The document discusses the assignment problem and provides examples of solving it using different methods. It can be summarized as:
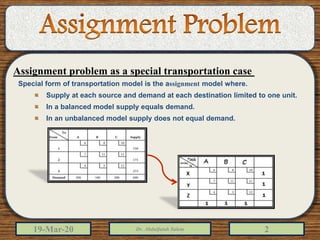
1) The assignment problem involves allocating tasks or jobs to workers or machines in the most efficient way, often to minimize costs. It has special characteristics as each job can only be assigned to one worker.
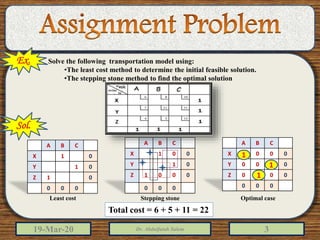
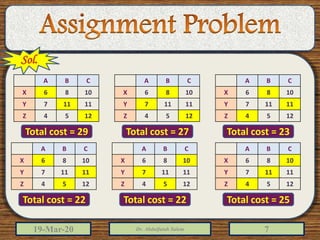
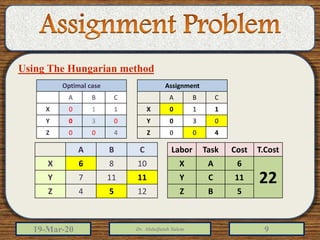
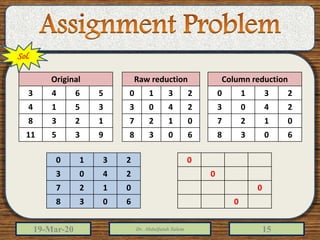
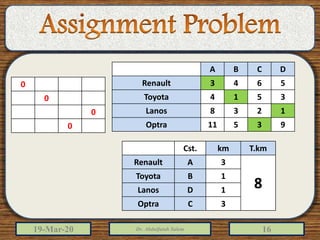
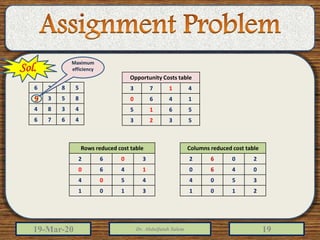
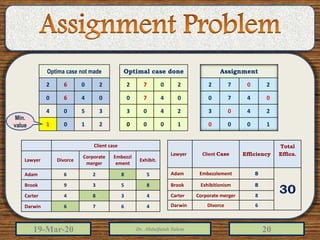
2) The document provides examples of solving assignment problems using methods like the least cost method, stepping stone method, and the Hungarian method.
3) It also discusses how to model assignment problems as transportation problems and how to solve maximization versions by converting to minimization problems.