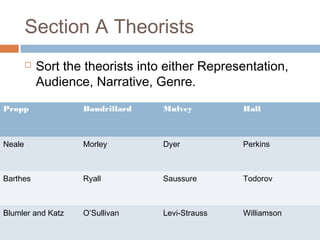
1) The document provides guidance and sample questions for a media exam, outlining the two sections and what will be required for each. Section A focuses on discussing the student's coursework and progression, while Section B involves analyzing representations of collective identity.
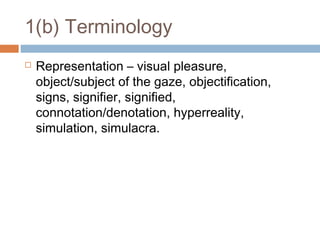
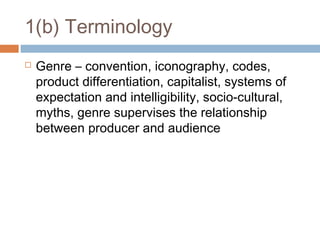
2) Key advice includes using specific examples from coursework, showing conceptual understanding, and balancing theory and textual analysis when answering questions. Theorists are provided for each section to help students incorporate relevant ideas.
3) Time management is important, with students advised to spend an hour on each section, using terminology appropriately, and demonstrating learning across their A-Level studies in responses.