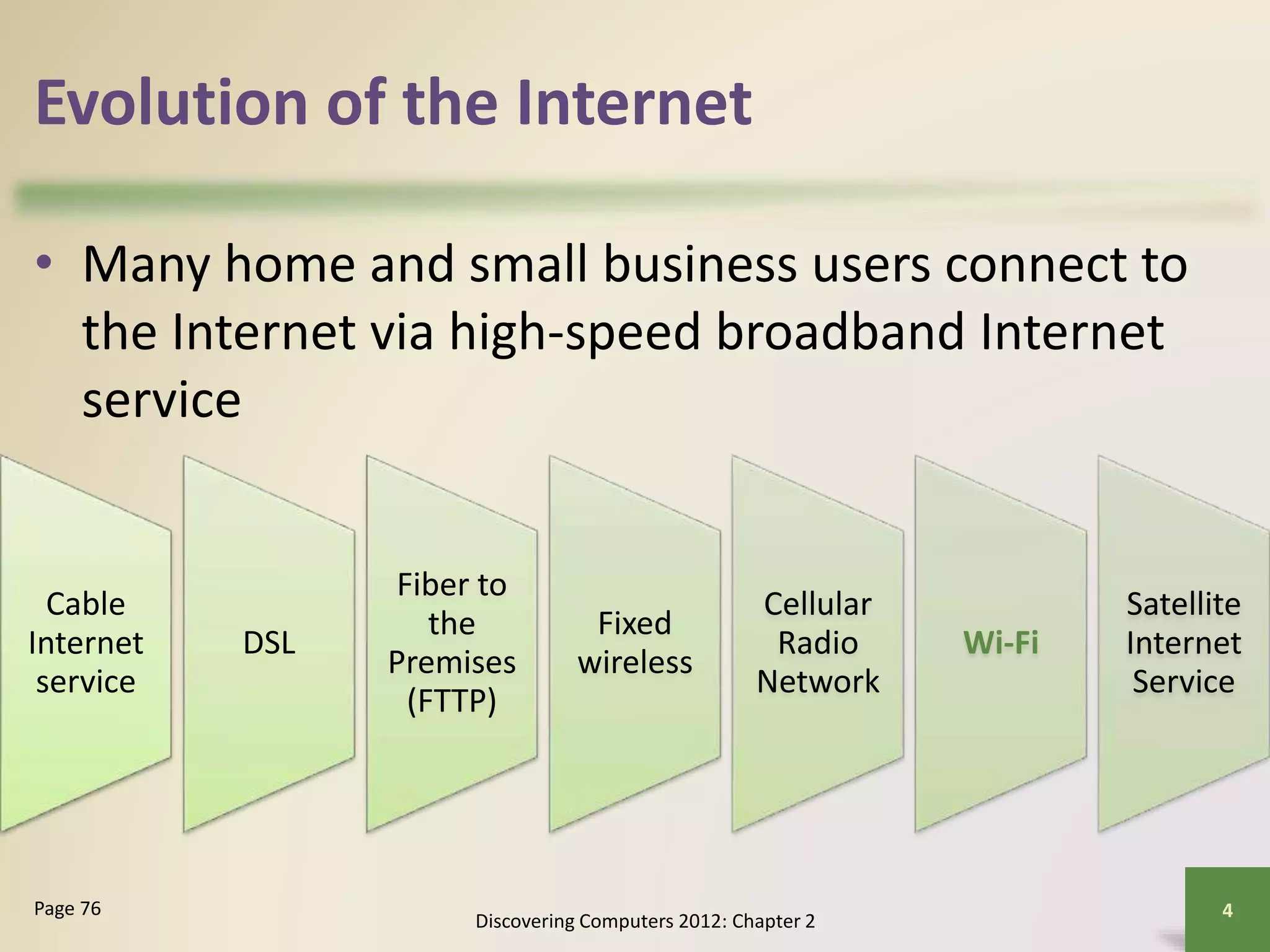
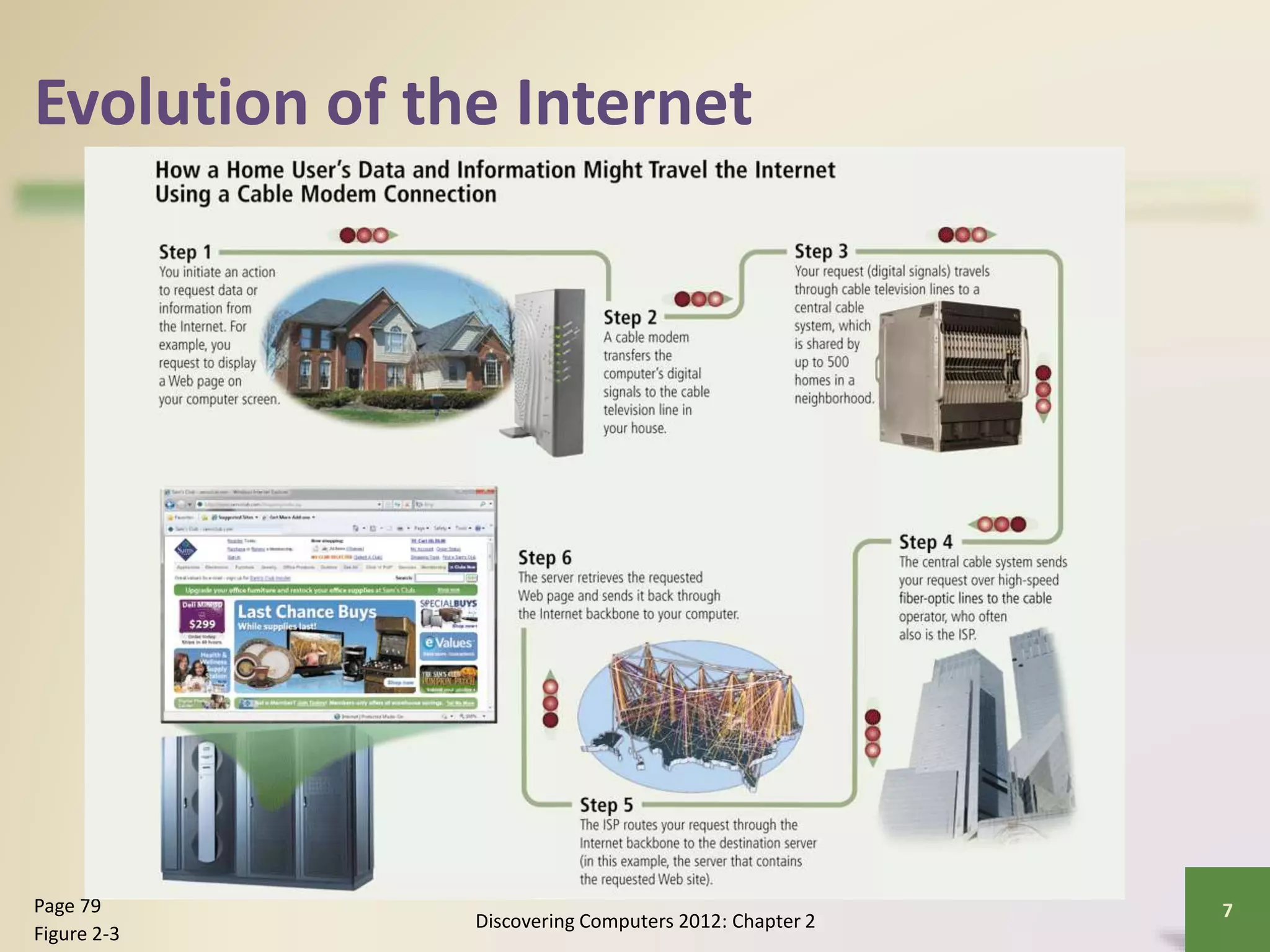
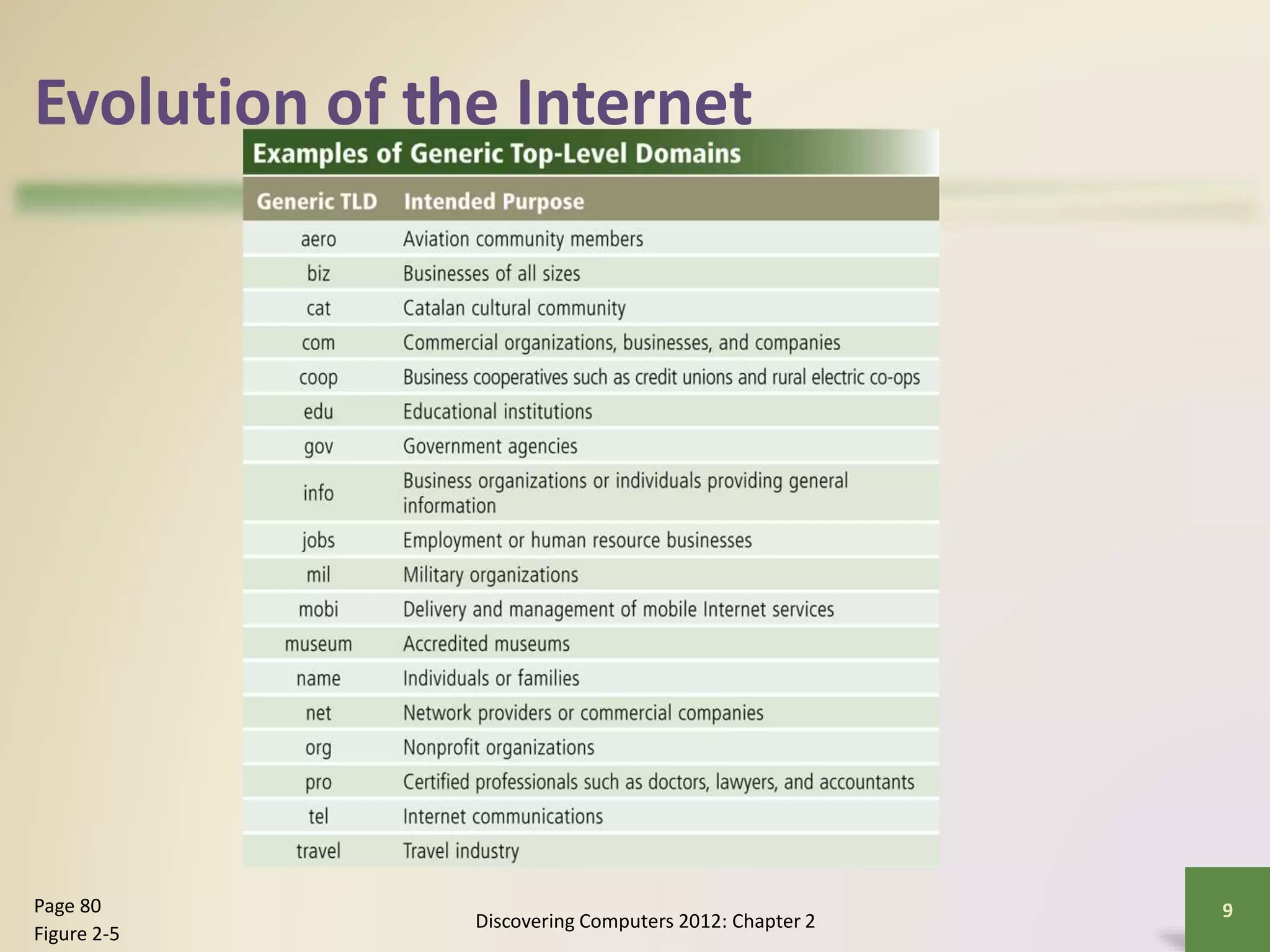
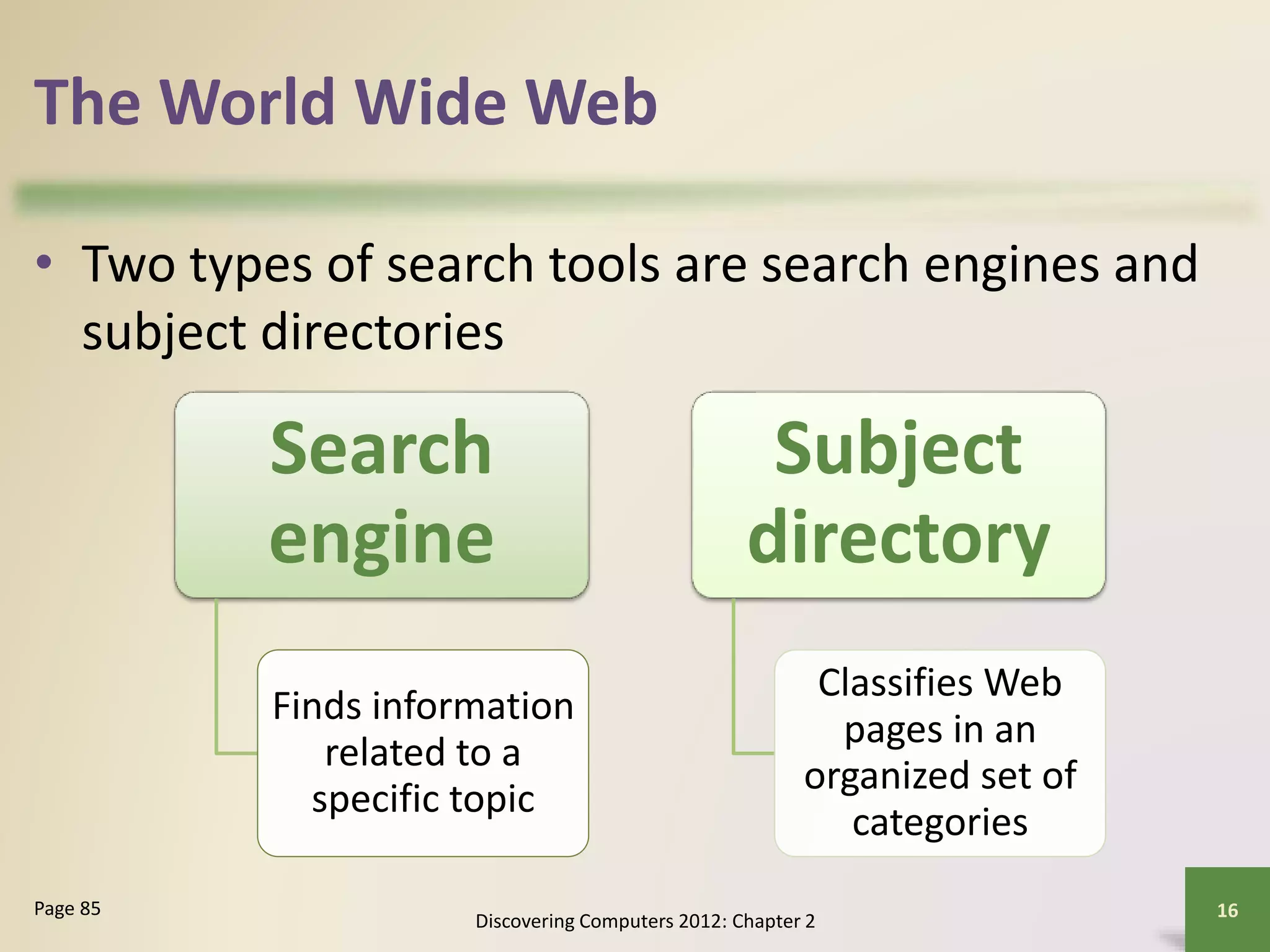
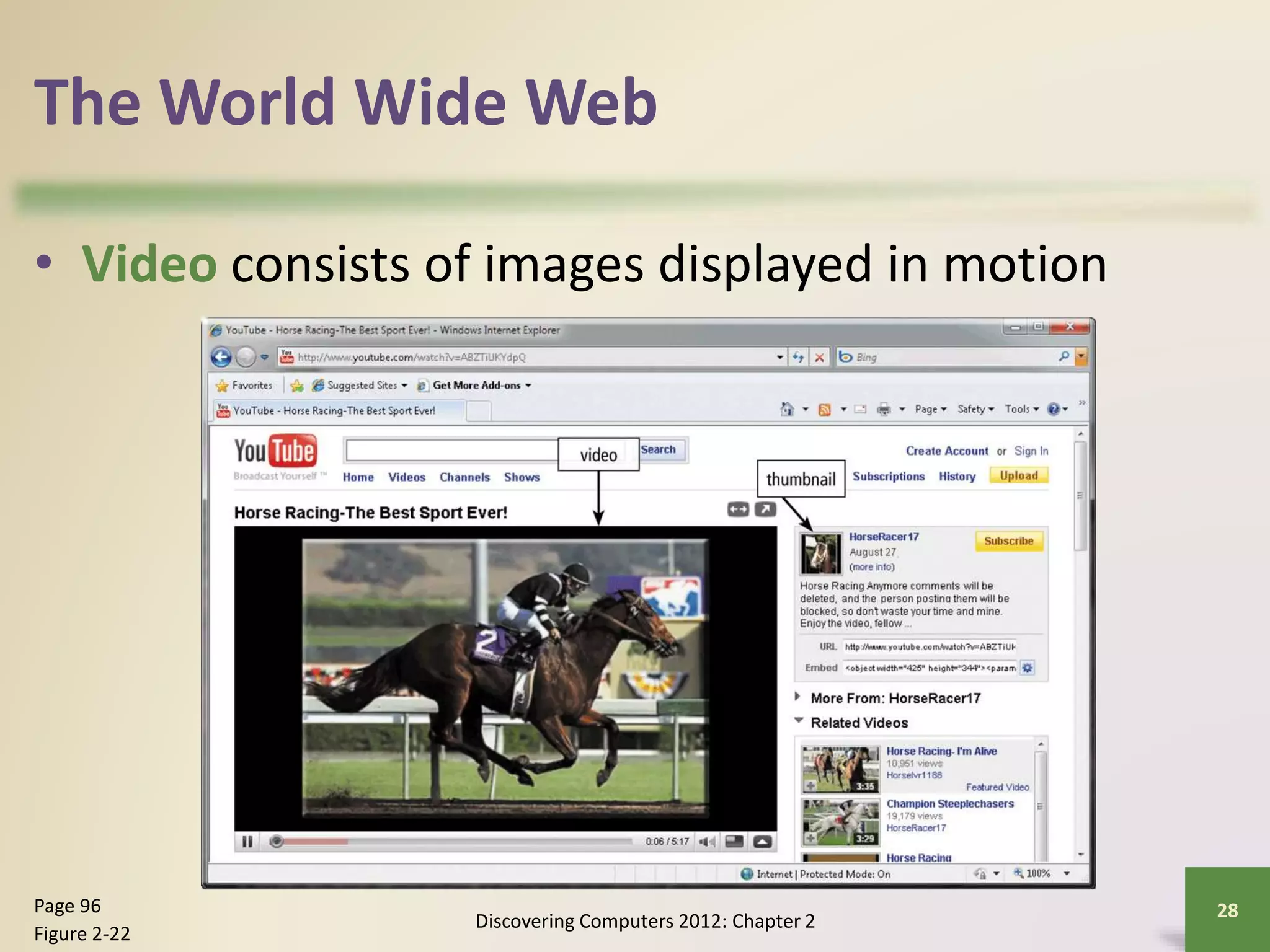
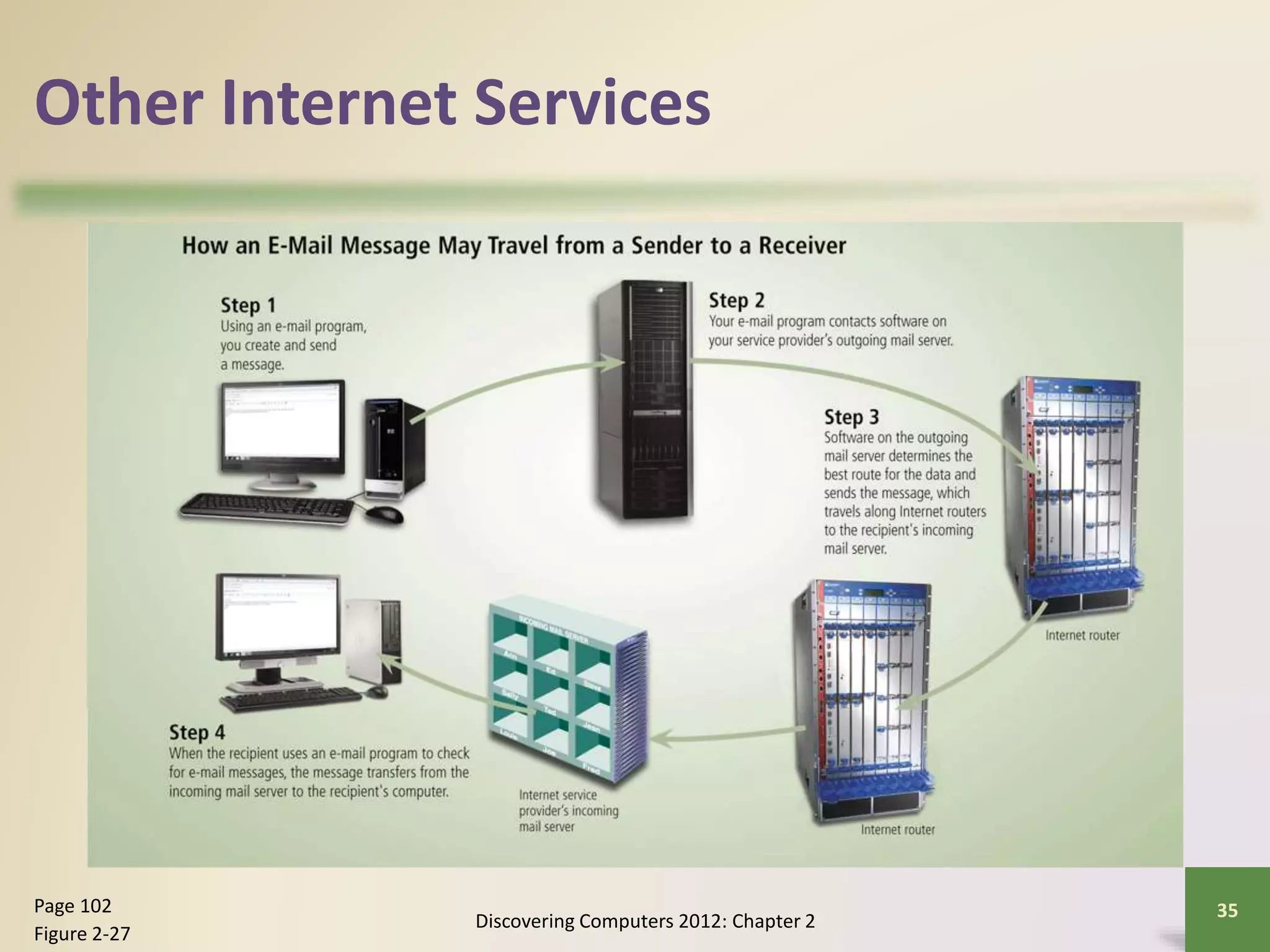
The document provides an overview of the history and components of the Internet and World Wide Web. It discusses how the Internet originated as ARPANET to allow scientists to share information across locations. It describes how individuals and organizations can access the Internet via providers and IP addresses. It also summarizes the basic functions and elements that make up the World Wide Web, such as browsers, URLs, search engines, and different types of websites. Finally, it covers other Internet services like email, instant messaging, voice chat, and newsgroups.