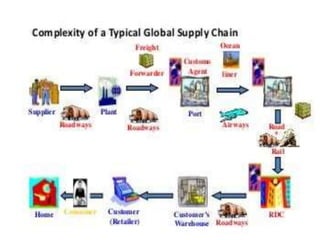
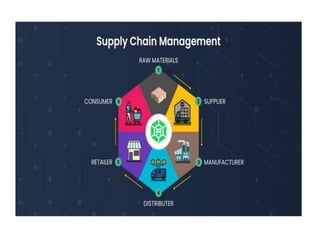
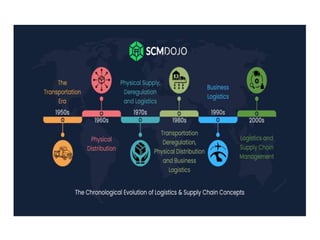
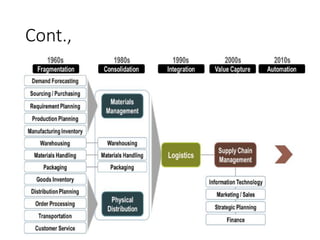
The document discusses the basics of logistics, including its importance and evolution. It defines logistics as the planning and execution of efficient movement and storage of goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption to meet customer needs. Logistics involves activities like procurement, inventory control, transportation, and warehousing. It is considered a subset of supply chain management, which coordinates networks of companies involved in delivering products to market. The evolution of logistics has expanded its focus from internal activities to coordination across company boundaries in the supply chain.