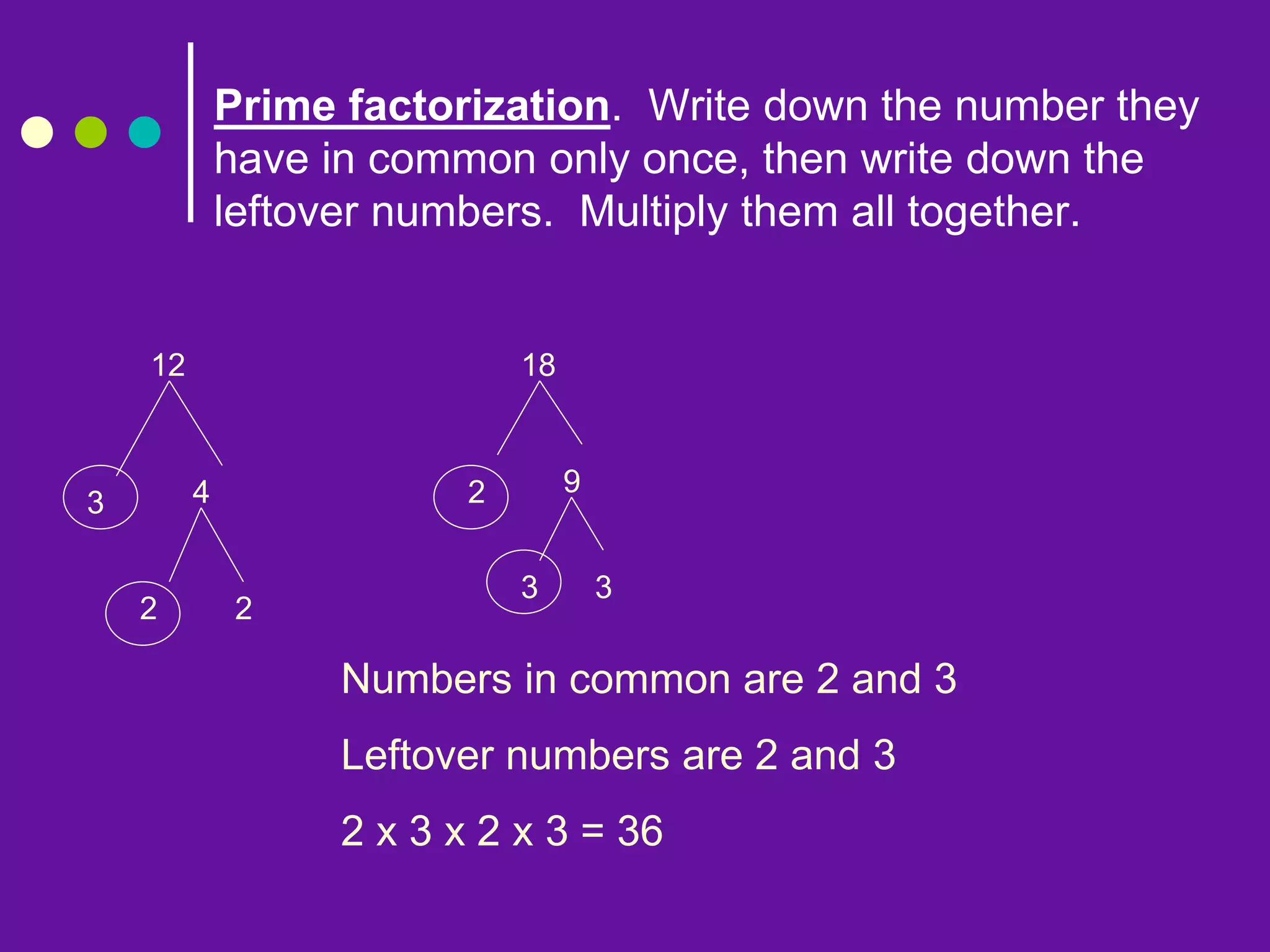
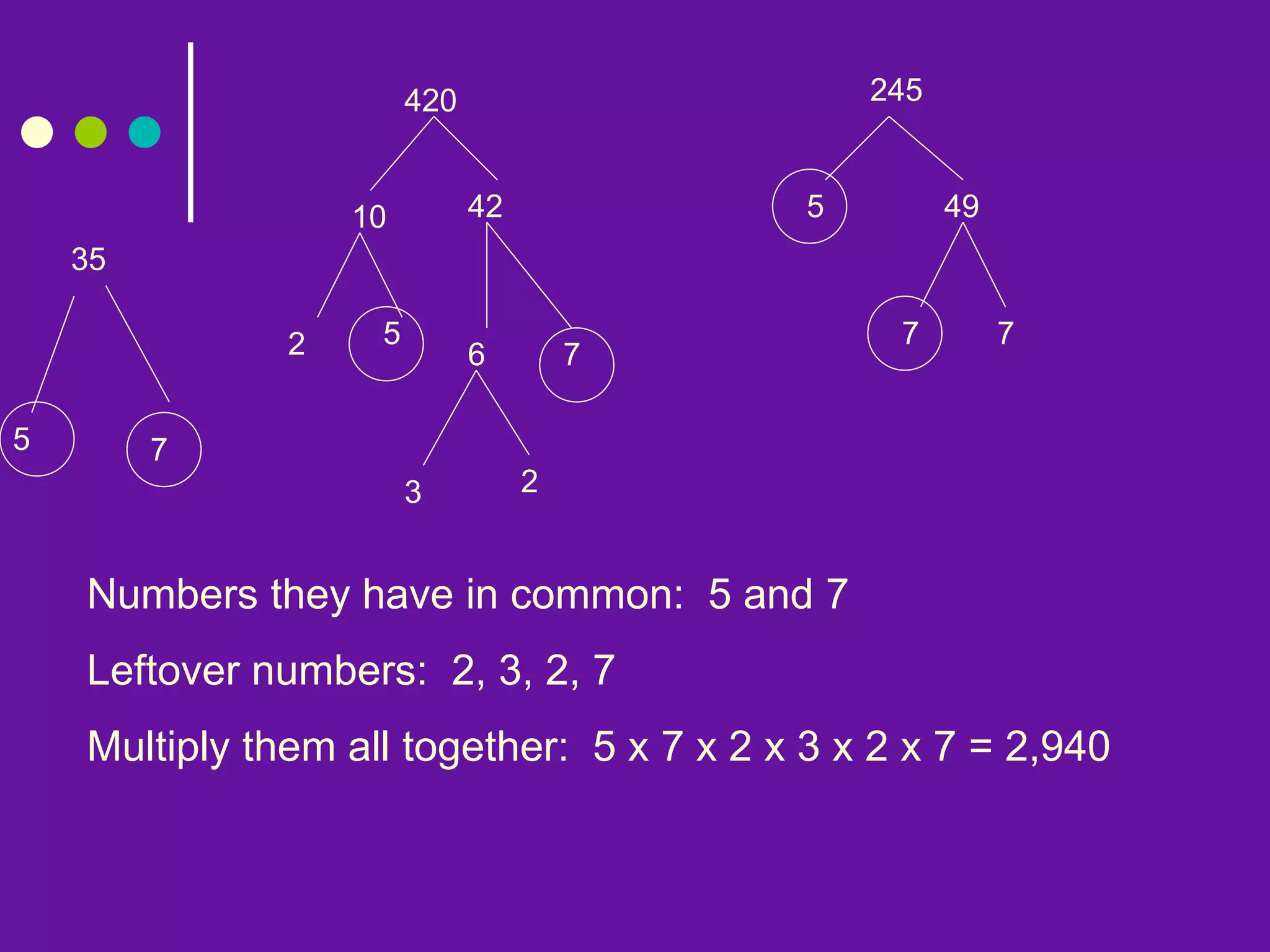
This document provides information about greatest common factors (GCF) and least common multiples (LCM). It defines what a factor and a multiple are, and gives examples of each. It then describes the three main methods for finding the GCF and LCM of two numbers: listing factors/multiples, prime factorization, and the ladder/birthday cake method. The document provides word problems to demonstrate when to use GCF versus LCM. It concludes with a quiz asking students to identify which concept is required to solve various word problems and to work through some example calculations.