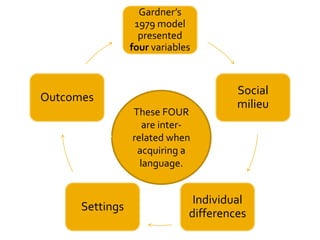
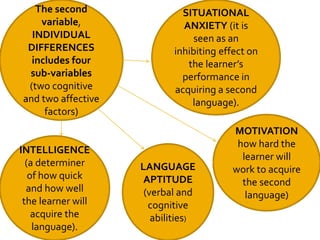
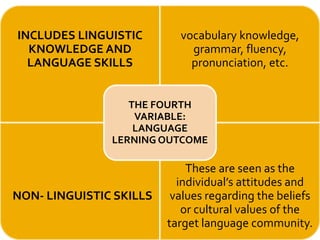
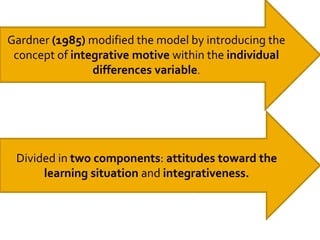
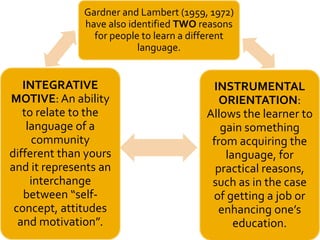
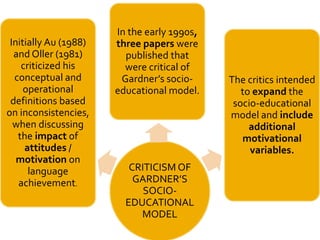
Gardner's socio-educational model of second language acquisition proposes that individual differences in ability and motivation impact language learning outcomes. The model involves four interrelated variables: social environment, individual differences in language aptitude and affective factors like motivation and anxiety, learning contexts both formal and informal, and linguistic and non-linguistic outcomes. Gardner later distinguished between instrumental and integrative motivation, with integrative motivation relating to identification with the target language community. While influential, the model has also received some criticism for its conceptual definitions and for not accounting for all relevant motivational variables.