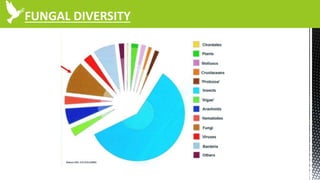
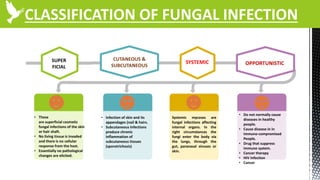
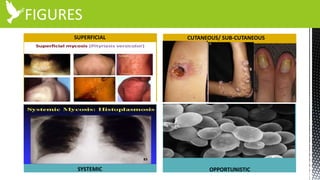
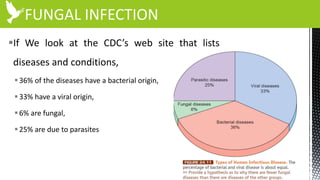
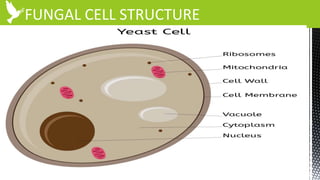
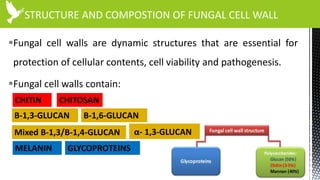
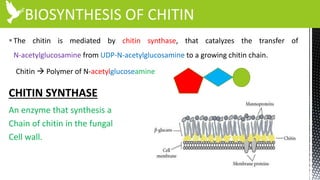
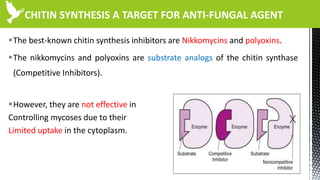
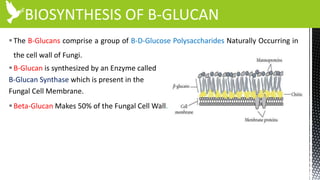
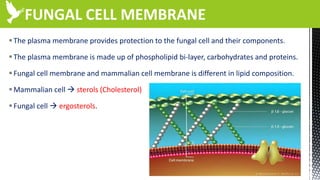
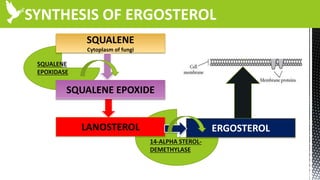
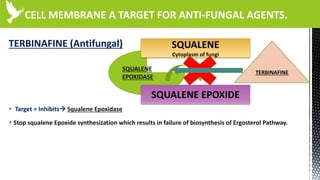
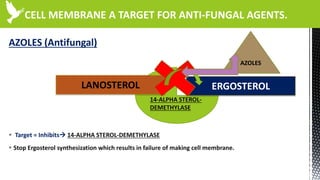
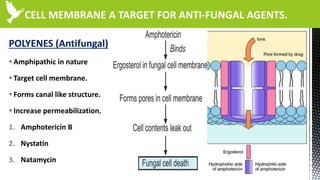
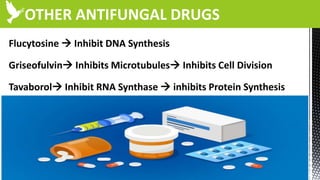
The document discusses anti-fungal drugs that target the fungal cell membrane and cell wall biosynthesis. It provides an overview of fungal cell structure, focusing on the cell wall components of chitin and beta-glucans. It explains how drugs like echinocandins inhibit beta-glucan synthase to disrupt cell wall formation, and how azoles and terbinafine inhibit ergosterol biosynthesis in the cell membrane. The summary highlights the main cellular targets of anti-fungal drugs and how inhibiting key processes like chitin, beta-glucan, and ergosterol synthesis impacts fungal growth and viability.