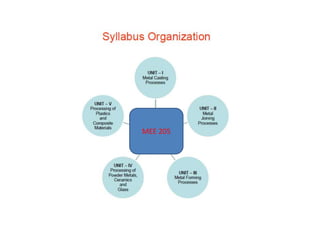
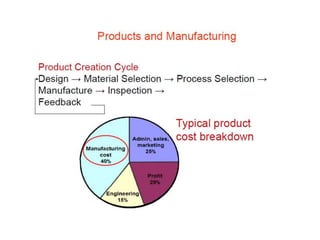
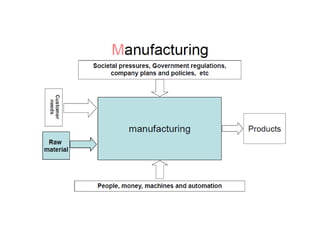
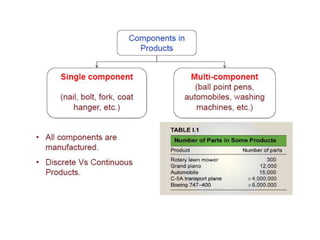
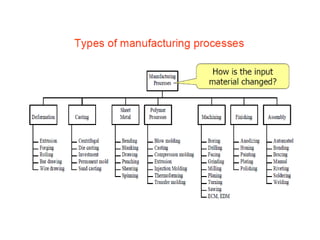
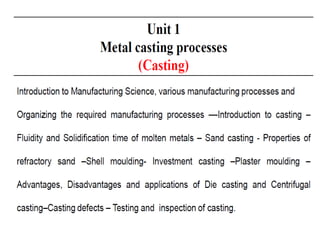
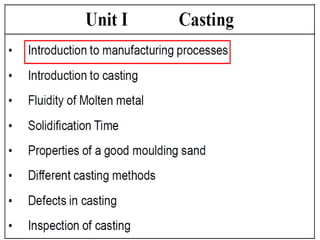
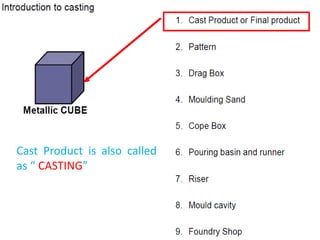
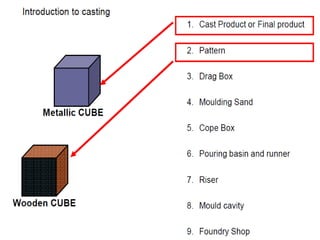
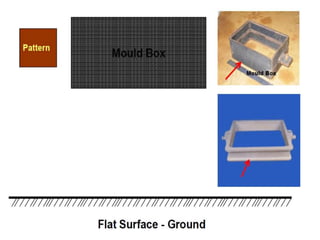
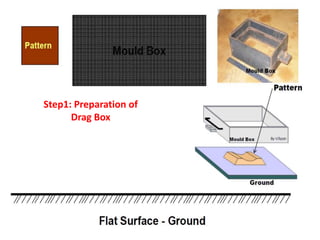
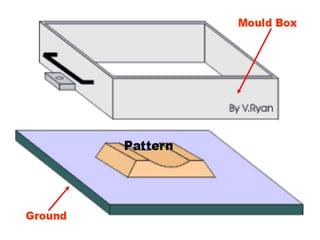
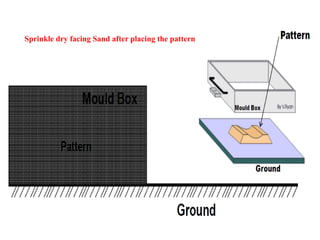
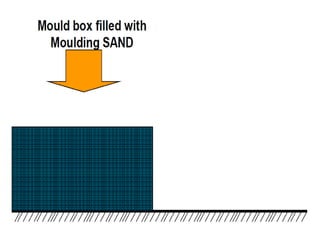
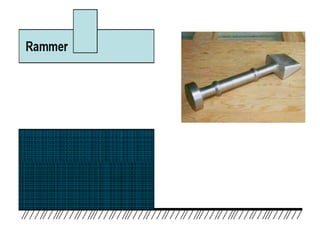
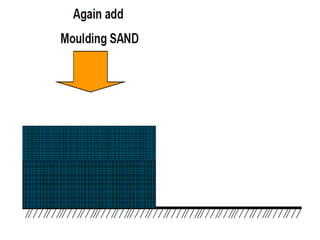
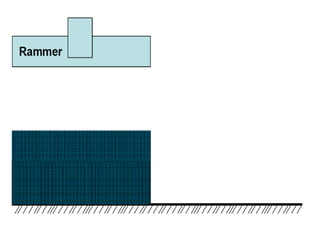
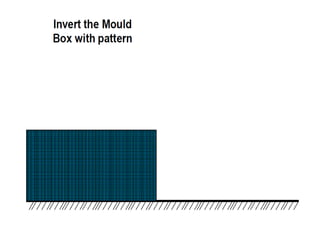
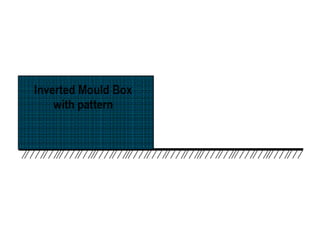
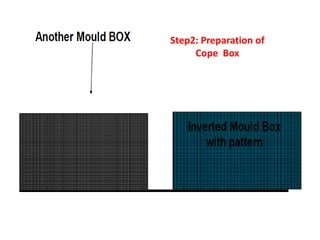
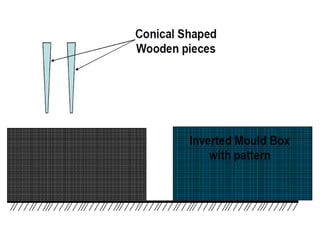
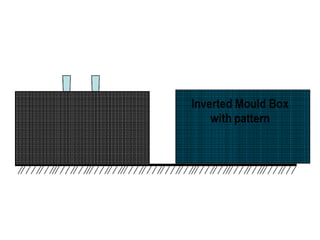
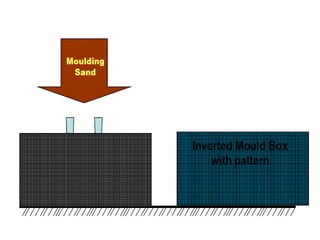
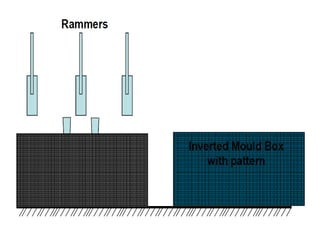
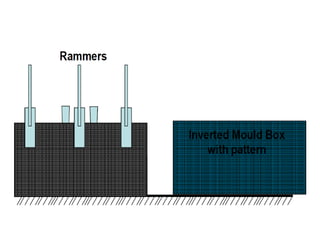
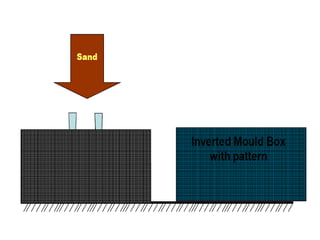
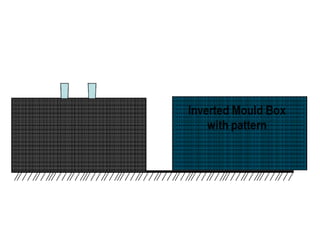
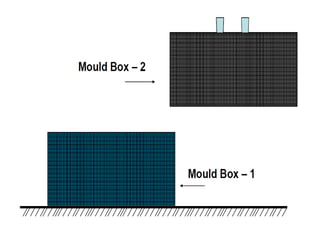
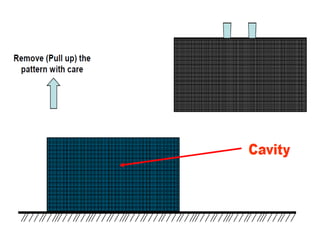
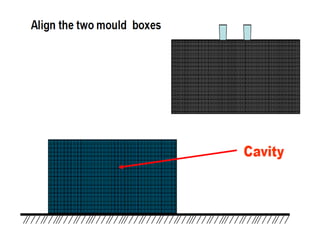
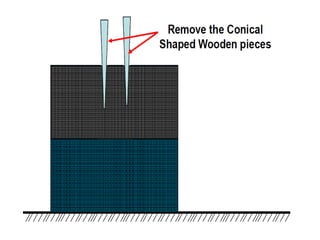
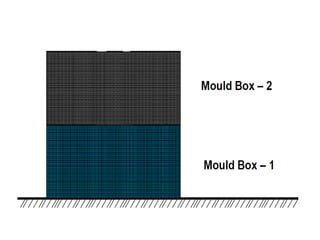
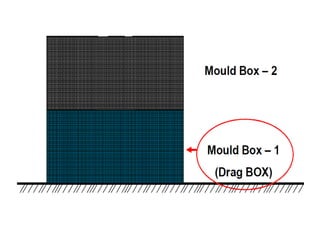
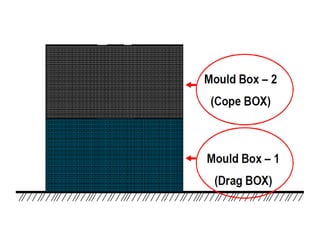
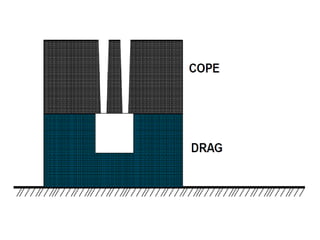
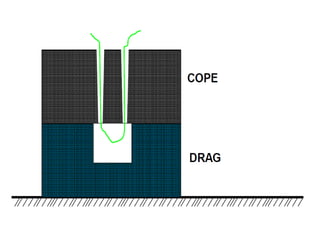
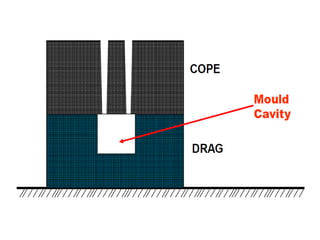
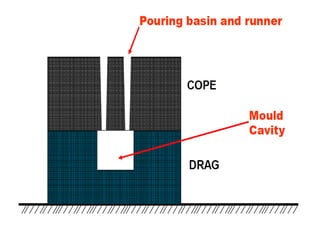
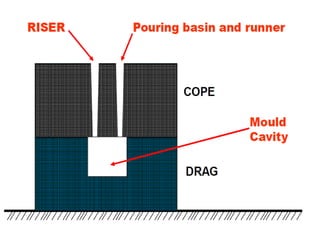
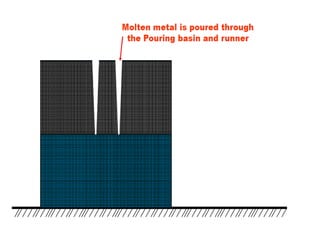
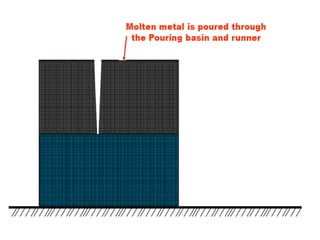
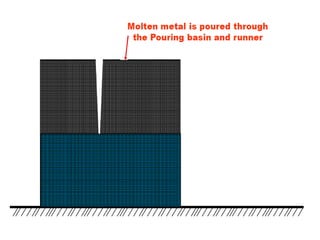
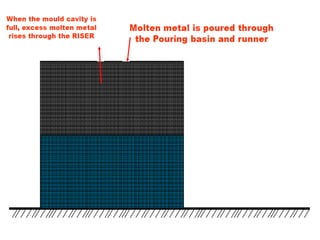
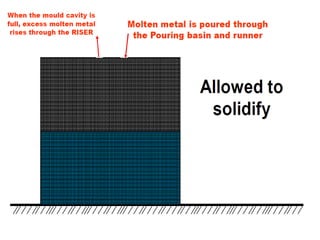
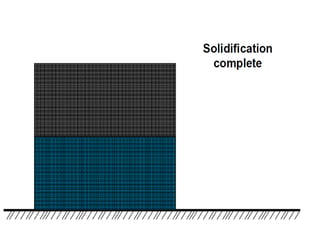
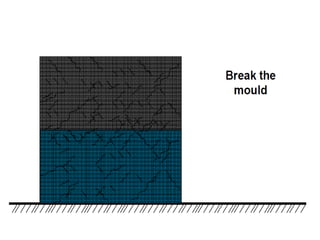
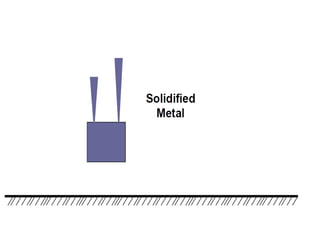
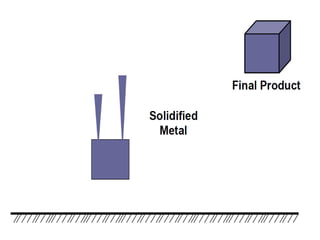
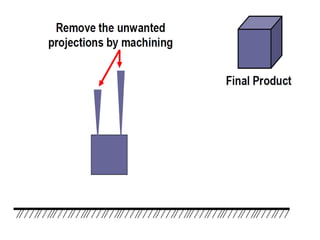
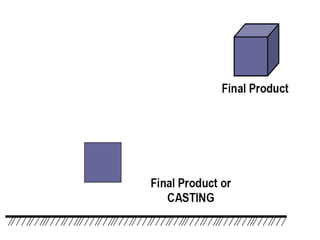
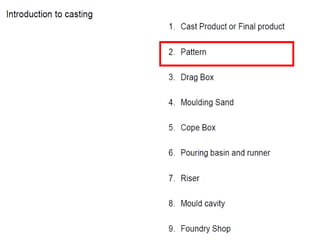
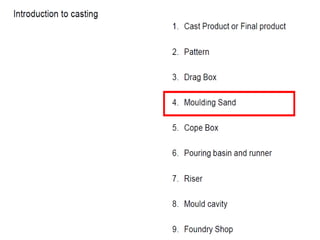
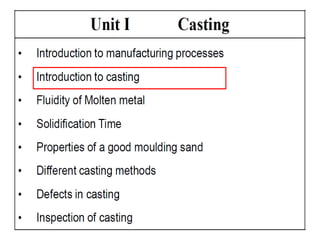
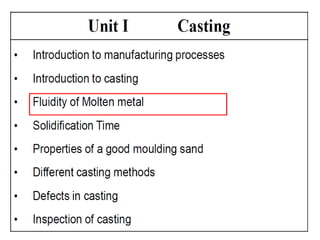
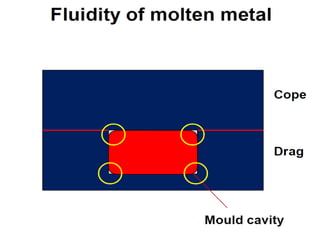
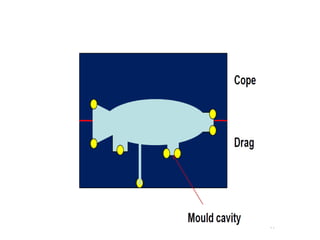
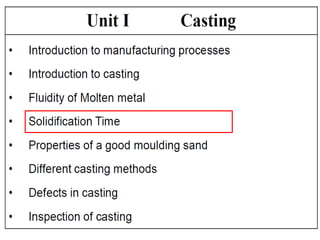
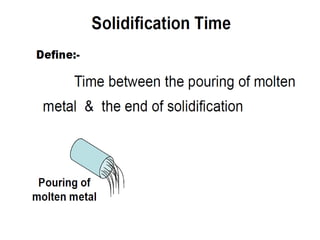
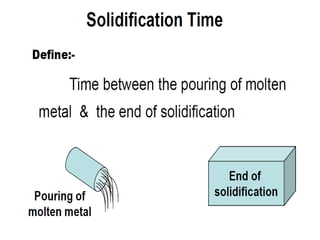
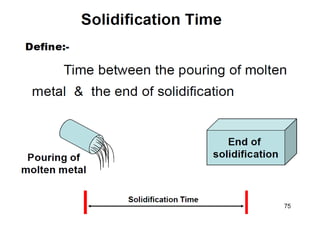
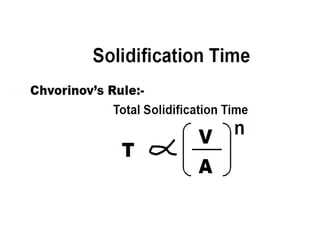
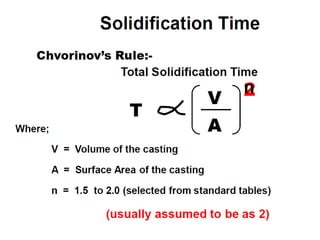
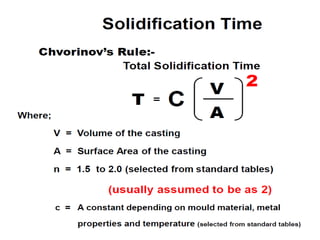
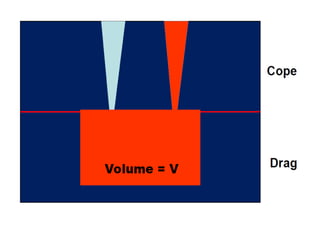
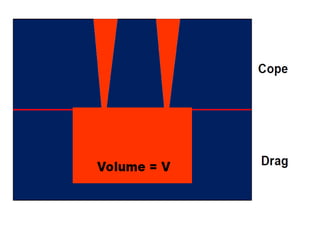
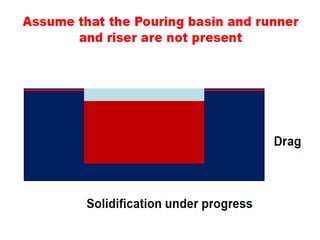
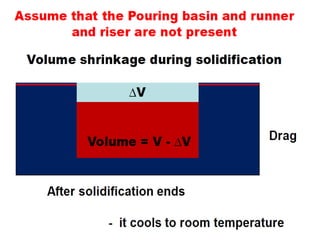
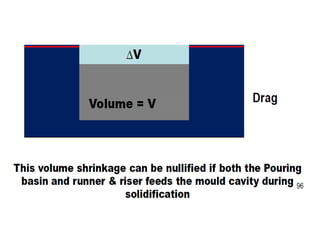
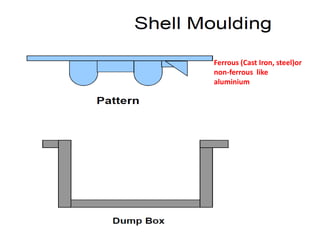
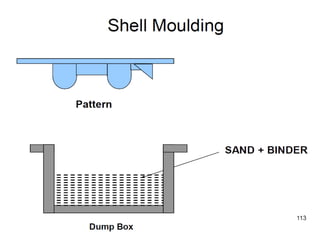
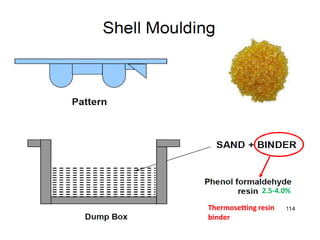
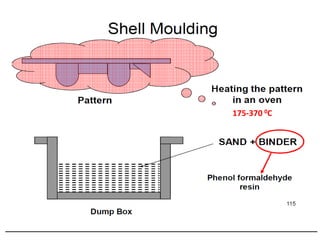
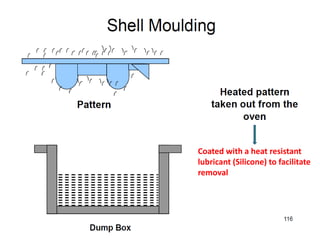
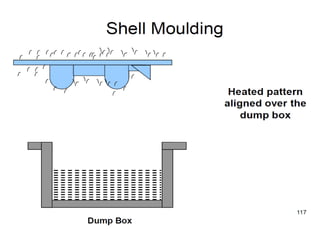
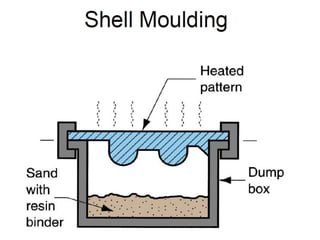
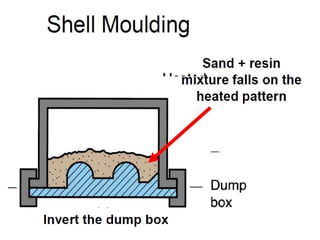
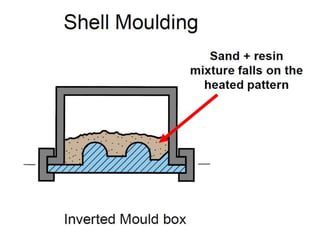
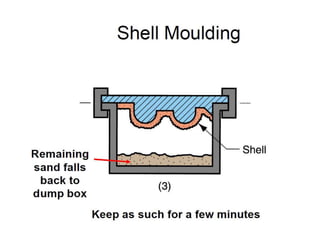
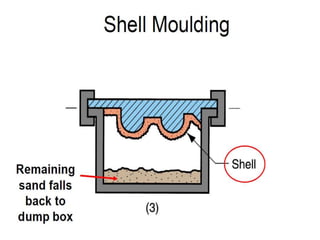
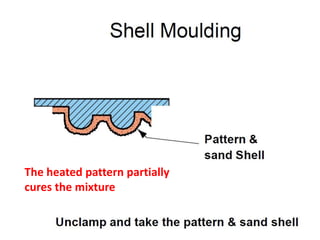
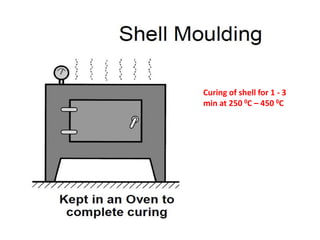
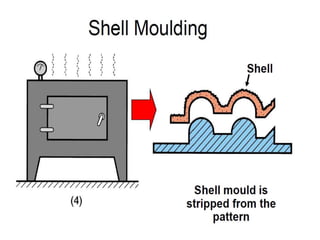
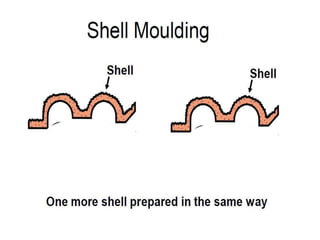
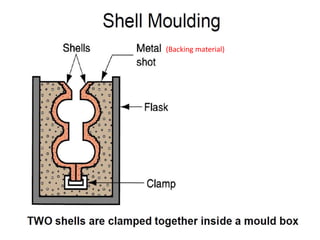
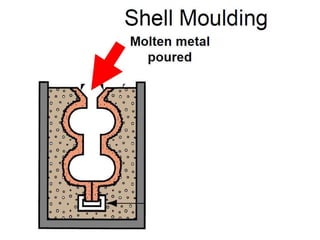
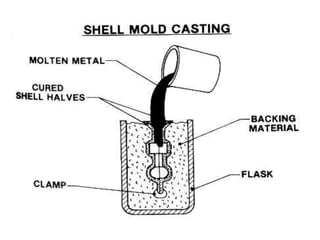
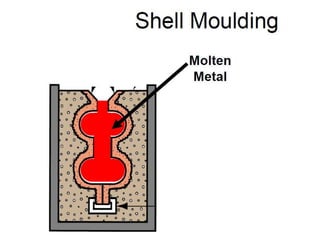
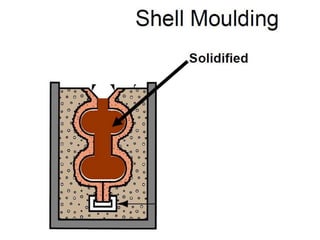
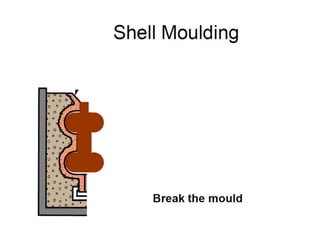
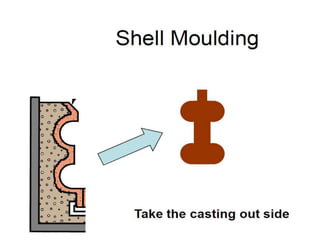
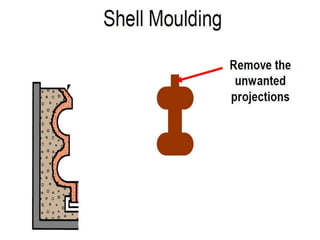
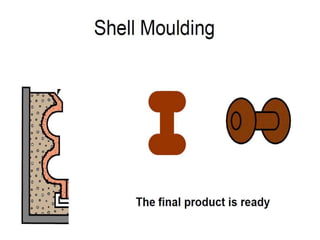
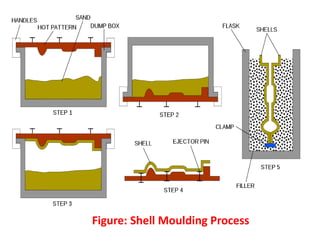
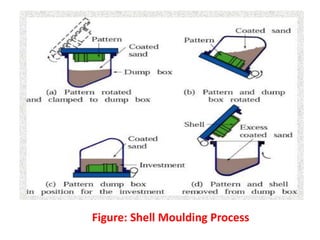
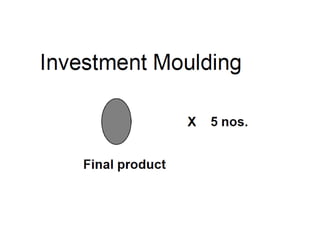
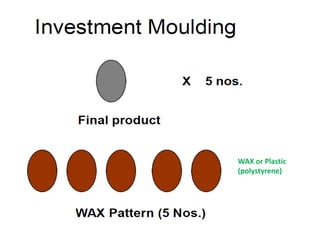
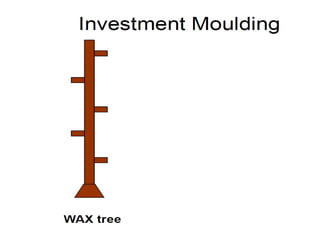
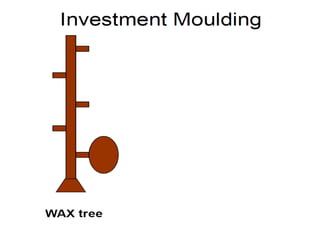
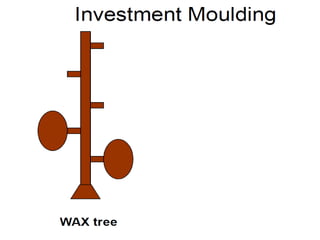
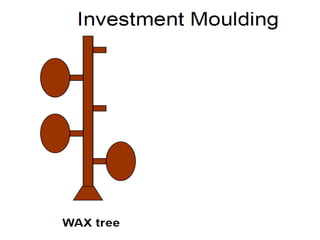
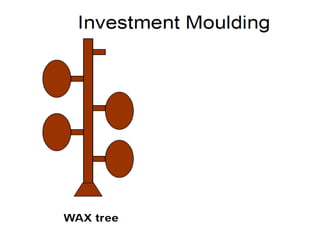
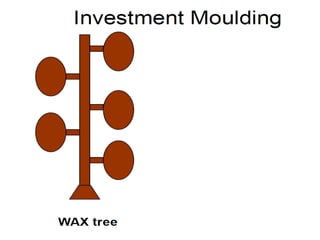
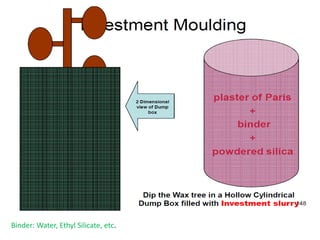
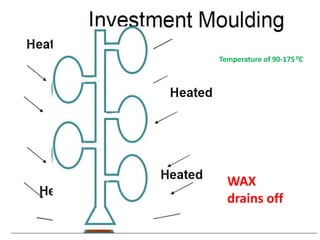
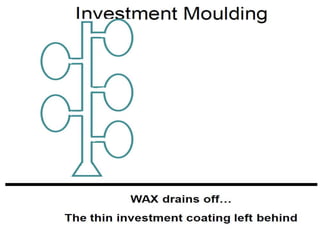
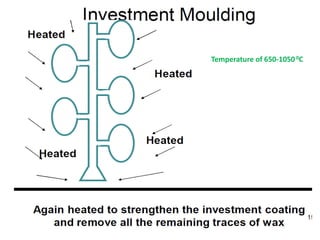
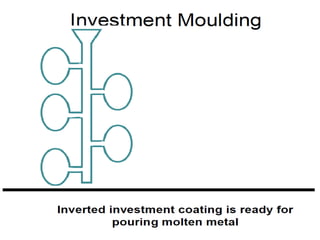
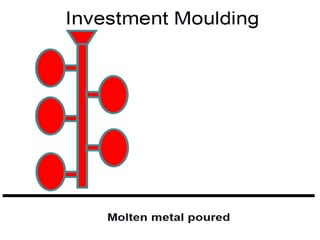
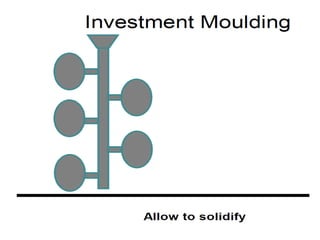
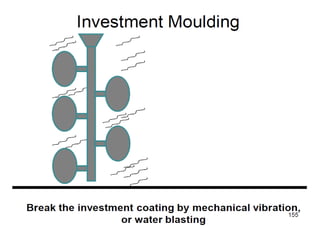
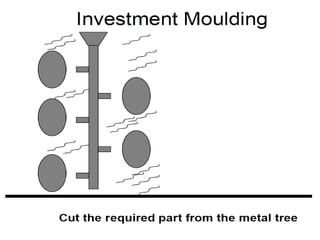
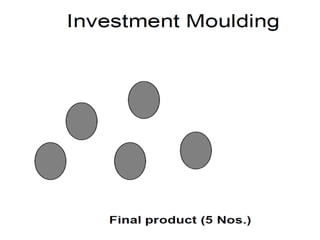
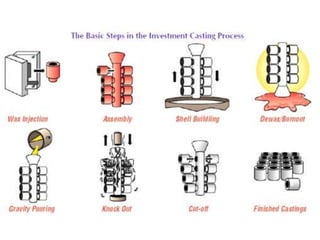
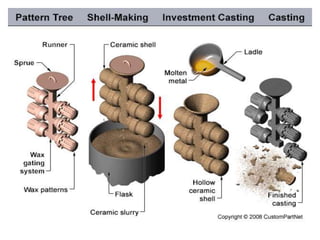
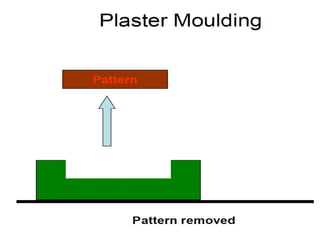
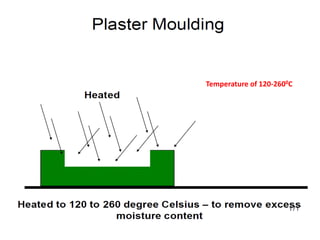
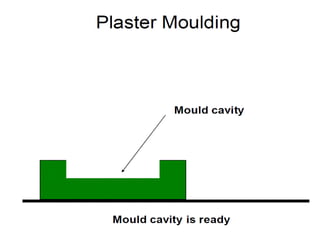
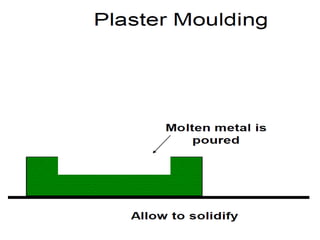
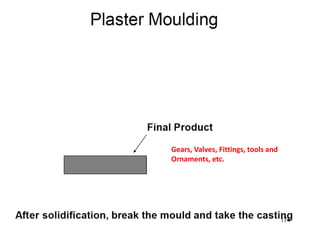
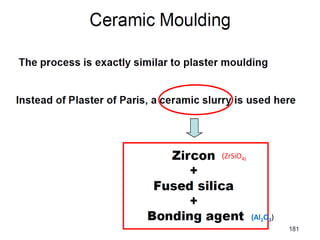
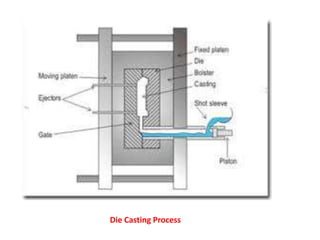
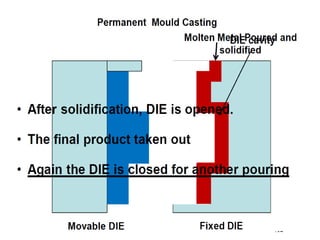
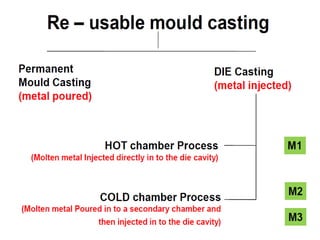
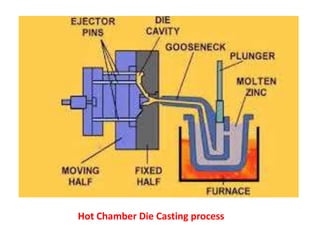
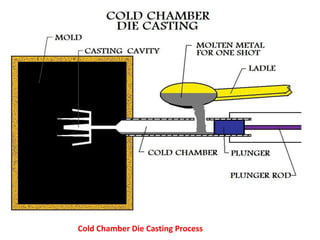
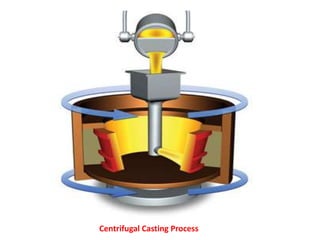
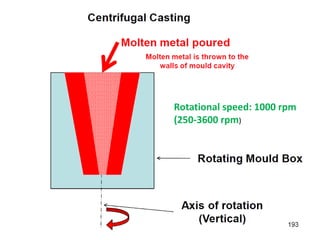
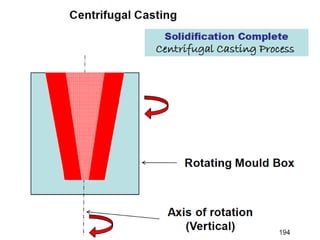
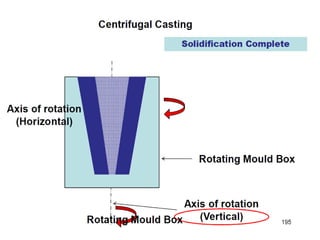
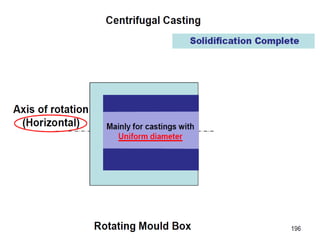
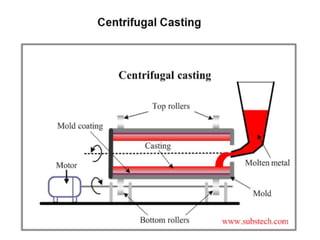
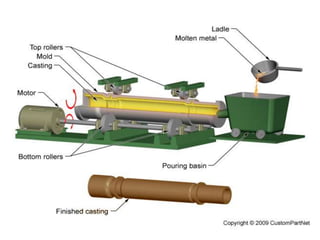
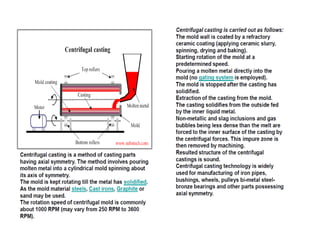
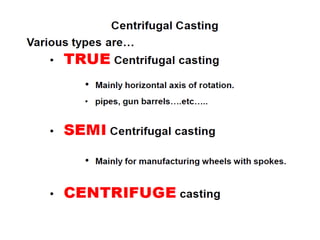
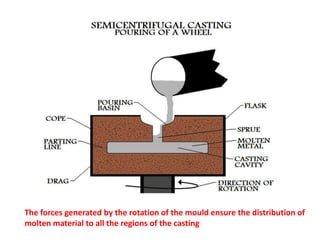
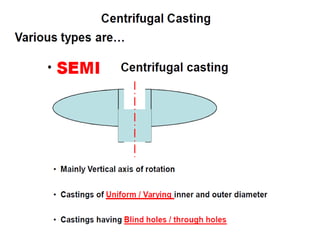
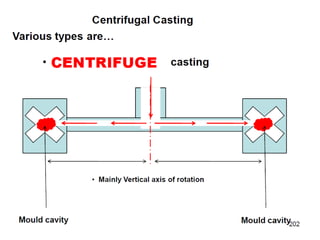
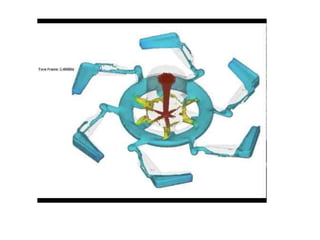
This document provides an overview of course material on fundamentals of manufacturing processes. It discusses various casting processes like sand casting, shell mold casting, investment casting, die casting, and centrifugal casting. Key steps and terminology related to sand casting like preparation of drag box and cope box are explained. Important properties of molding sand like permeability, refractory, and hot strength are also defined.