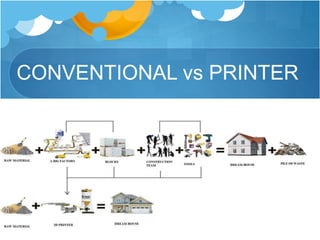
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, builds a product layer by layer using a computer-controlled process. A CAD software program is used to design a 3D model, which is then sent to the 3D printer. The printer deposits material in successive layers, starting from the bottom, to construct the item. Applications of 3D printing include printed soil, emergency accommodations like housing, and cool bricks. 3D printed structures can achieve strengths of up to 10,000 psi, using hollow walls that save on materials while maintaining structural integrity.