This document summarizes a lecture on game theory given by Dr. D. B. Naik. The lecture covers the key concepts of game theory including the definition of a game, two-person zero-sum games, saddle points, pure and mixed strategies, dominance rules, solving for the value of a game using algebraic and graphical methods, and approximate iterative methods. Solution techniques discussed include sub-games, linear programming, and the simplex method. The document provides examples to illustrate the various game theory concepts and solution approaches.


![(7) Value of game for given Mixed Strategies of both
players
(8) Algebraic Method for 2x2 Mixed Strategy game
problems
(9) Methods to solve 2xN or Nx2 games :
[a] Method of sub-games
[b] Graphical Method
(10) Application of LP to solve game problem
(11) Iterative / Approximate Method to solve game
problem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-3-320.jpg)
![[ 1 ] What is a game ?
B
1 2 ……………. n
1
2
A .
.
m
Pij
Aim of A is to get maximum
A’s payoffs / gains
(Payoff Matrix)
Aim of B is to see that A gets minimum
Game Problems are problems of “Decision Making
Under Conflicts” or “Decision Making Under
Competitive Situations”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-4-320.jpg)
![[ 2 ] “Two Person Zero Sum” game
( i ) Two competitors.
( ii ) Finite number of strategies by both players.
( iii ) Play of game results when each competitor
chooses a single strategy or combination of
strategies.
( iv ) After both have chosen strategy / strategies,
their respective gains are finite.
( v ) Gain of one will be loss of other.
( vi ) Gain of a competitor depends on his action
as well as action of opponent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-5-320.jpg)
![[ 3 ] Solution of game means ?
( 1 ) Optimal (Best) strategies by both players.
( 2 ) Value of game when both players choose
optimal strategies.
V *
= Optimal value of game
= Expected gain of A if both the players use
their best strategies.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-6-320.jpg)
![[ 4 ] Saddle Point :B
1 2 3 4
1
A 2
3
−5 3 1 20
5 5 4 6
−4 −2 0 −6
Minima
−5
4
−6
5Maxima 5 4 20
Maximin
Minimax
(Maximum out of
Minimums.)
(Minimum out of
Maximums.)
Saddle Point is P23
∴ V* = 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-7-320.jpg)

![[ 5 ] Pure Strategy and Mixed Strategy
1 2
2 3
1
2
2 3
∴ V = 2
Pure Strategy Case
1 8
6 4
1
4
6 8
∴ 4 ≤ V ≤ 6
Mixed Strategy Case](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-9-320.jpg)
![[ 6 ] Dominance Rule
Dominance Rule is applied to reduce the size of game
problem.
j
i
k
If Pij ≥ Pkj for each j then
kth
strategy of A is deleted.
≤](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-10-320.jpg)
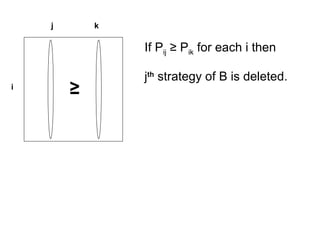
![[ 7 ] Value of game for given Mixed
Strategies of both players
B
(y1) (y2) (y3) (y4)
1 2 3 4
(x1) 1
A (x2) 2
(x3) 3
Pij
Mixed Strategy 3x4 game problem :
x1 + x2 + x3 = 1
y1 + y2 + y3 + y4 = 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-12-320.jpg)
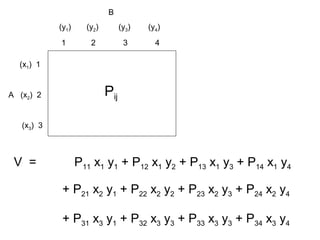
![[ 8 ] Algebraic Method for 2x2 Mixed
Strategy game problems
P11 P12
P21 P22
y1 y2
x1
x2
P11 x1 + P21 x2 ≥ V
P12 x1 + P22 x2 ≥ V
x1 + x2 = 1
P11 y1 + P12 y2 ≤ V
P21 y1 + P22 y2 ≤ V
y1 + y2 = 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-14-320.jpg)
![( )( )[ ] ( )( )[ ]
( ) ( ){ } ( ) ( ){ }[ ]12212211
12212211
PPPP
PPPP
V
+−+
−
=
( ) ( )
( ) ( )1211
2122
2
1
PP
PP
x
x
−
−
=
( ) ( )
( ) ( )2111
1222
2
1
PP
PP
y
y
−
−
=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-15-320.jpg)
![2 −1
−2 1
2 1
Solve following Game Problem :
−1
−2
−1 ≤ V ≤ 1
∴ Mixed Strategy
( )( )[ ] ( )( )[ ]
( ) ( ){ } ( ) ( ){ }[ ]2112
2112
−+−−+
−−−
=V
( ) ( )
( ) ( )12
21
2
1
−−
−−
=
x
x
( ) ( )
( ) ( )22
11
2
1
−−
−−
=
y
y
0
5
0
==
1
1
3
3
== ∴ x1 = ½, x2 = ½
2
1
4
2
== ∴ y1 = 1/3, y2 = 2/3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-16-320.jpg)
![[ 9 ] Methods to solve 2xN or Nx2 games :
[a] Method of sub-games
[b] Graphical Method
[a] Method of sub-games :
1
2
3
1 2
2 4
3 2
-2 6
2
2
-2
3 6
∴ 2 ≤ V ≤ 3
∴ Mixed Strategy
Dominance Rule
not applicable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-17-320.jpg)
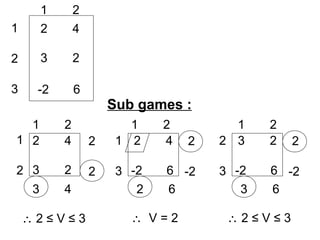
![1 2
1 2
1 2
1
2
1
3
2
3
2 4
3 2
2
2
3 4
2 4
-2 6
2
-2
2 6
3 2
-2 6
2
-2
3 6
( )( )[ ] ( )( )[ ]
( ) ( ){ } ( ) ( ){ }[ ]
66.2
3
8
4322
4322
==
+−+
−
=V
V = 2
( )( )[ ] ( )( )[ ]
( ) ( ){ } ( ) ( ){ }[ ]
44.2
9
22
2263
2263
==
+−−+
−−
=V
∴V* = 2.66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-19-320.jpg)
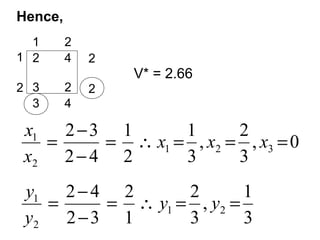
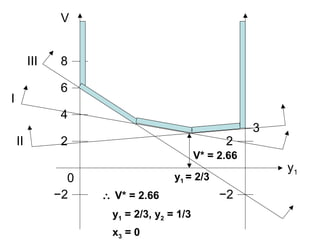
![[b] Graphical Method
1
2
3
1 2
2 4
3 2
-2 6
2y1 + 4y2 ≤ V
3y1 + 2y2 ≤ V
−2y1 + 6y2 ≤ V
y1 + y2 = 1
∴ 2y1 + 4 (1−y1) ≤ V
3y1 + 2 (1−y1) ≤ V
−2y1 + 6 (1−y1) ≤ V
∴ V + 2y1 ≥ 4
V − y1 ≥ 2
V + 8y1 ≥ 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-21-320.jpg)
![[ 10 ] Application of LP to solve game problem
−2 3 4
−1 4 −3
3 −4 5
3 4 5
−2
−3
−4
−2 ≤ V ≤ 3
Add +3 to each element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-23-320.jpg)
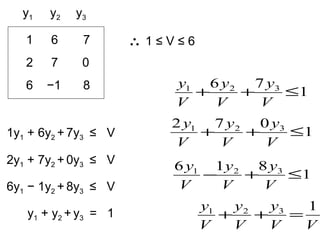


![[ 11 ] Approximate method / Method of Iteration
1 6 7
2 7 0
6 −1 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gametheory-lecture-140806215234-phpapp01/85/Game-theory-lecture-27-320.jpg)

