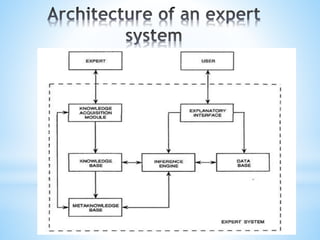
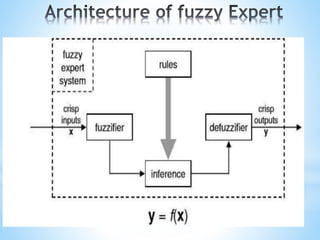
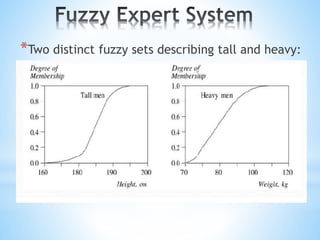
The document discusses fuzzy expert systems, including their components, knowledge representation, and applications. It describes fuzzy expert systems as using fuzzy rules, fuzzy logic, and fuzzy sets to represent knowledge. The key components are a knowledge base containing fuzzy production rules, an inference engine that uses fuzzy logic to make inferences, and an interface that allows users to engage with the system. Fuzzy expert systems can be applied in various domains like agriculture, sports, and engineering to provide expert advice and solutions.