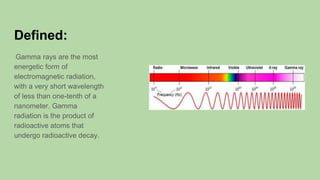
Gamma rays are the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, with very short wavelengths. They are produced during radioactive decay when the nucleus emits high-energy photons to rid itself of excess energy. Paul Villard discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted from radium. Gamma rays cause damage at the cellular level and can induce cancer or genetic damage from low levels of exposure or acute tissue damage at high levels.