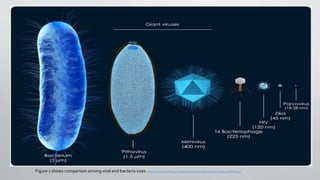
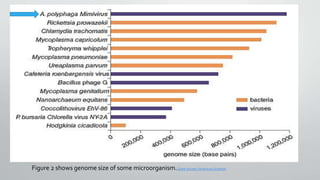
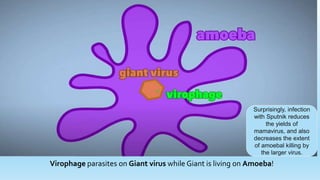
The document discusses the discovery and characteristics of giant viruses, which are significantly larger than typical viruses and possess complex genomes, raising questions about their role in ecology and medicine. It details their history, comparison of sizes and genomes with other microorganisms, and their peculiar interactions, such as virophages that infect giant viruses. The document concludes with ongoing research into their impact on human health and evolutionary origins.