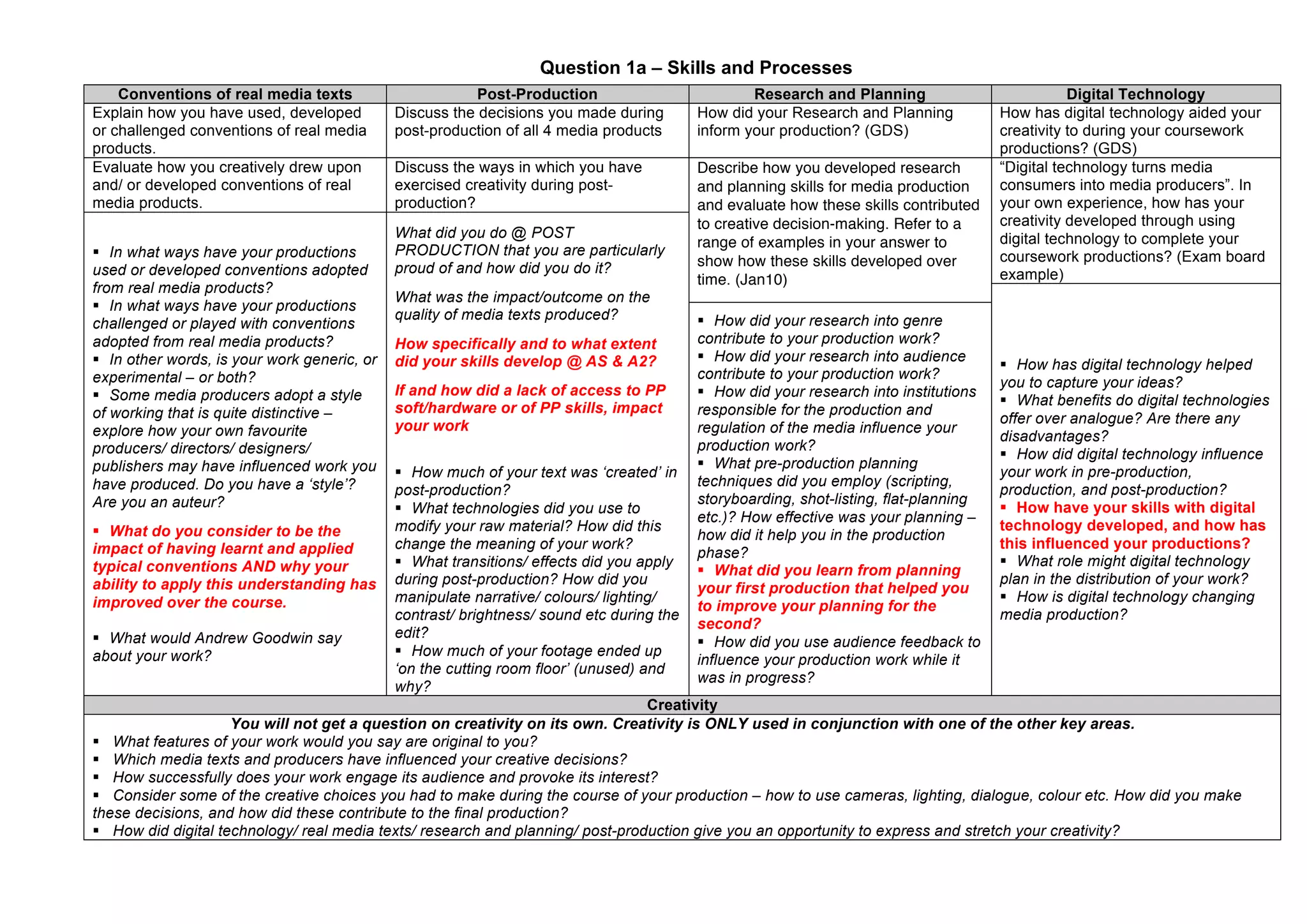
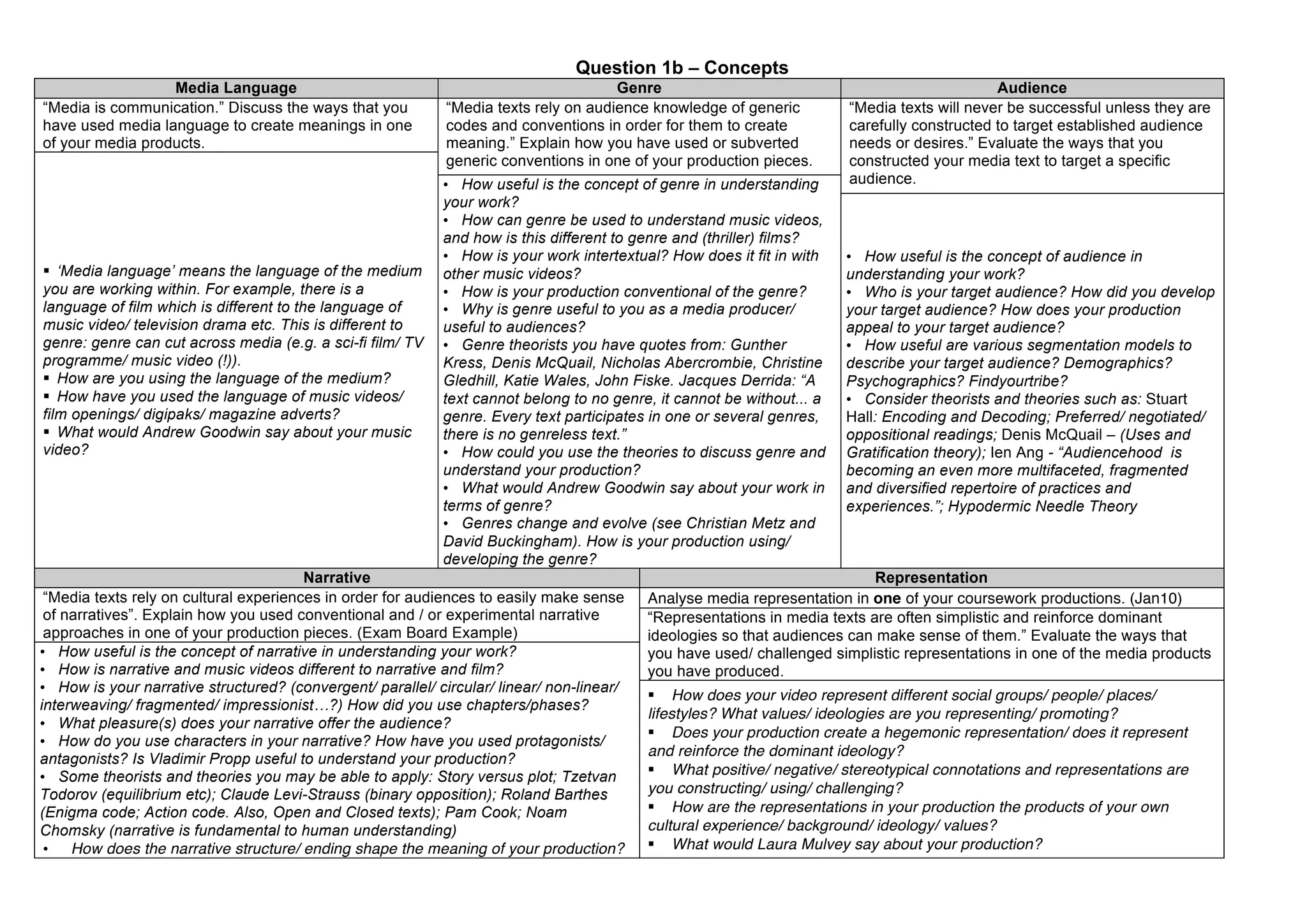
The document contains questions about media concepts and skills used in media coursework productions. It asks the student to discuss concepts like media language, genre, audience, narrative, and representation in their work. It also prompts the student to reflect on how they developed skills like research and planning, digital technology use, post-production techniques, and creativity over the course of their AS and A2 studies. The student is asked to provide examples from their productions and evaluate how these concepts and skills were applied and developed.