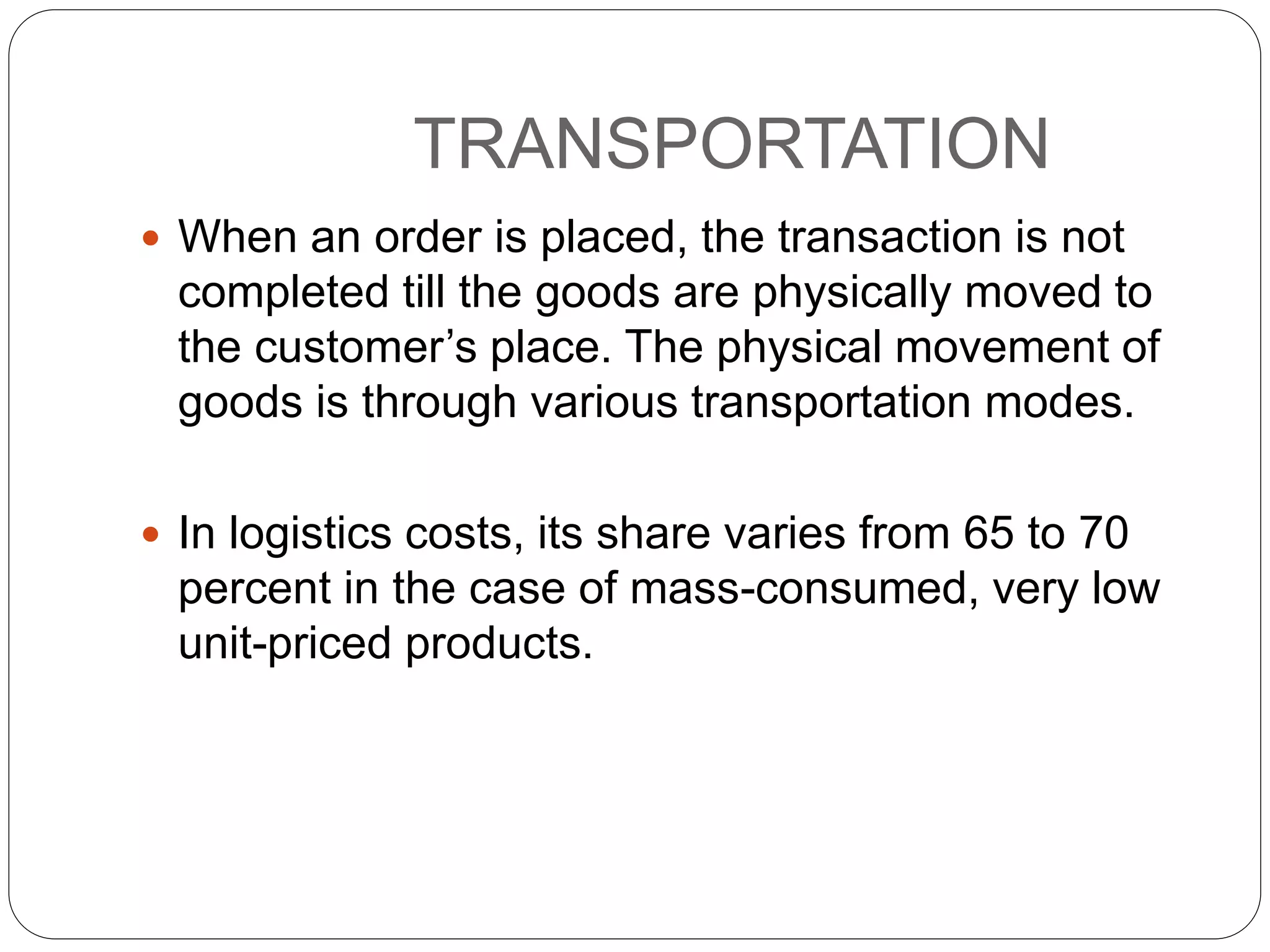
This document discusses the key functions of logistics and outsourcing. It identifies the main functions of logistics as order processing, inventory control, warehousing, transportation, material handling, storage, logistical packaging, and information. It also discusses outsourcing, defining it as using outside parties to perform logistics activities traditionally handled internally. The purpose is to manage a company's supply chain and allocate resources effectively.