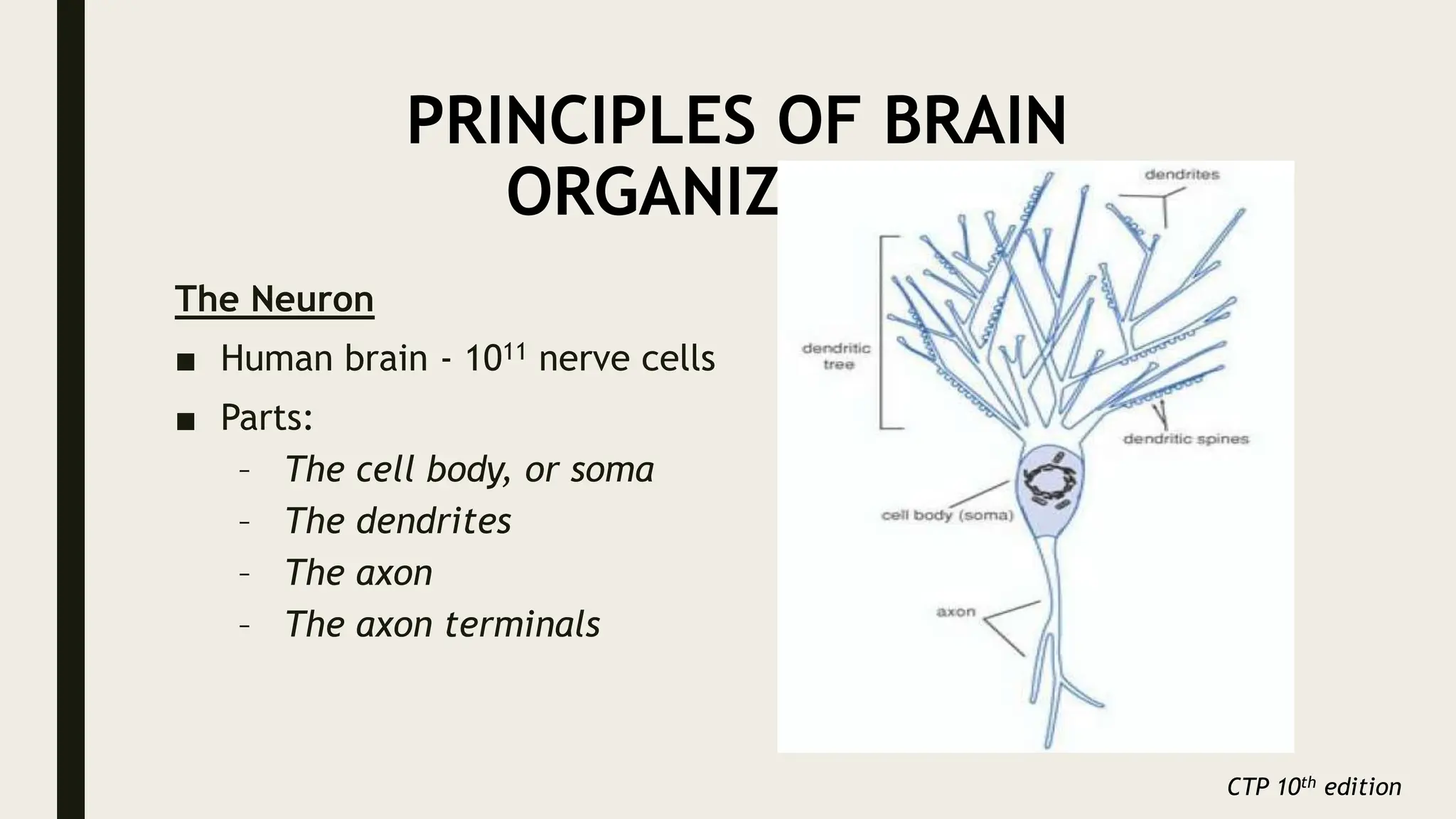
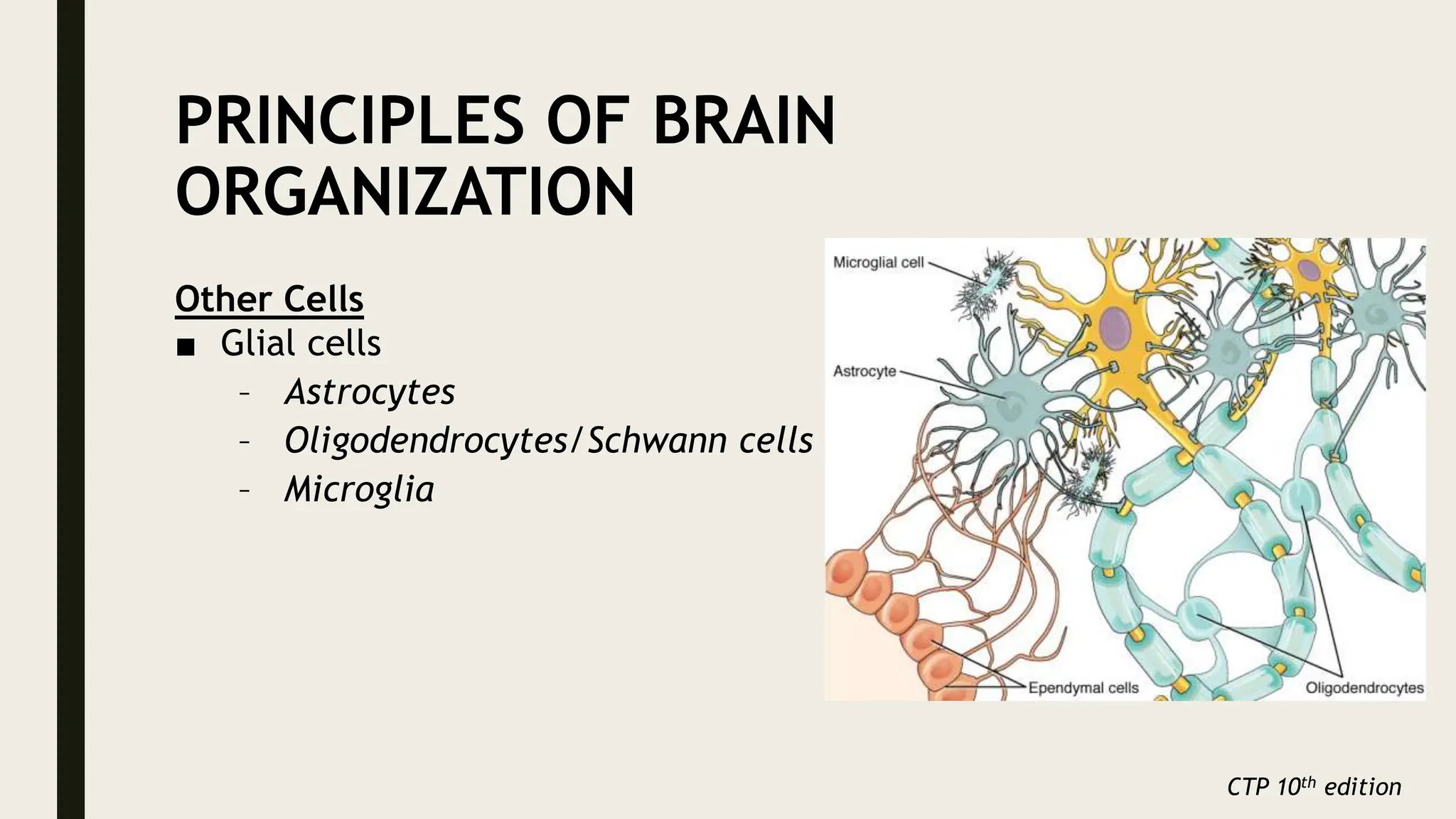
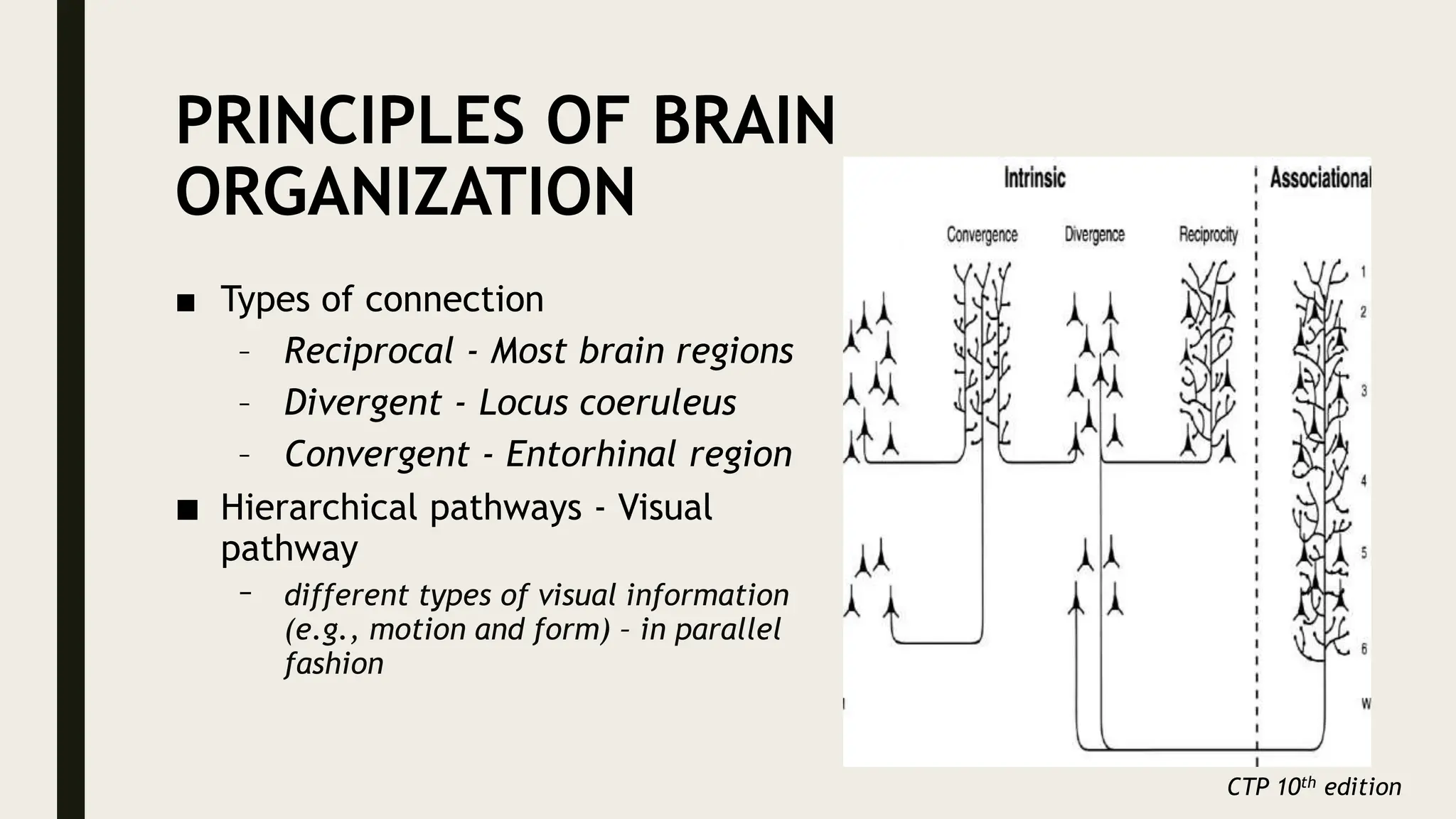
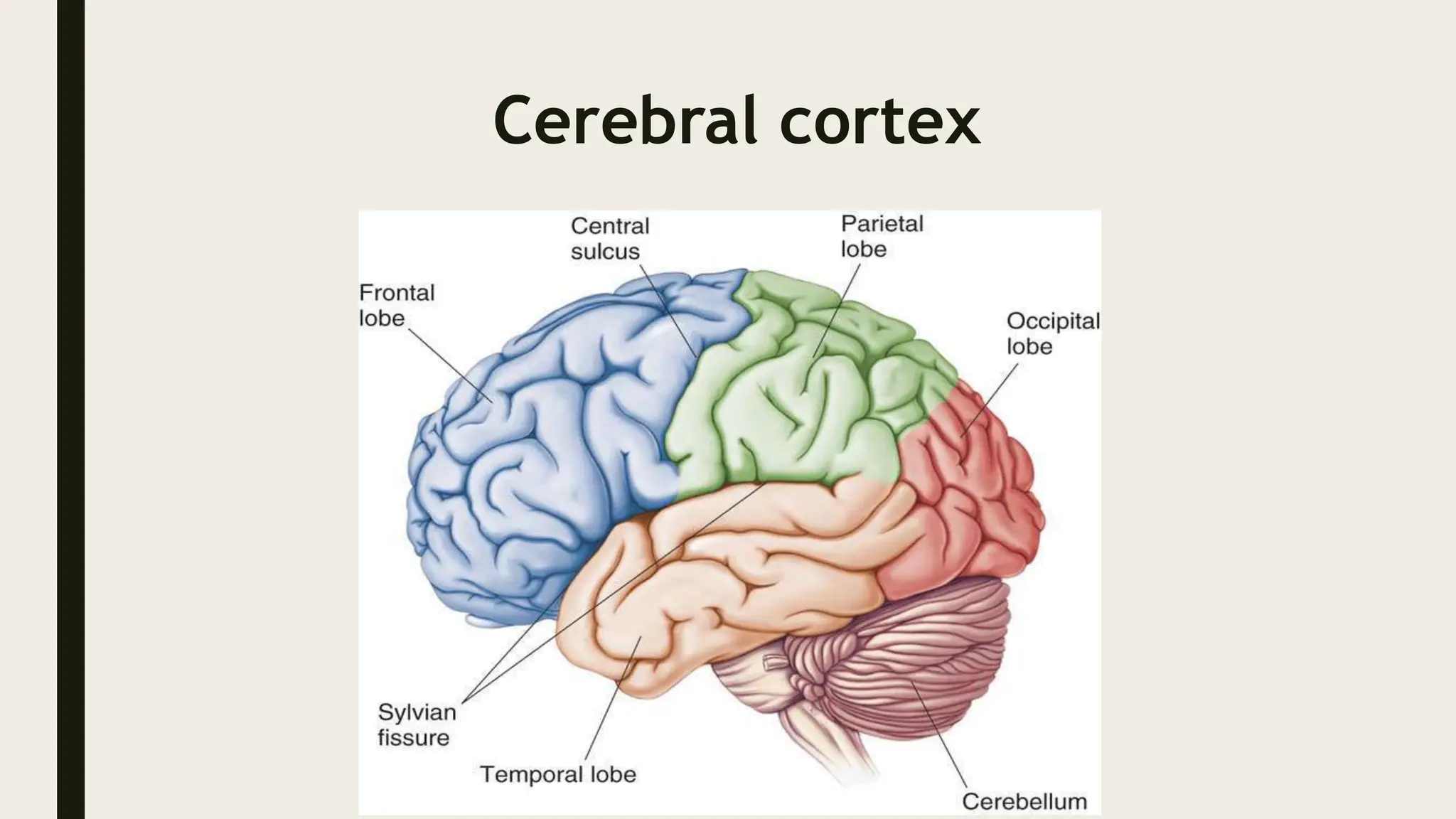
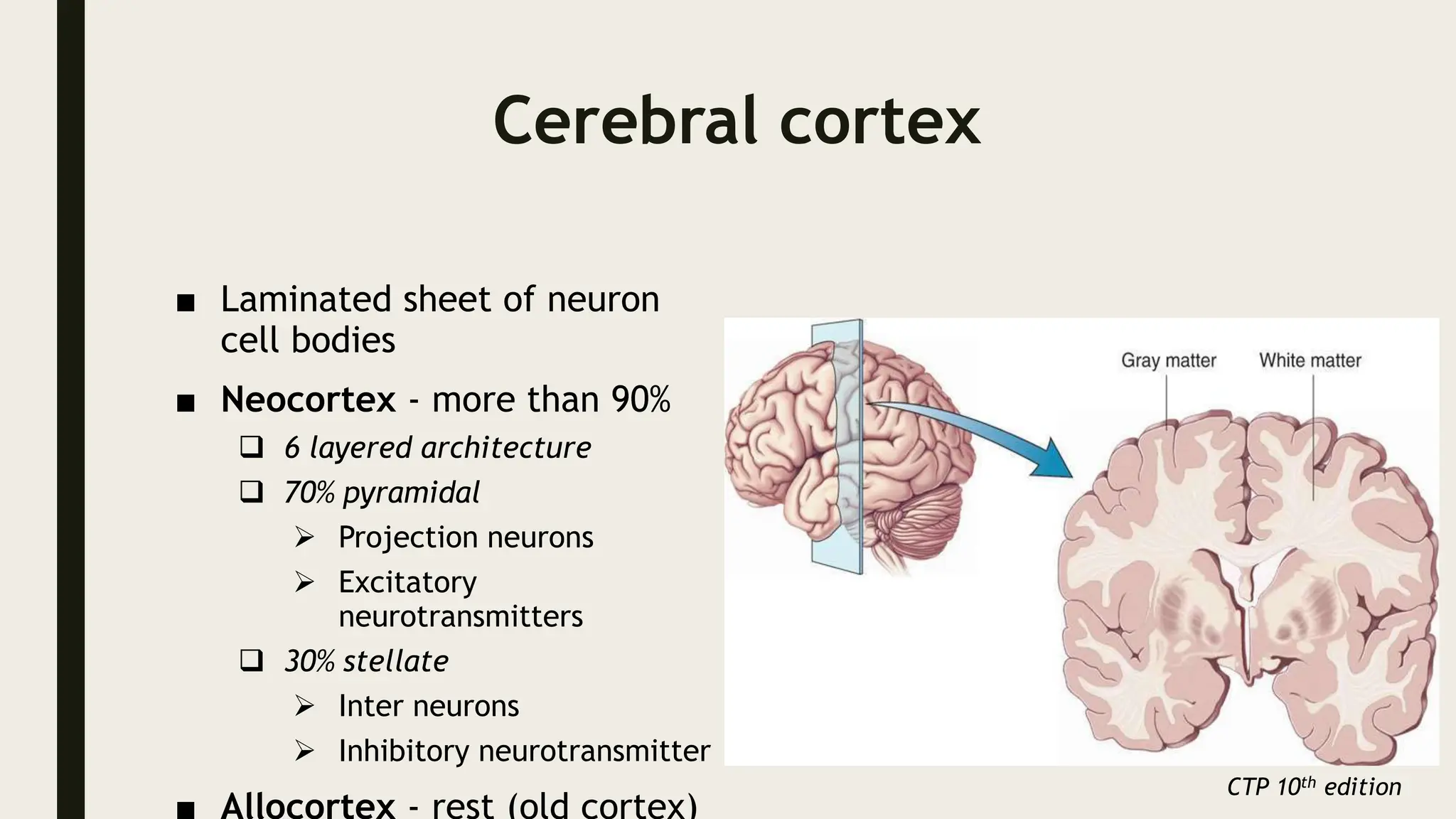
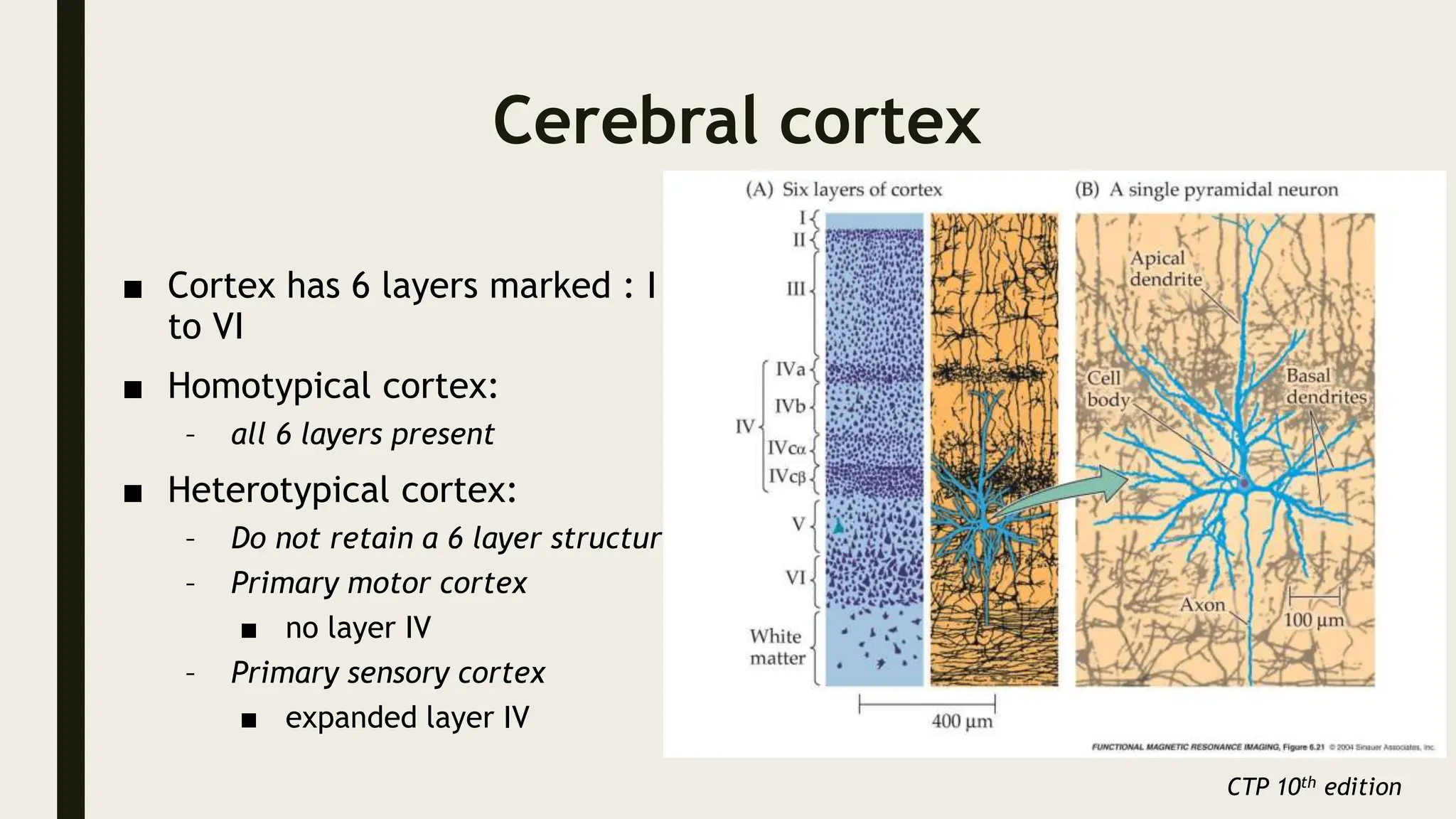
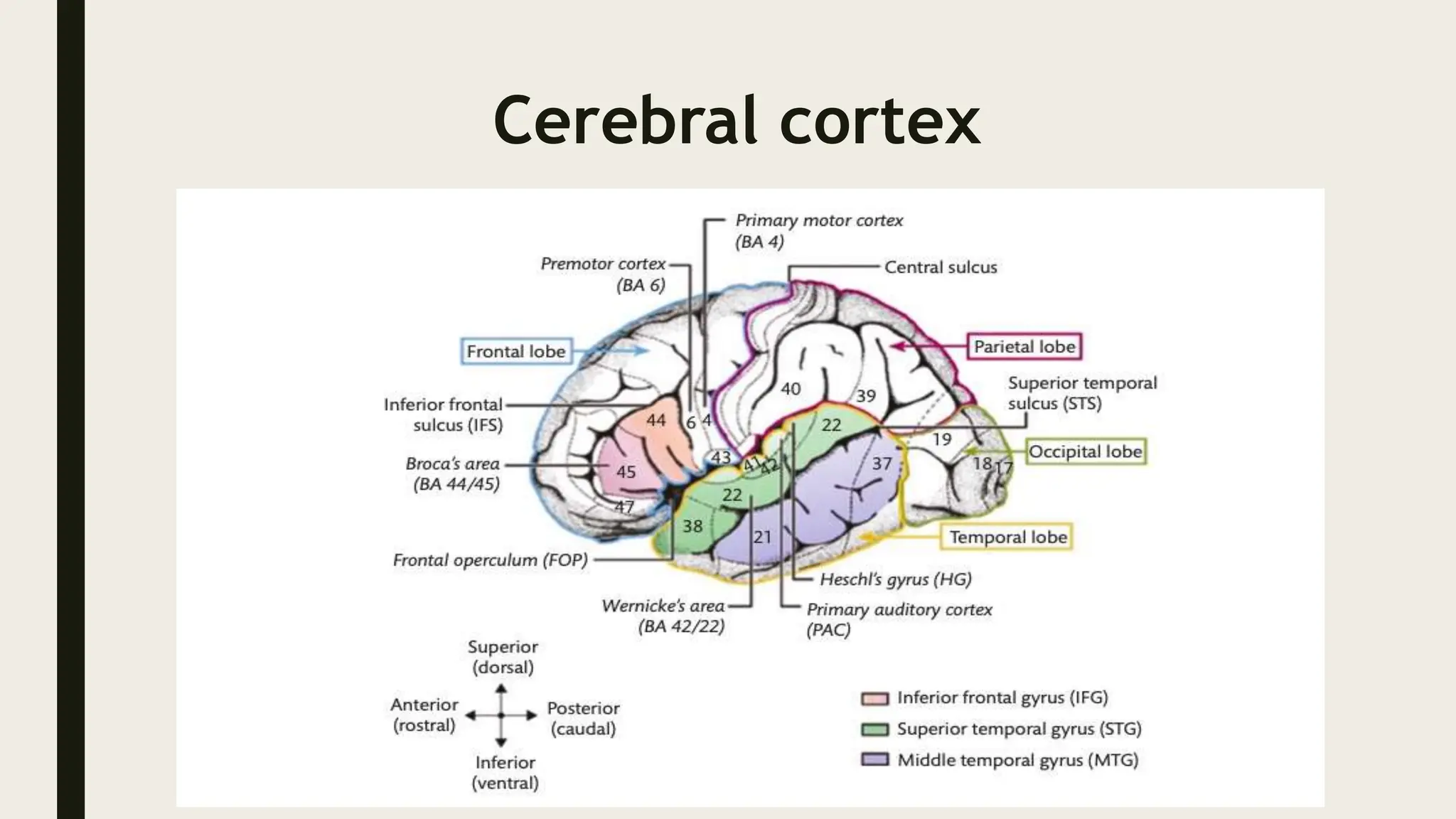
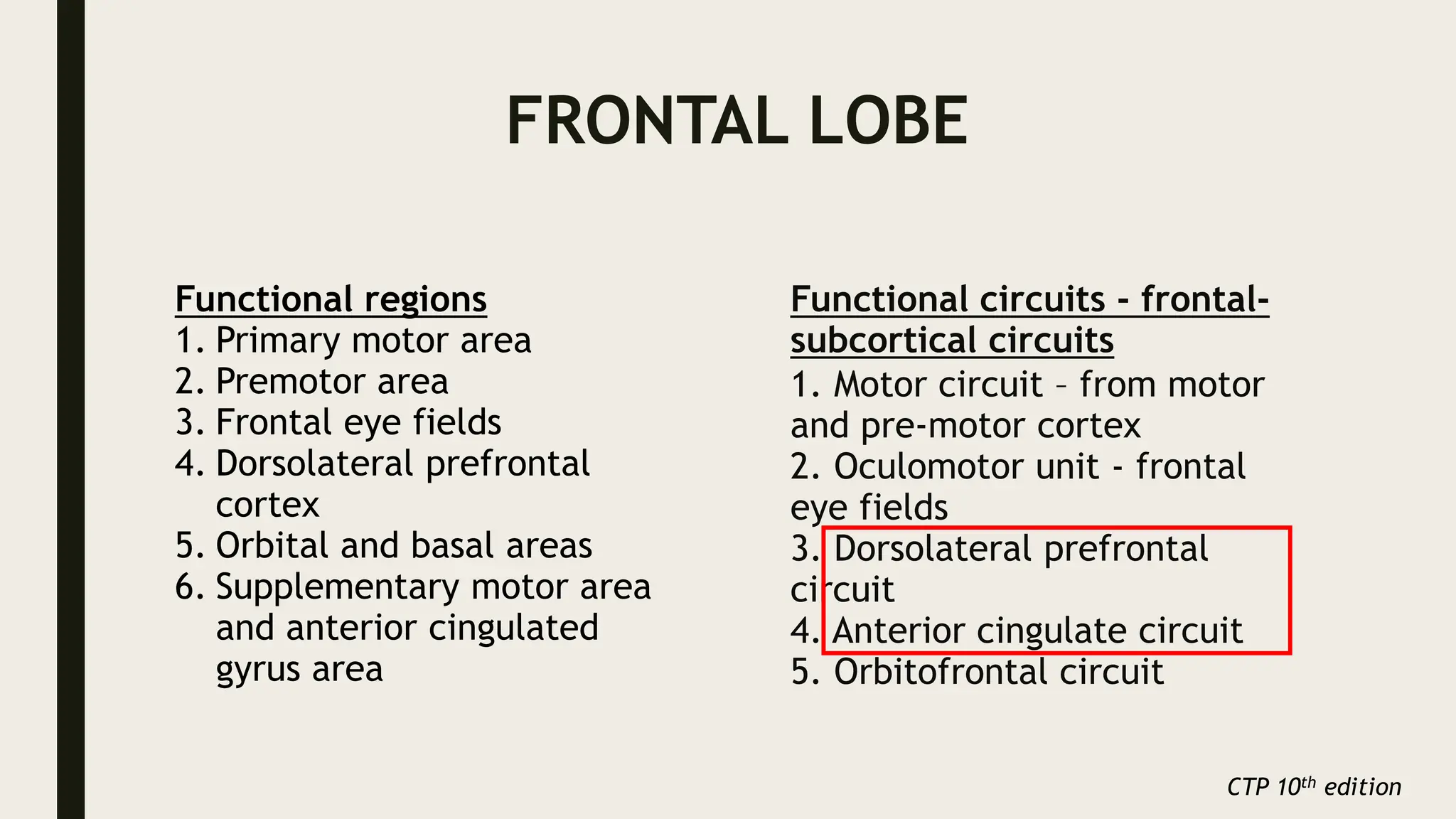
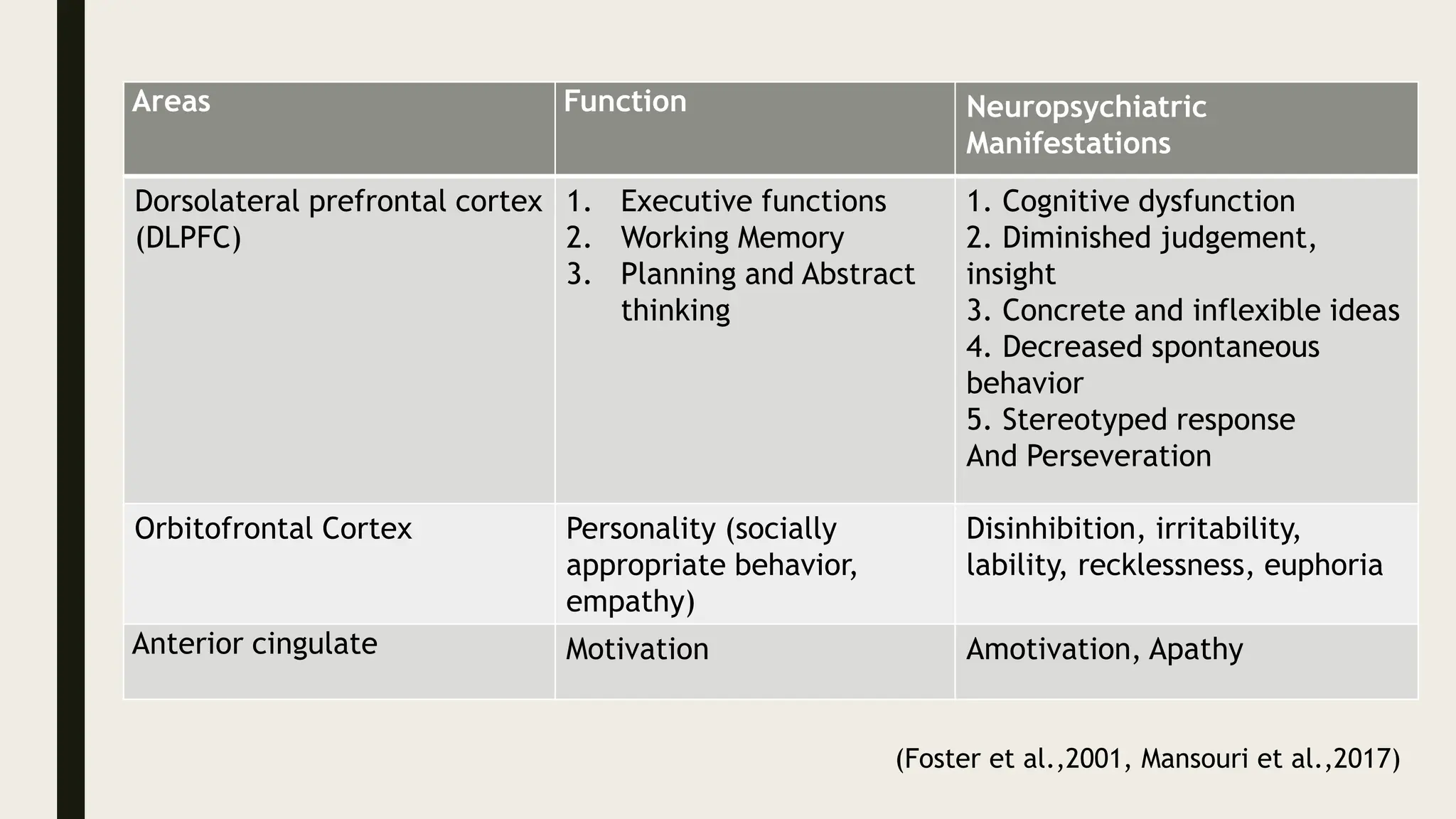
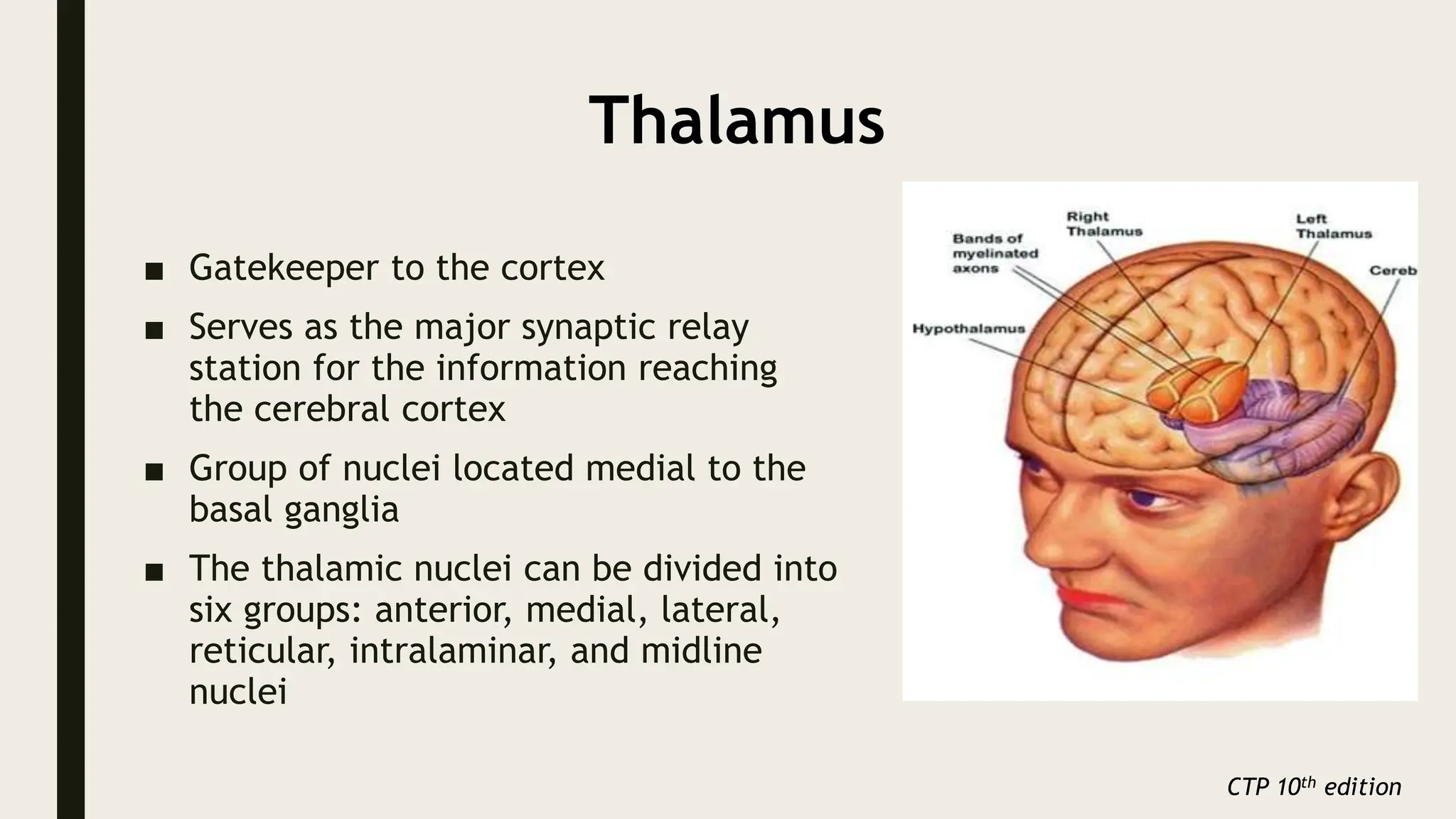
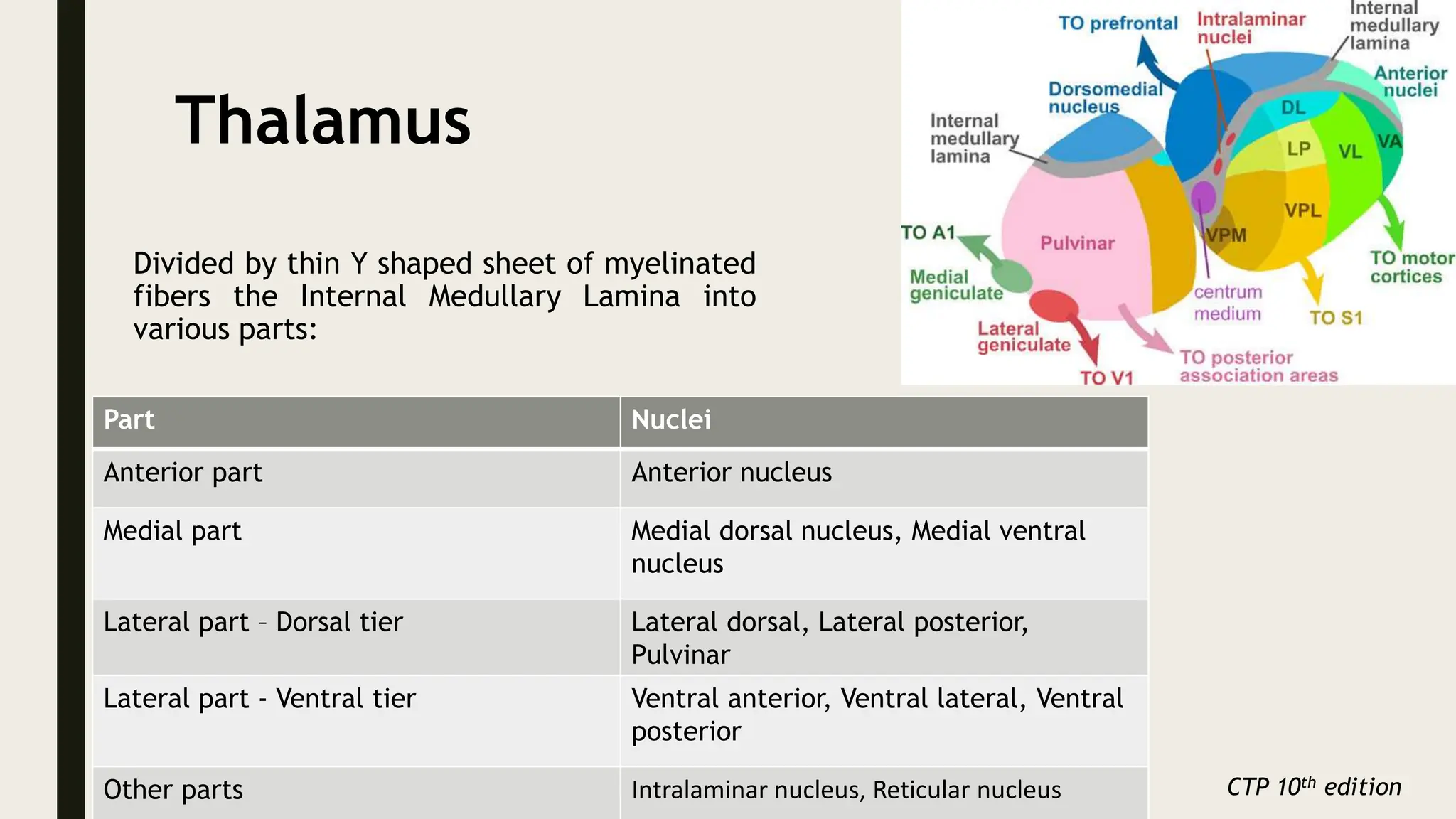
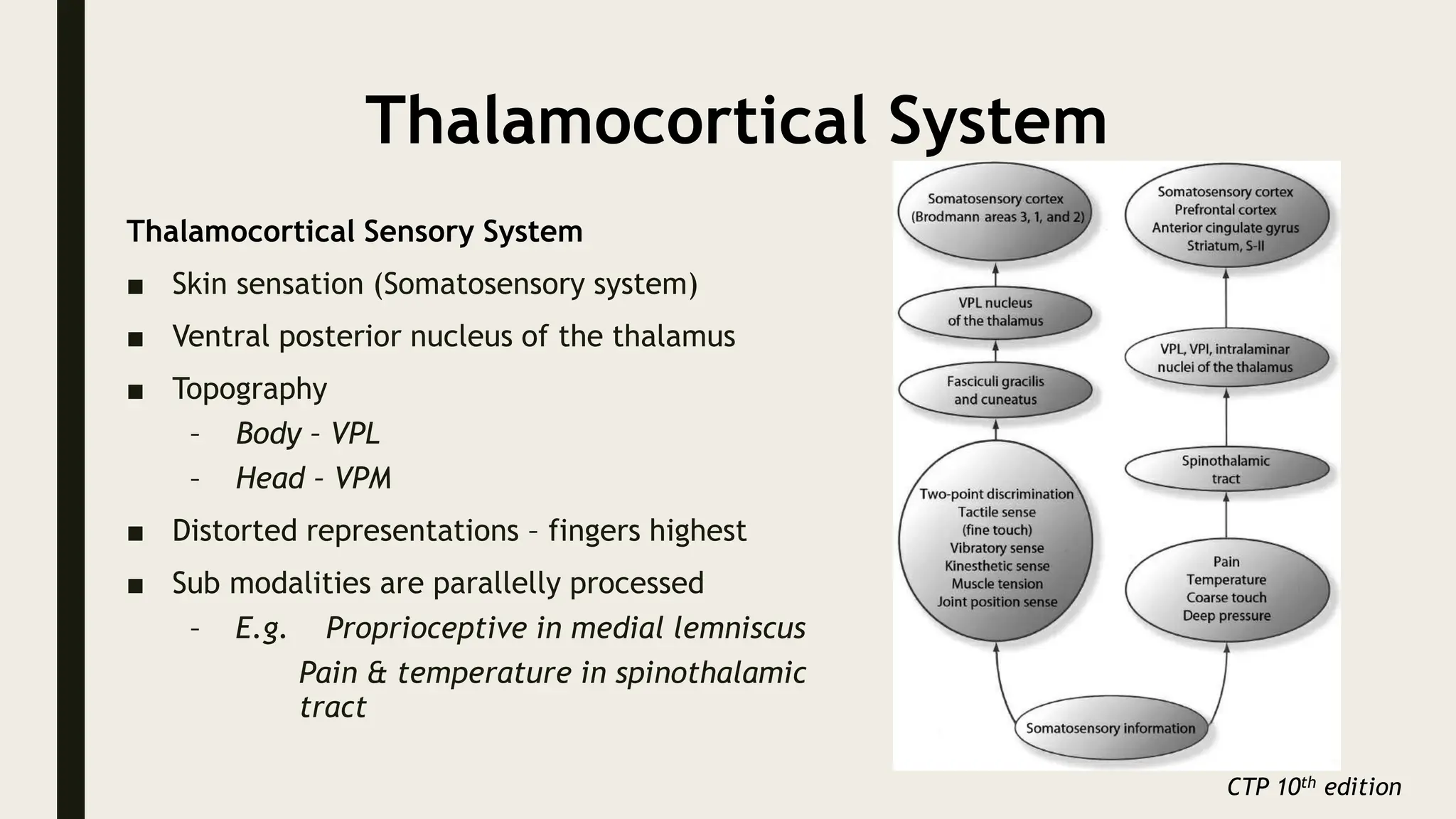
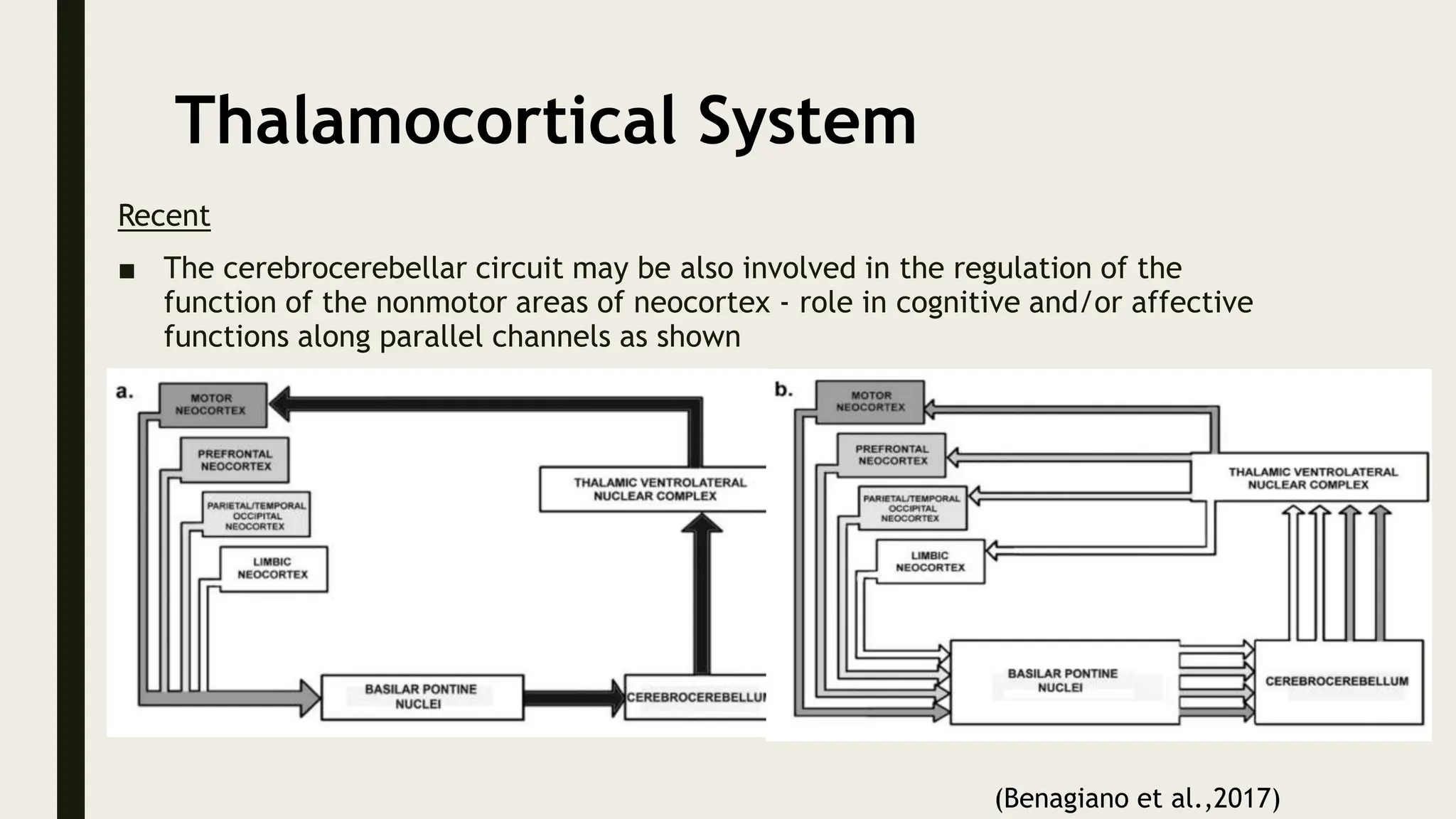
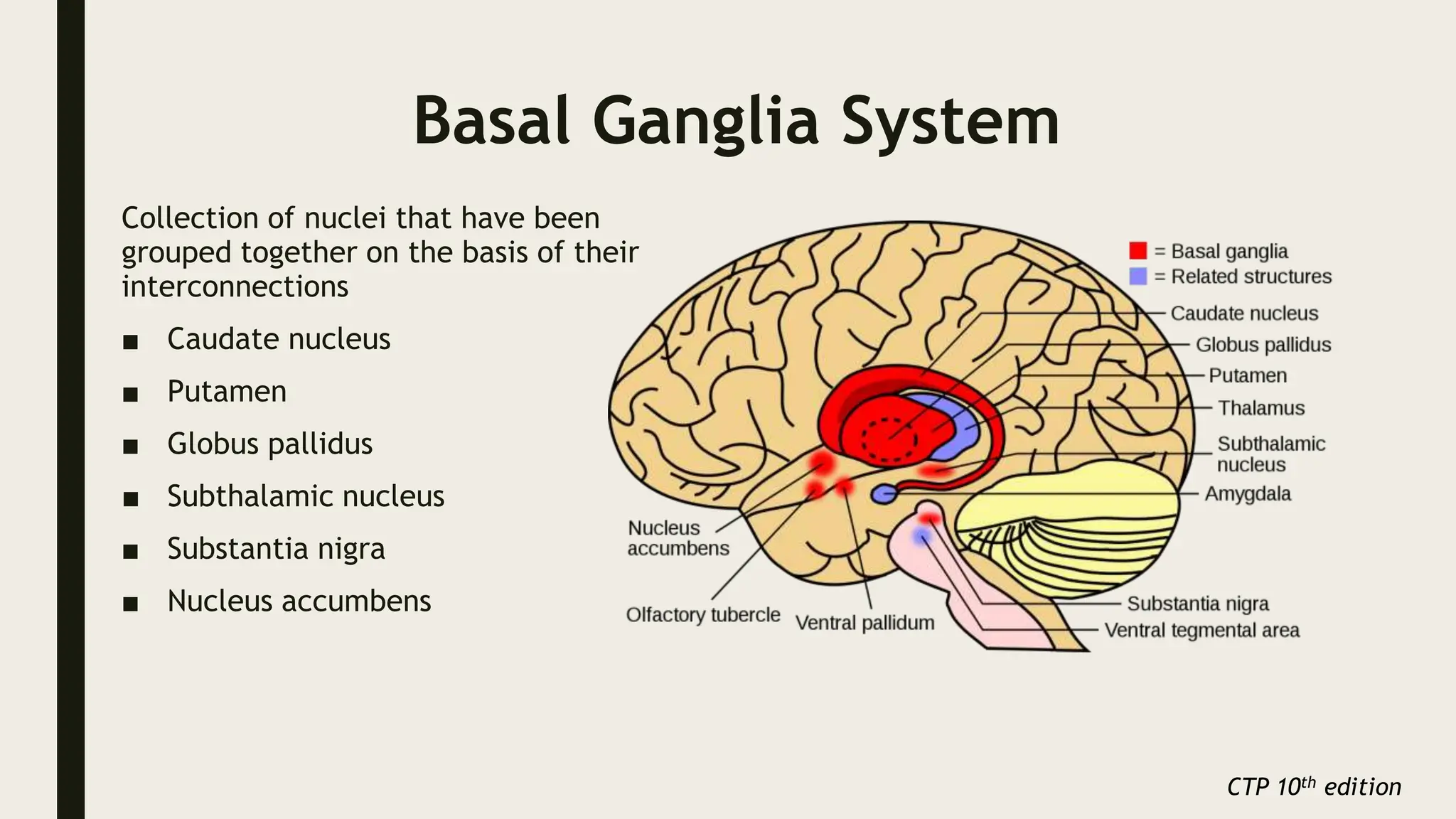
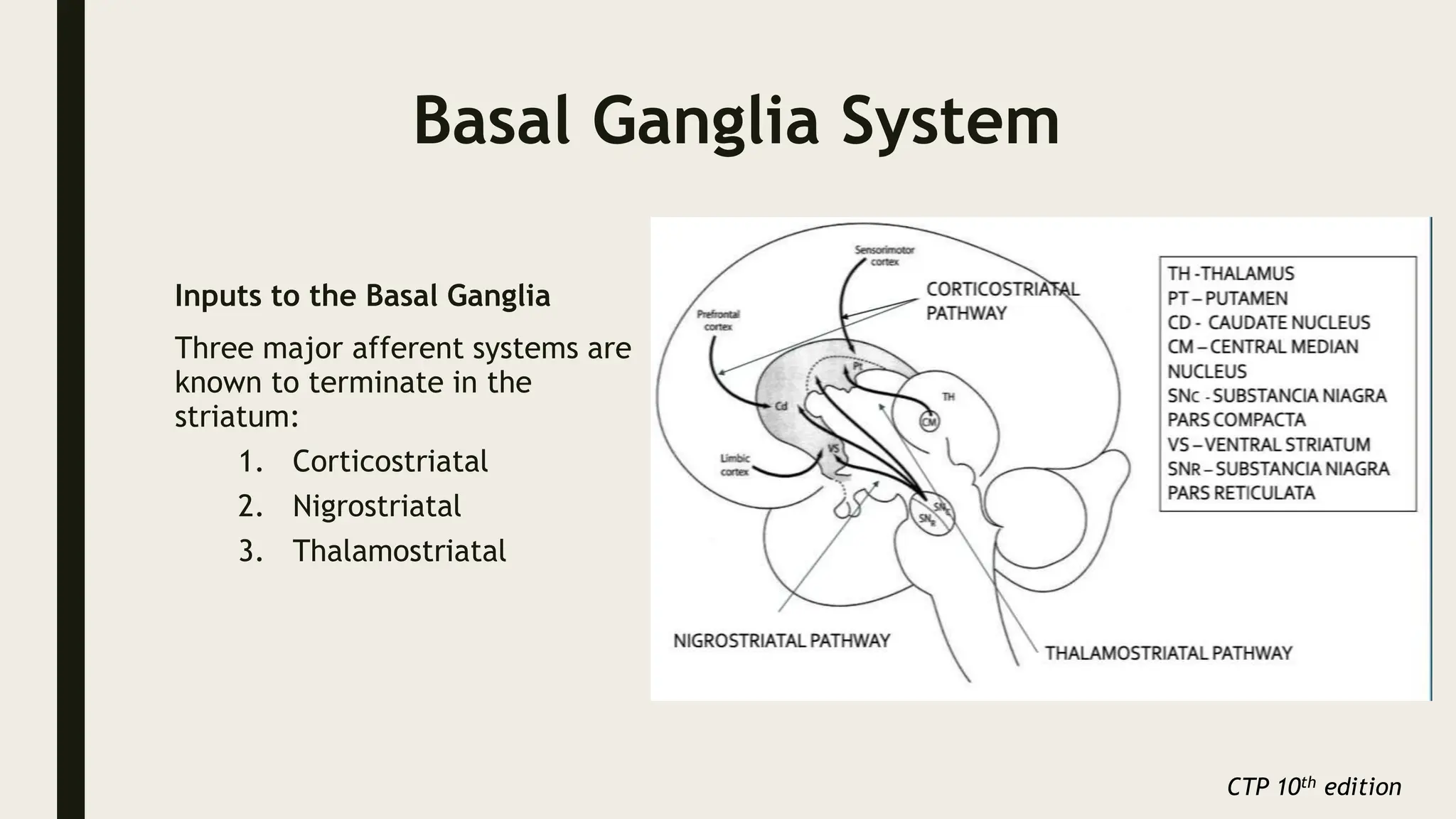
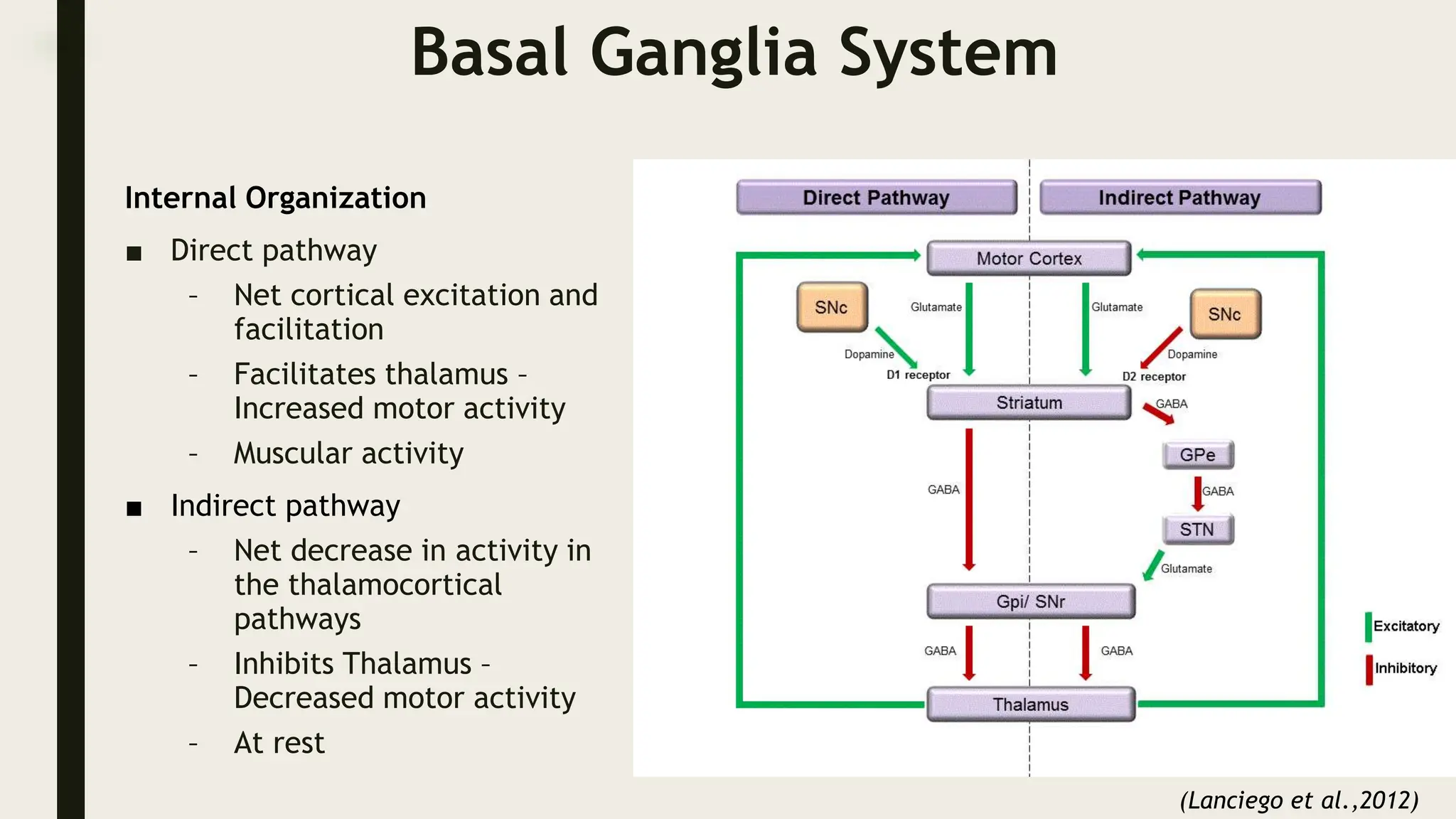
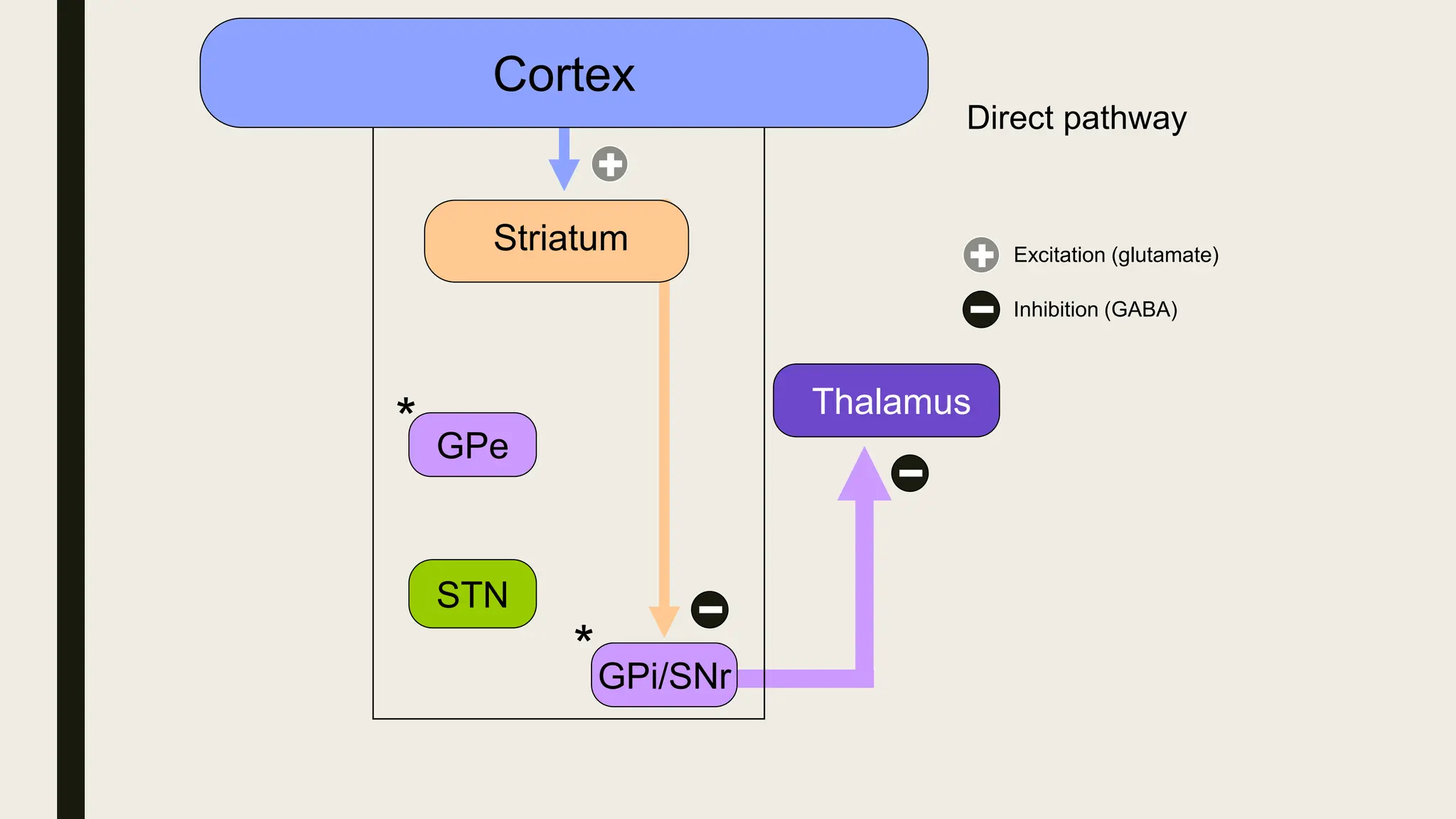
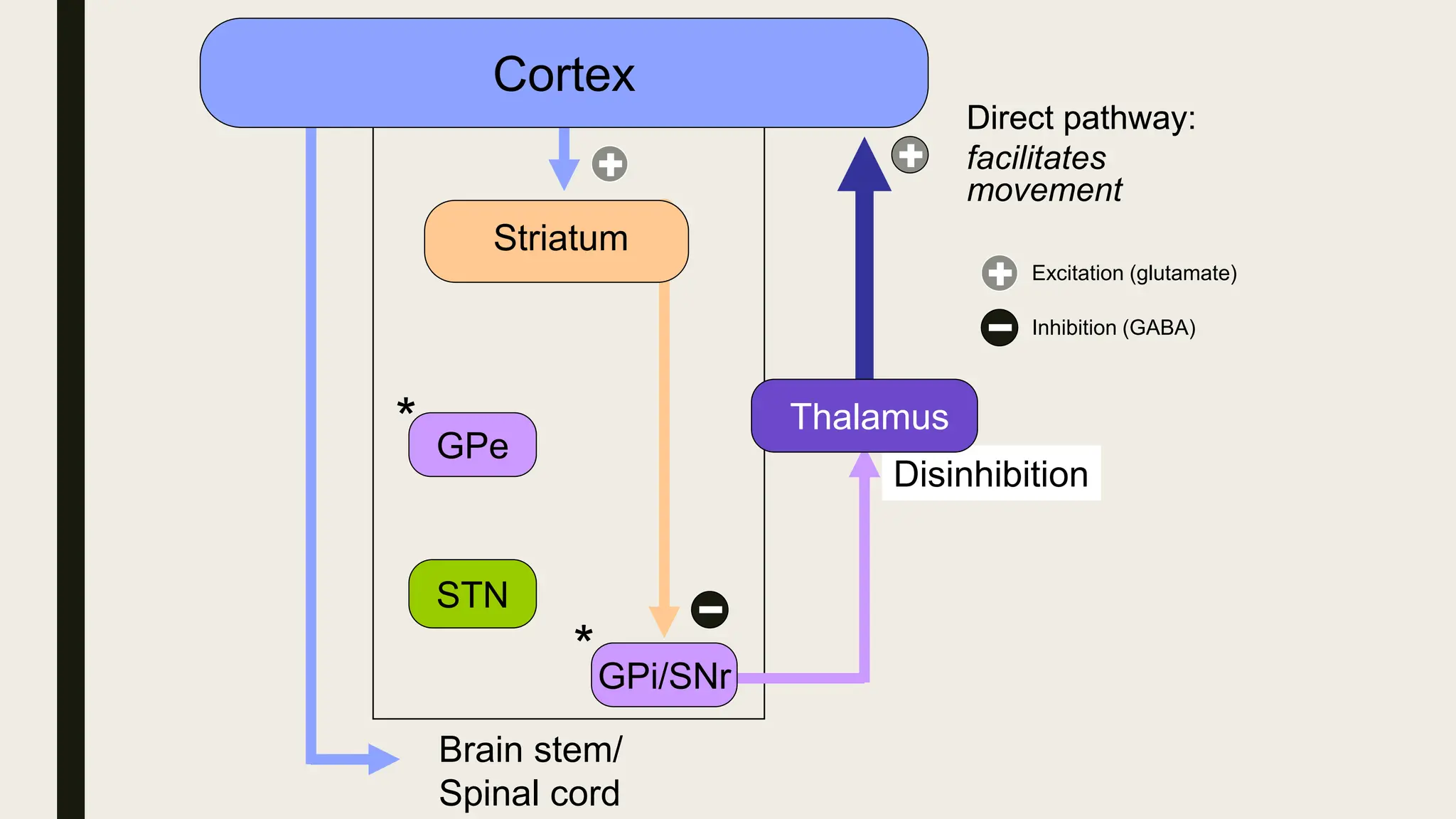
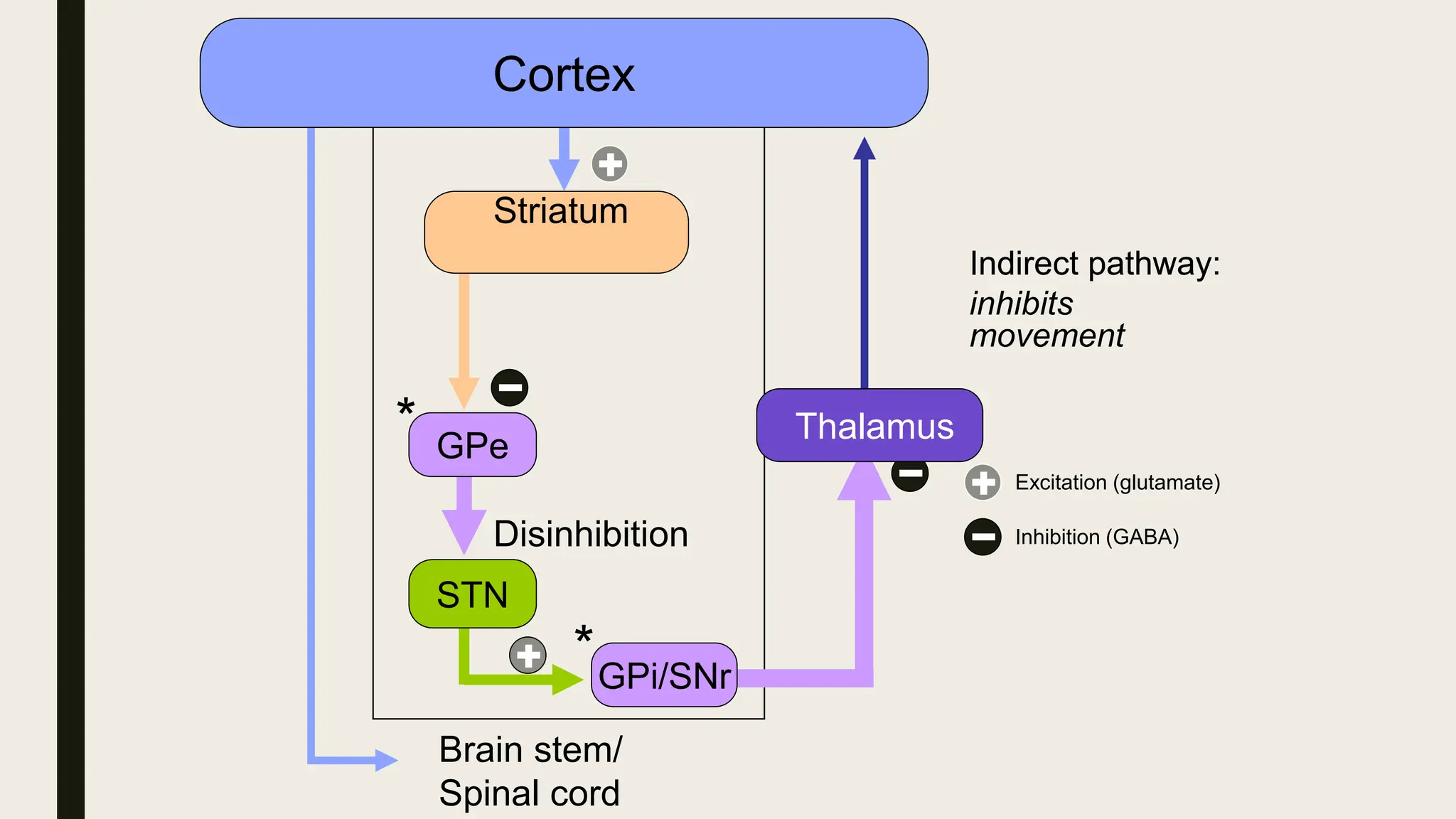
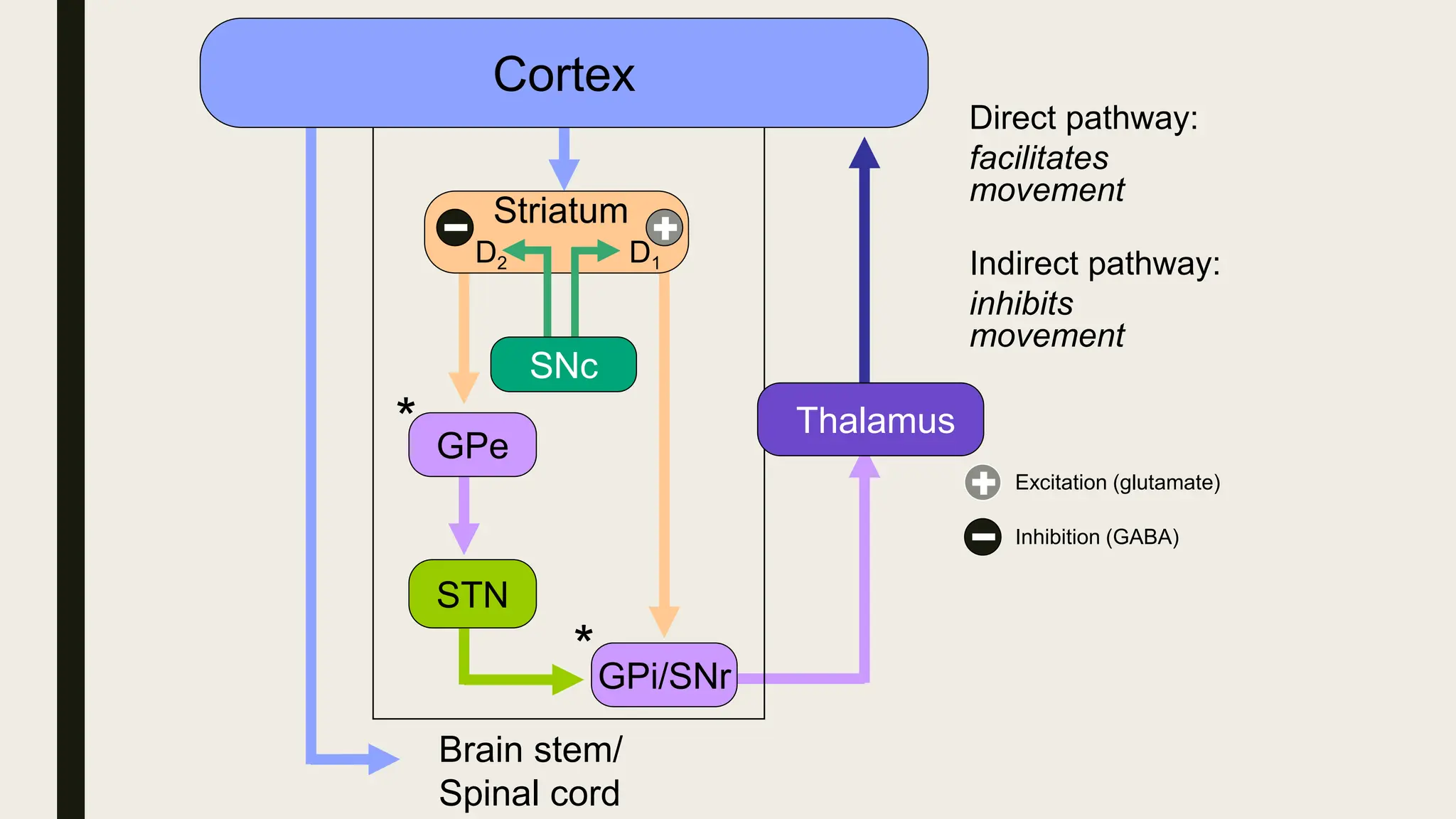
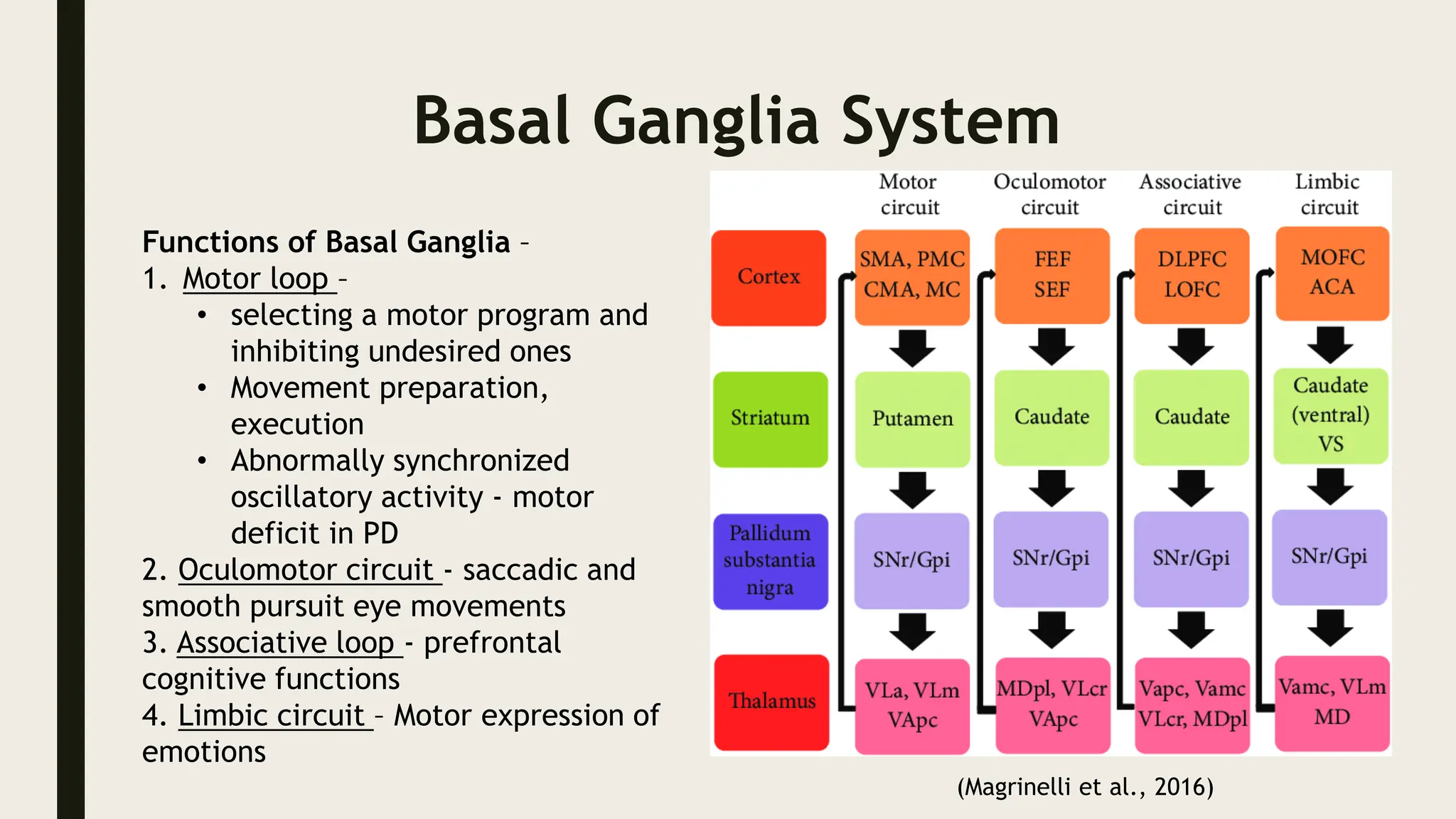
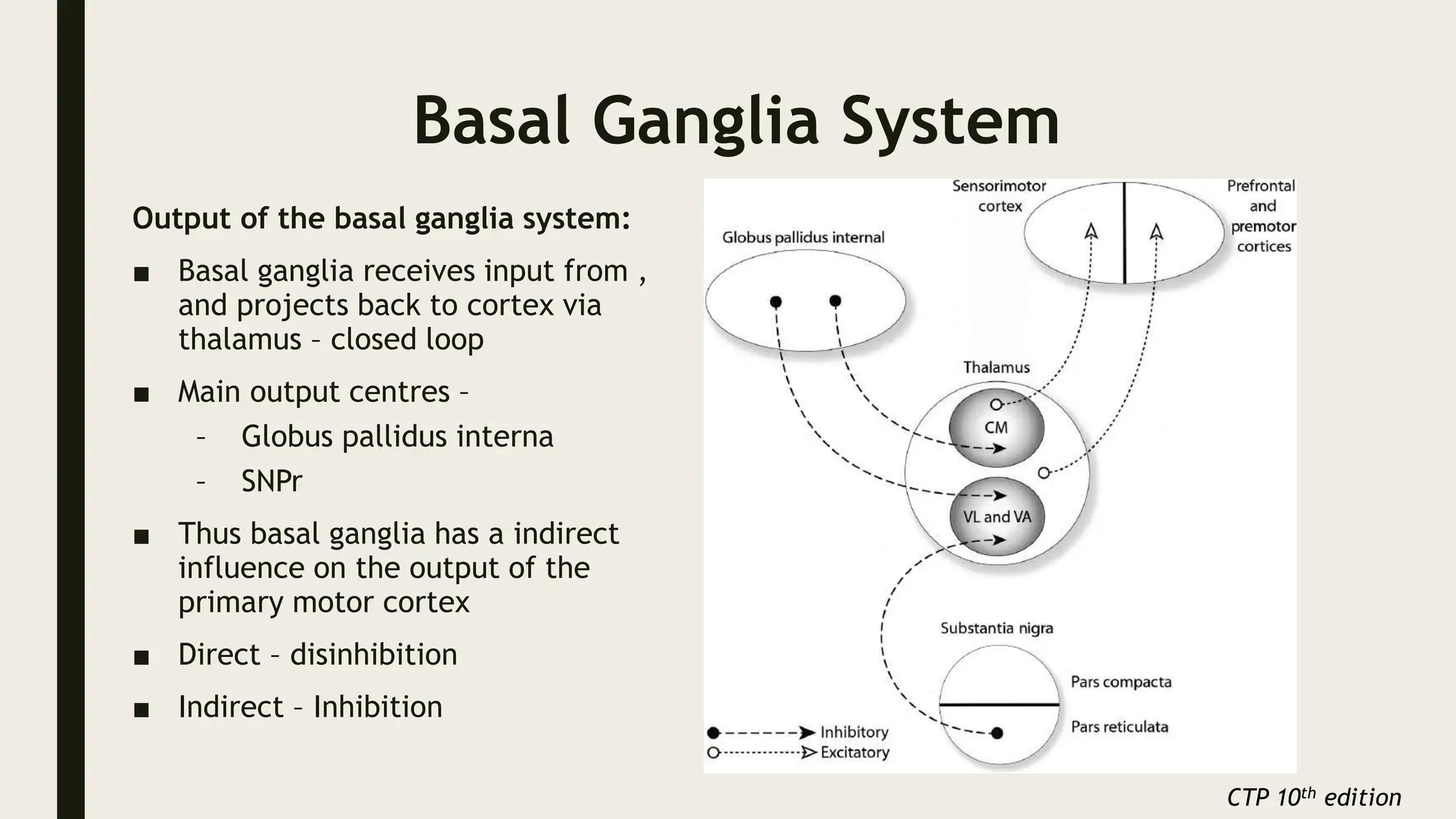
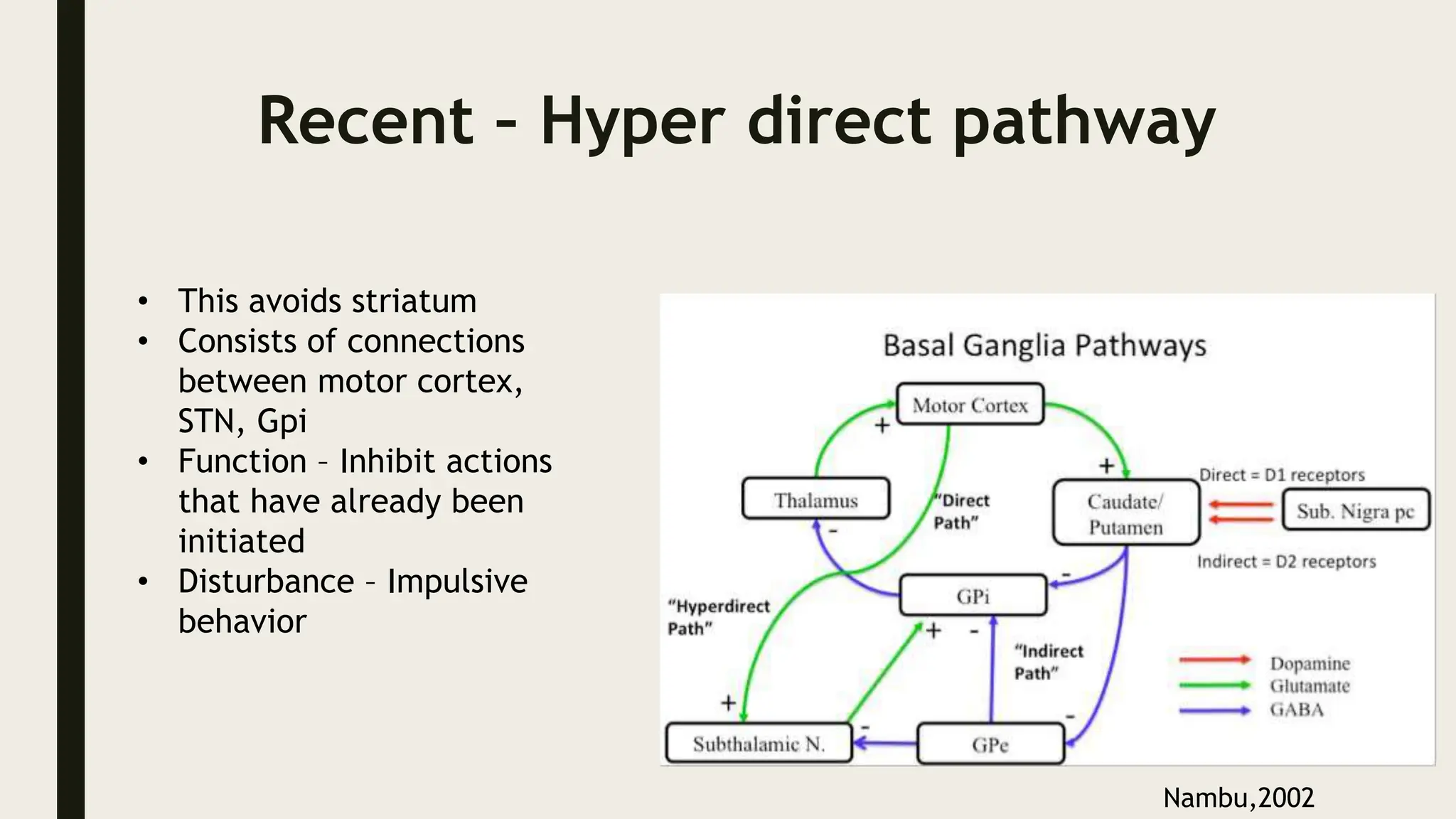
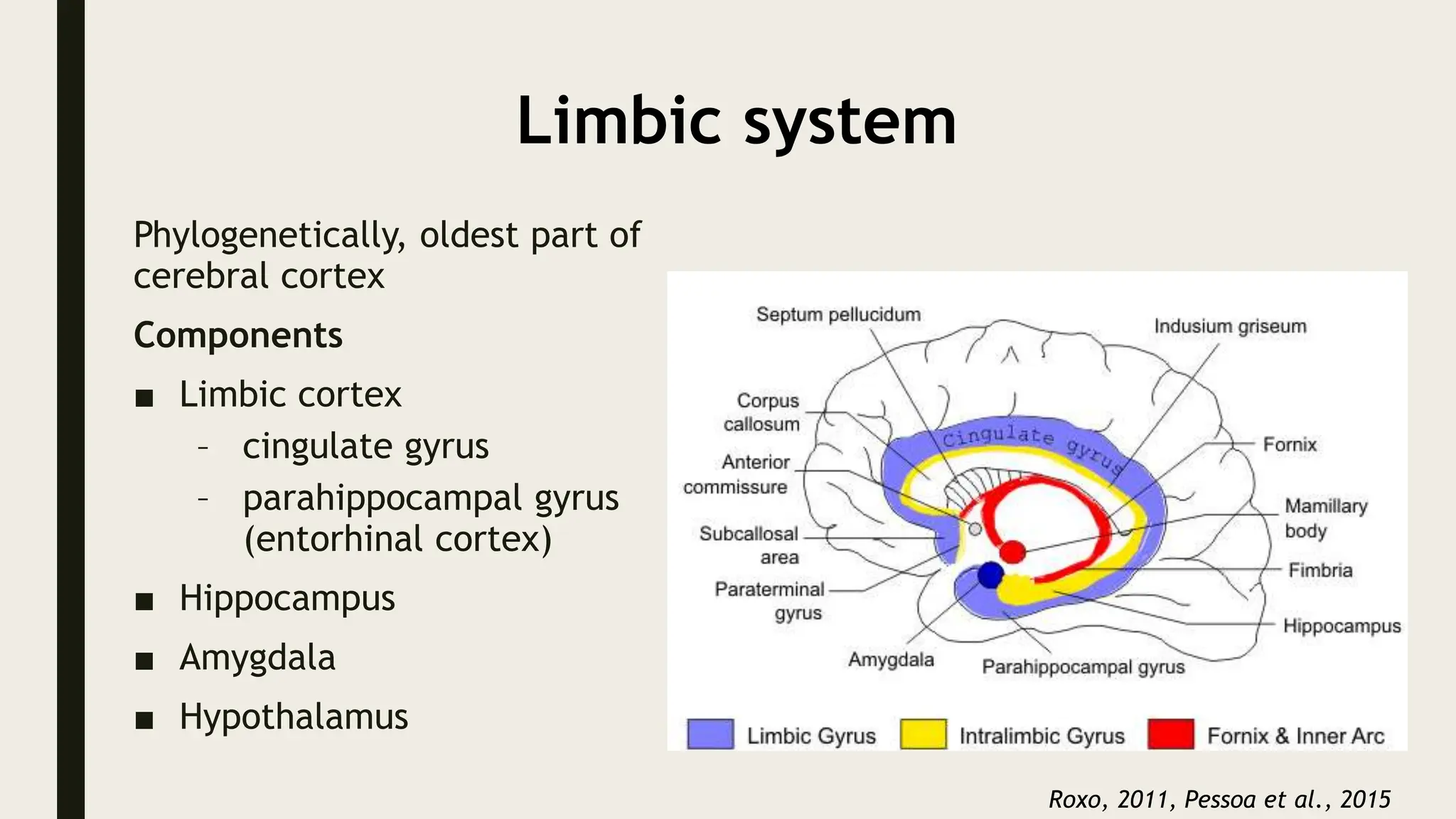
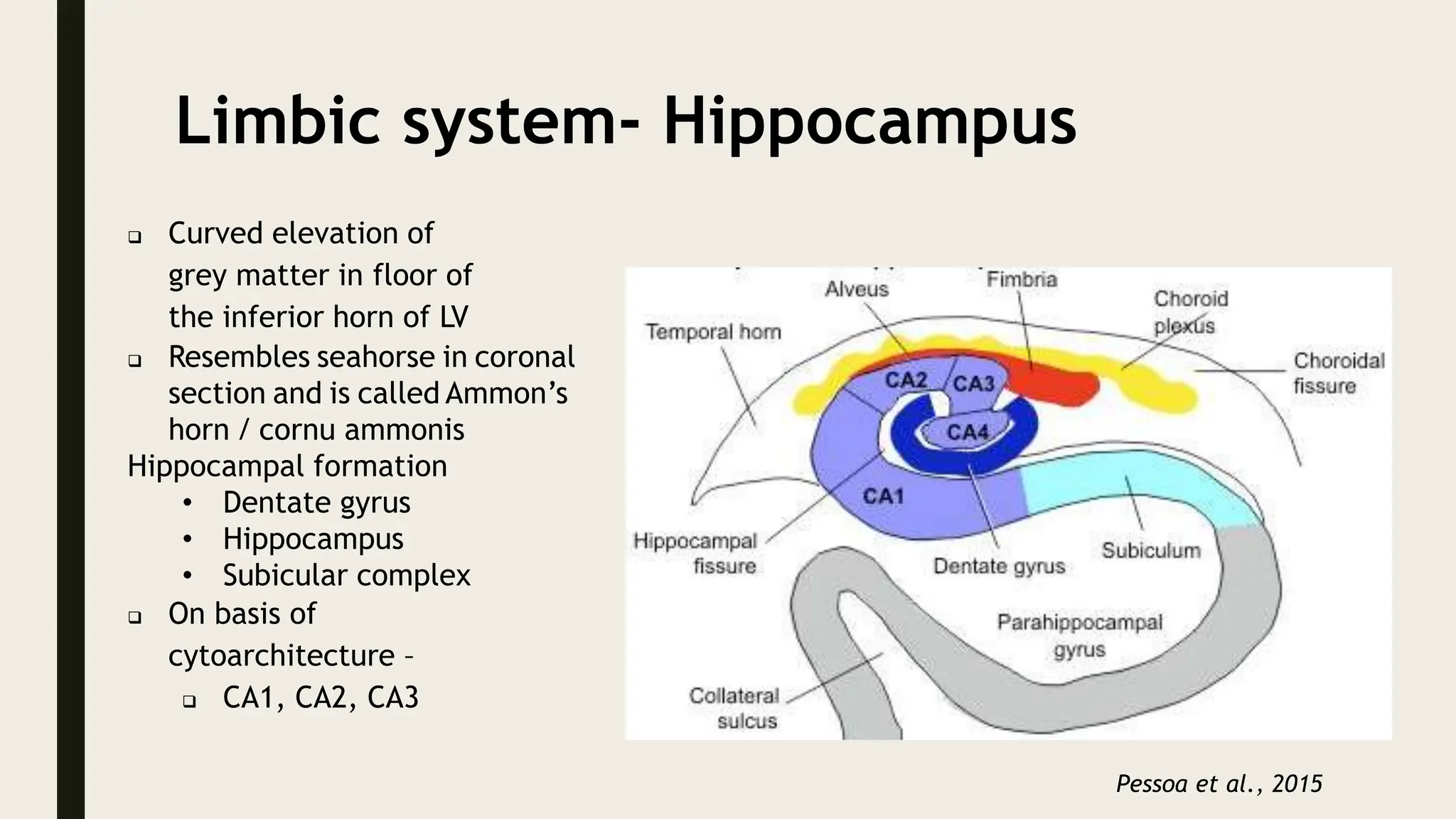
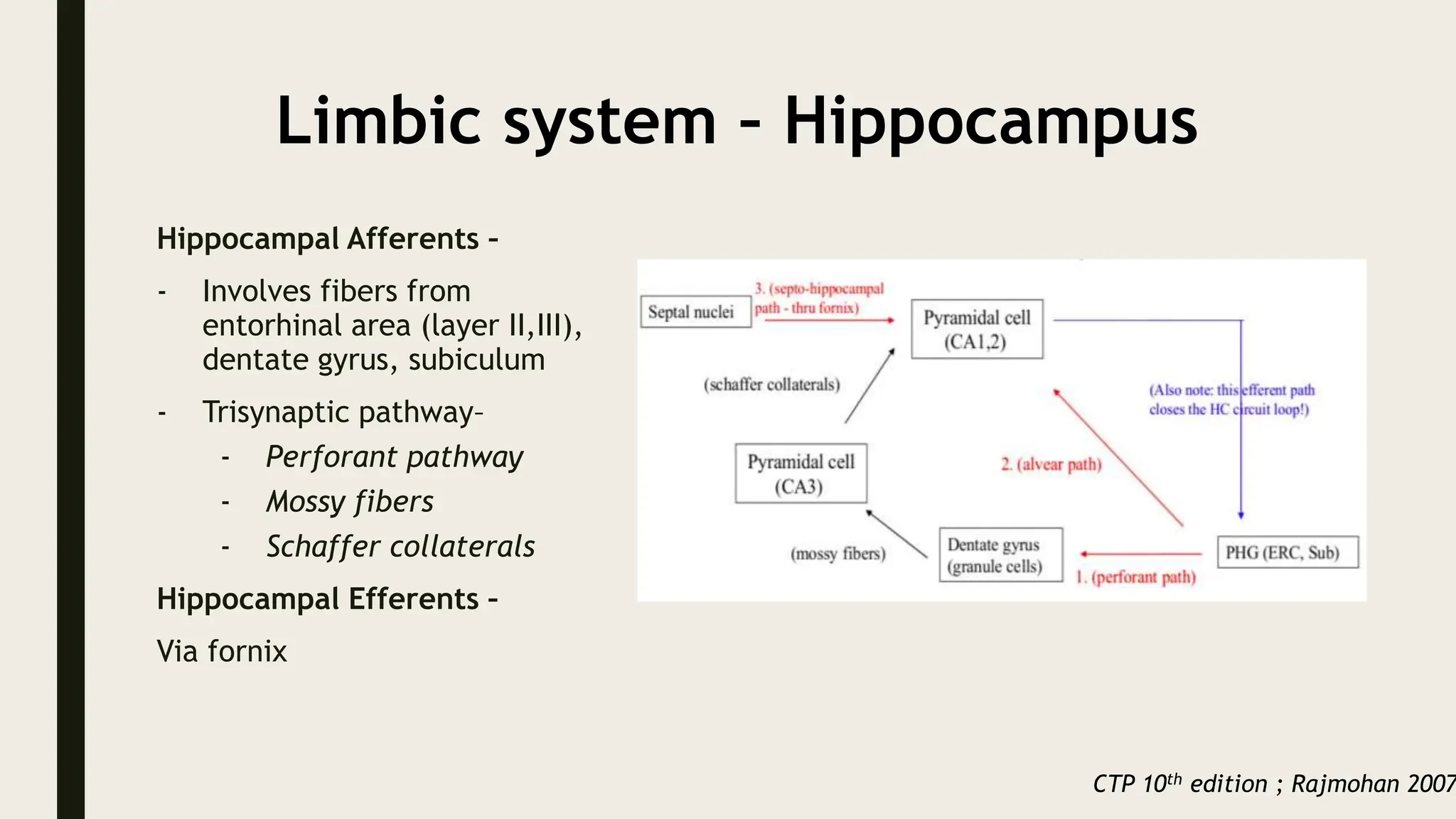
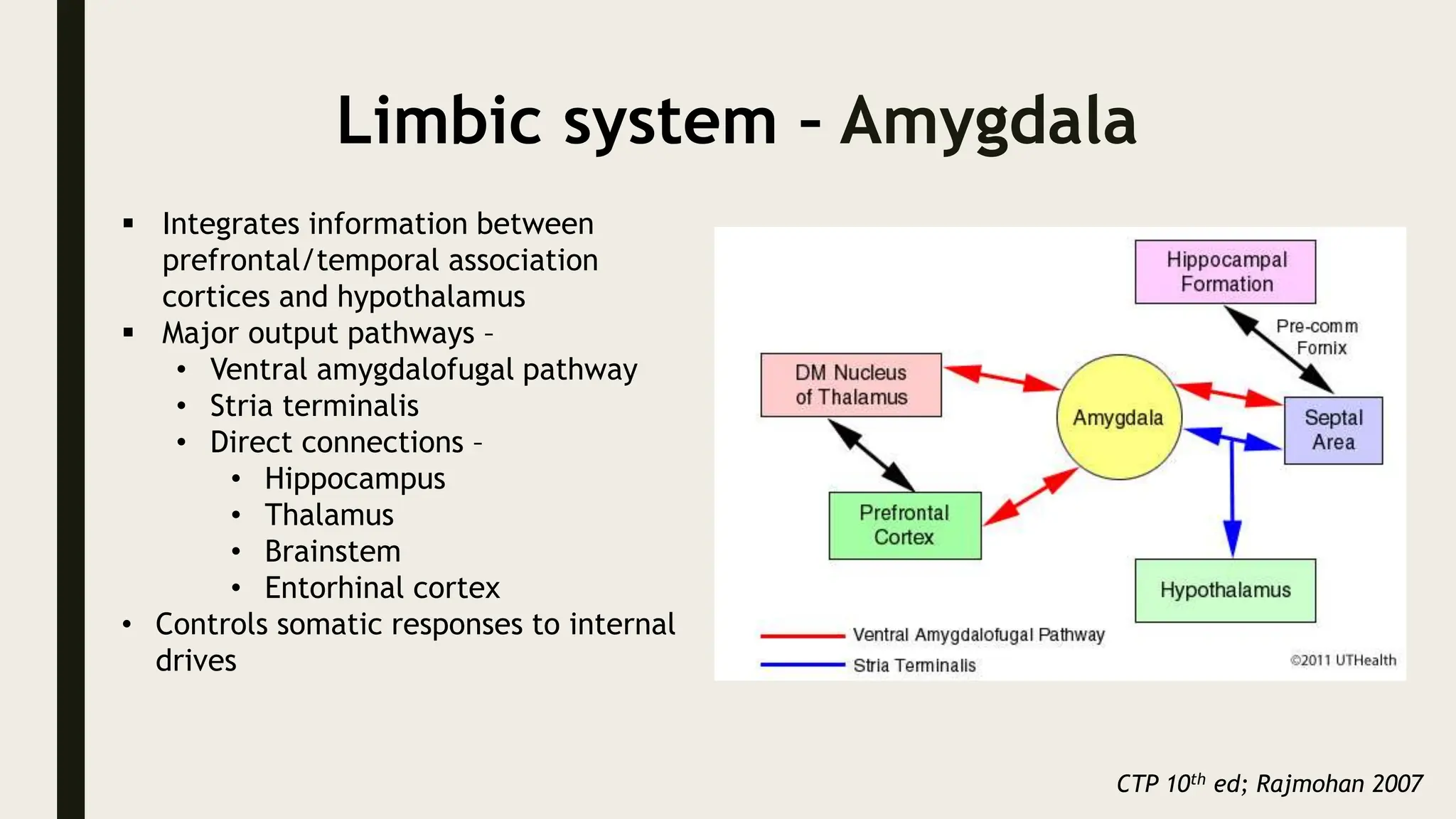
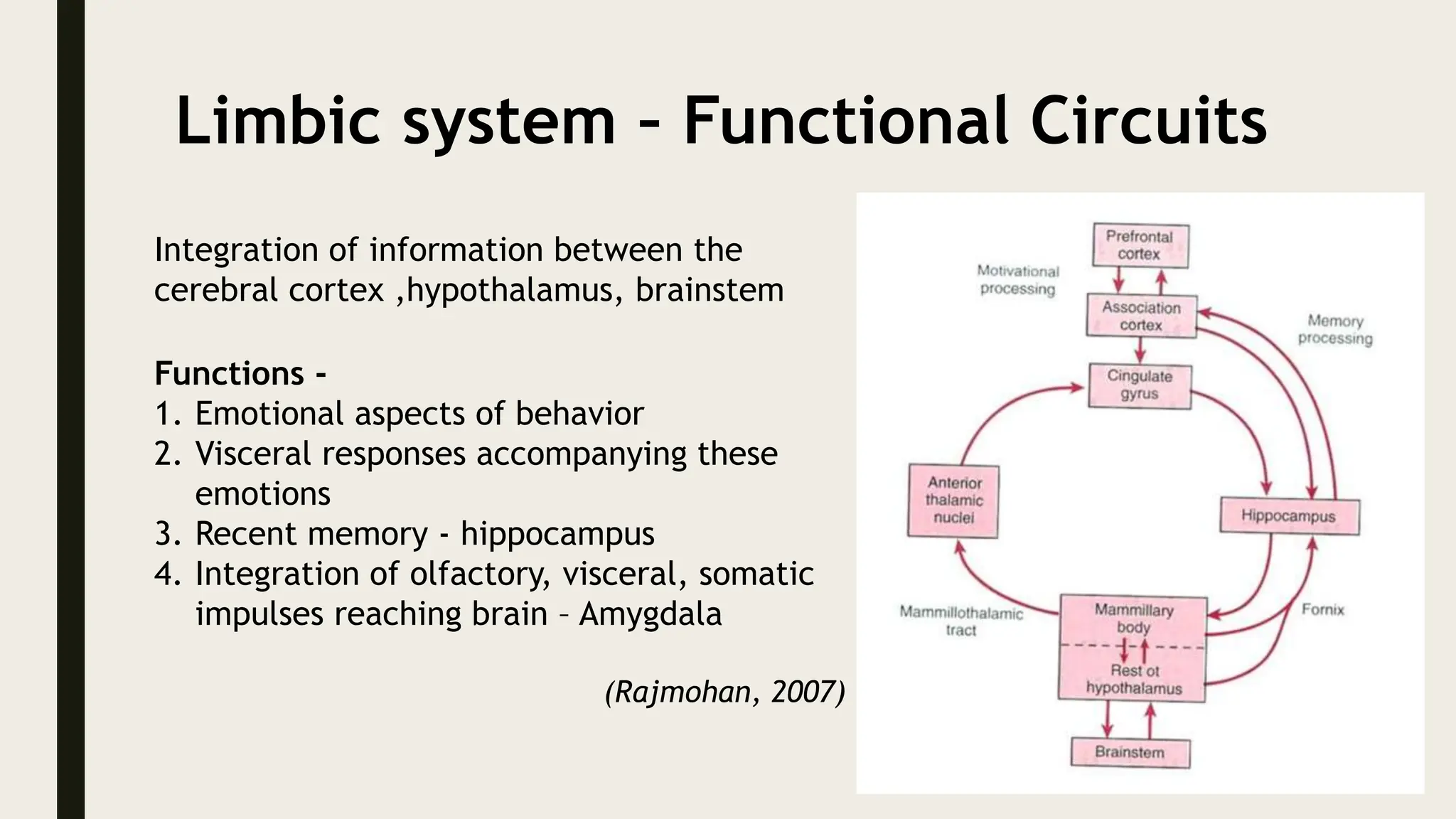
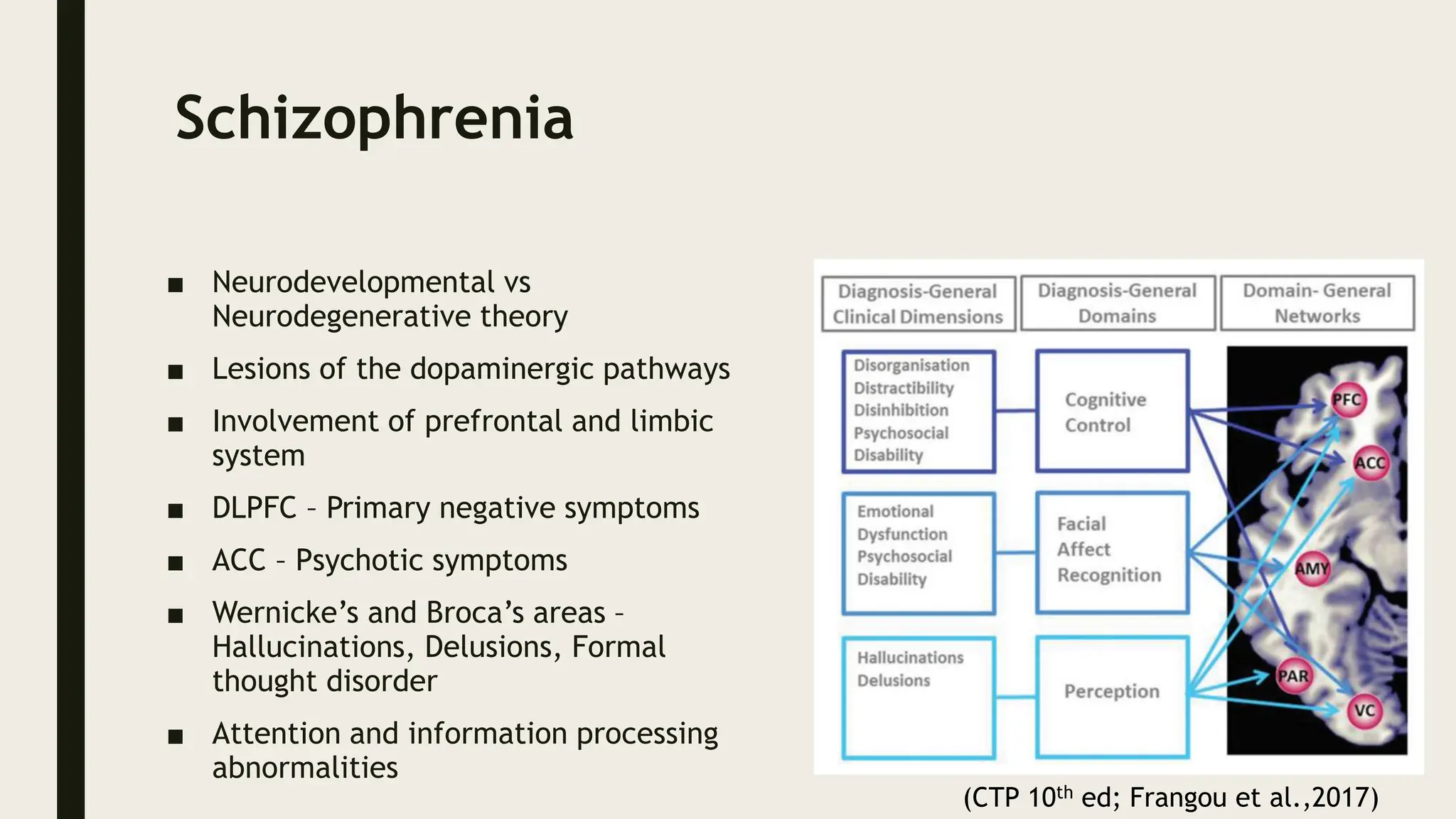
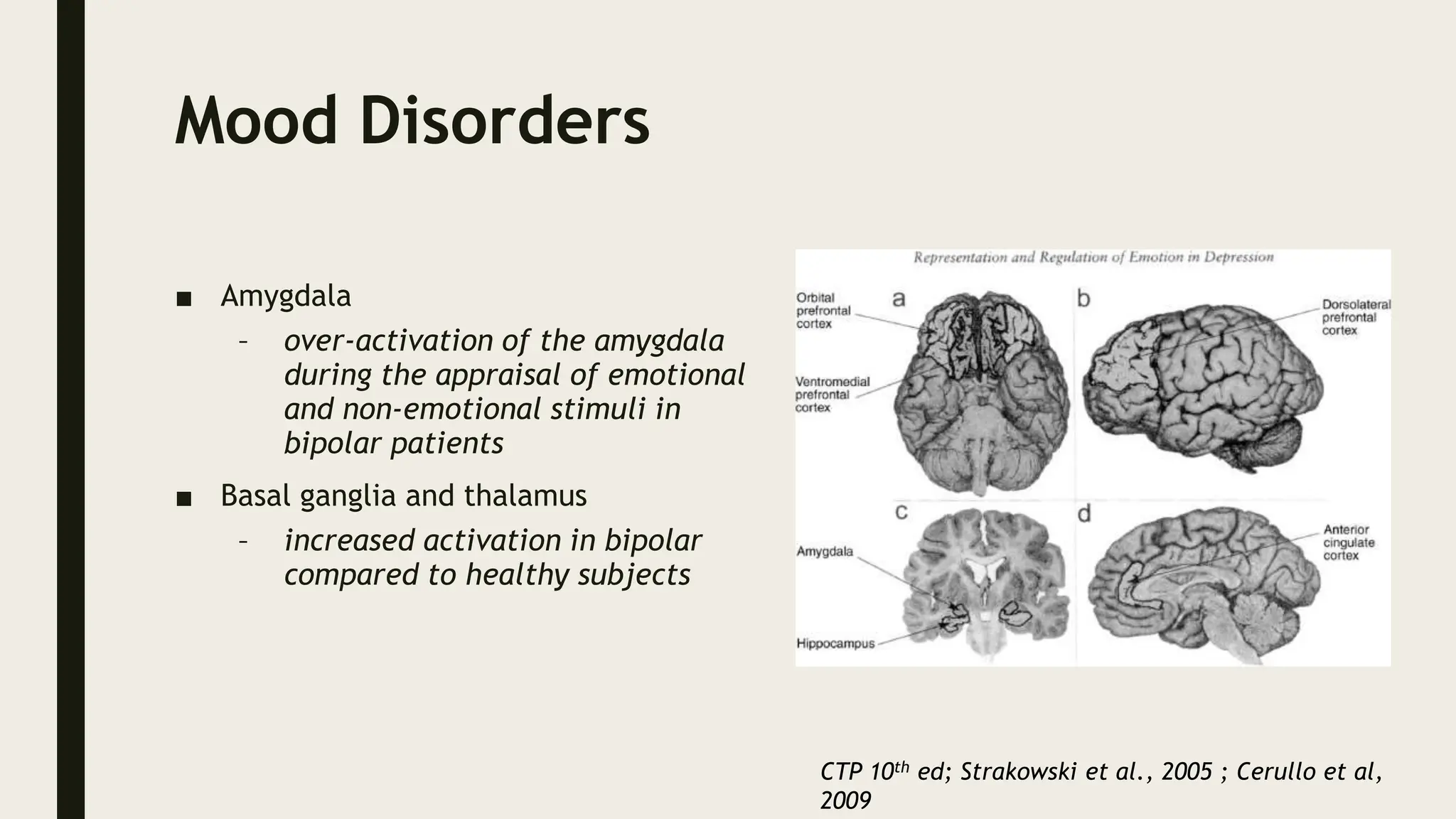
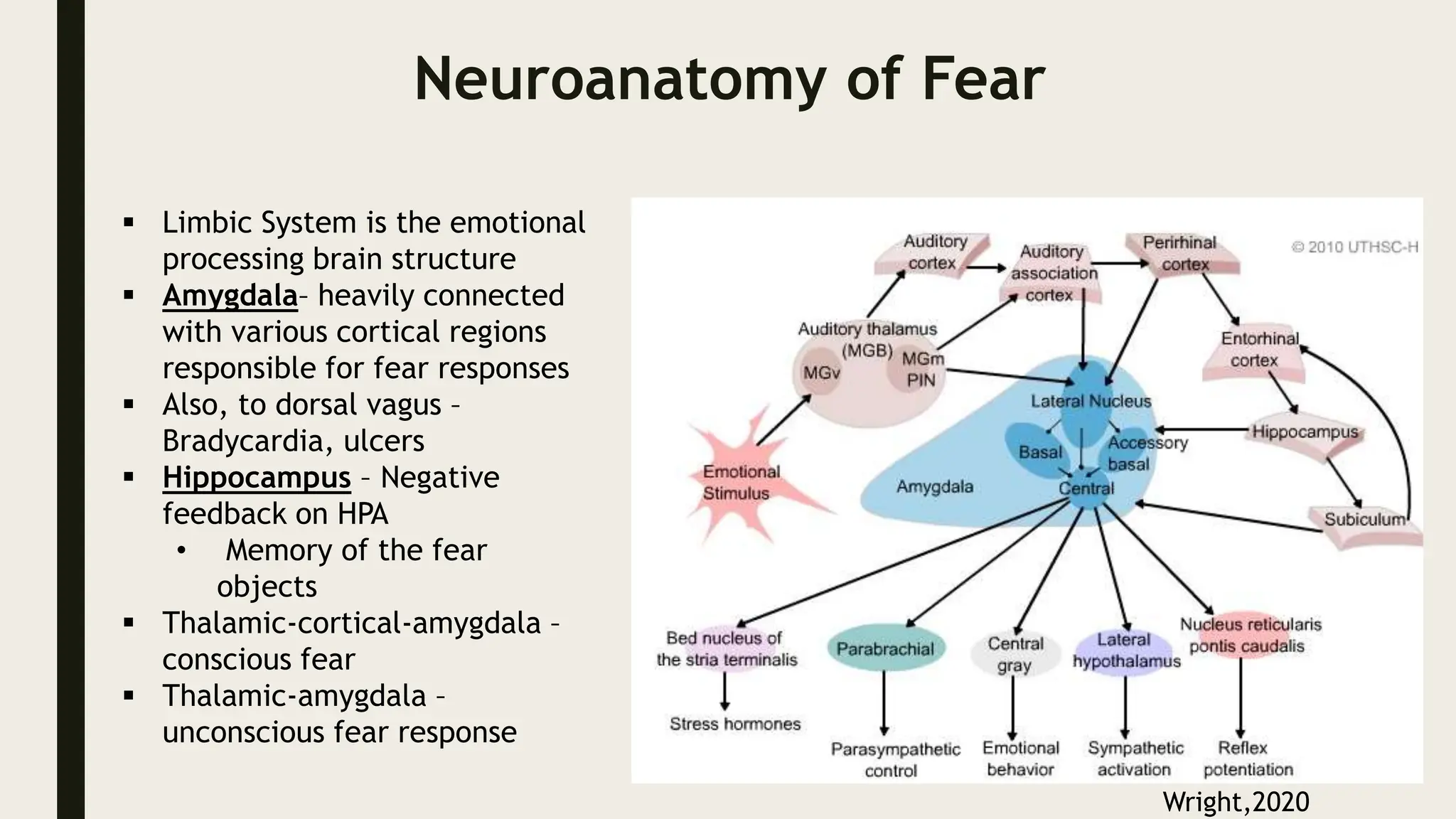
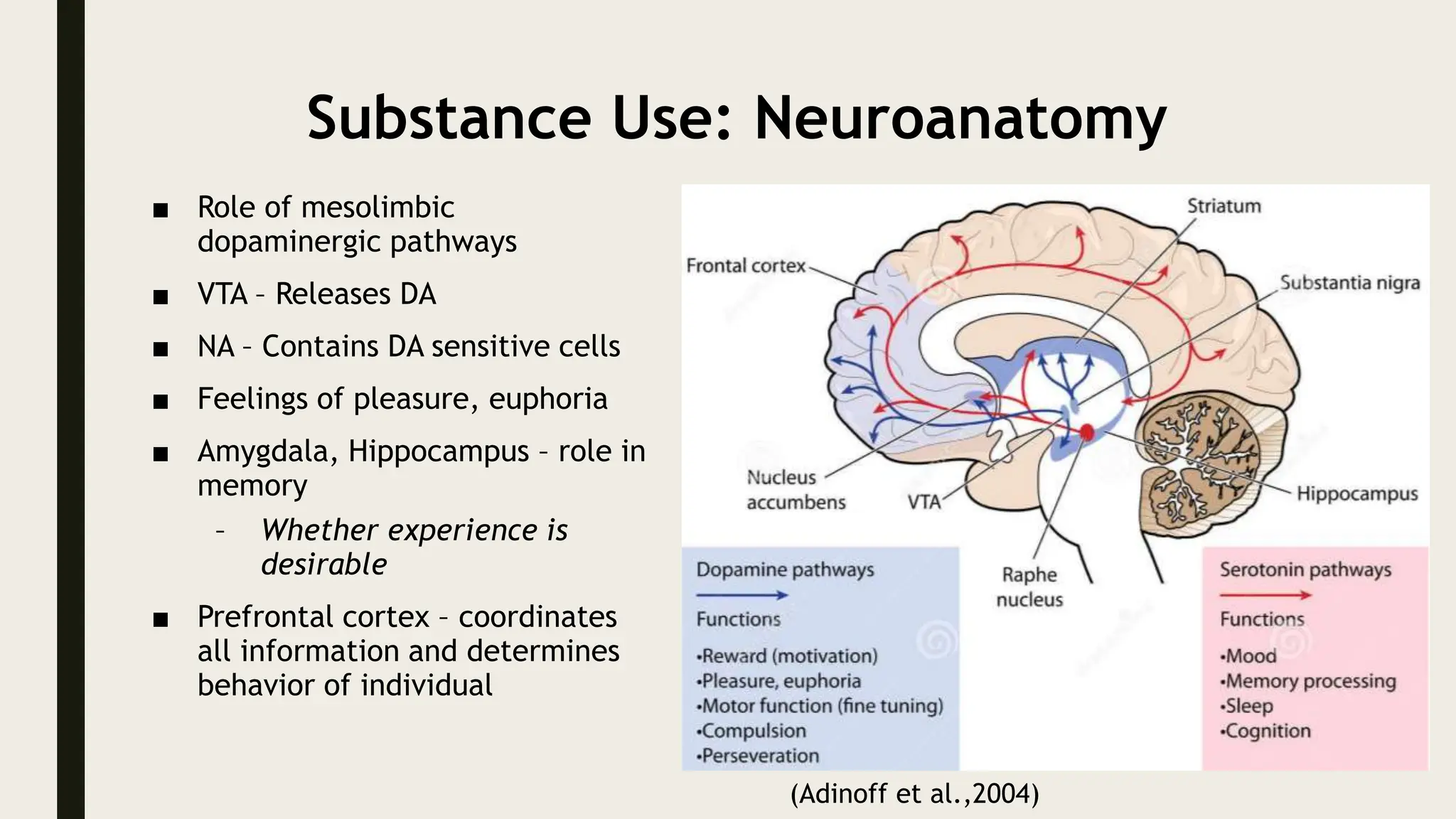
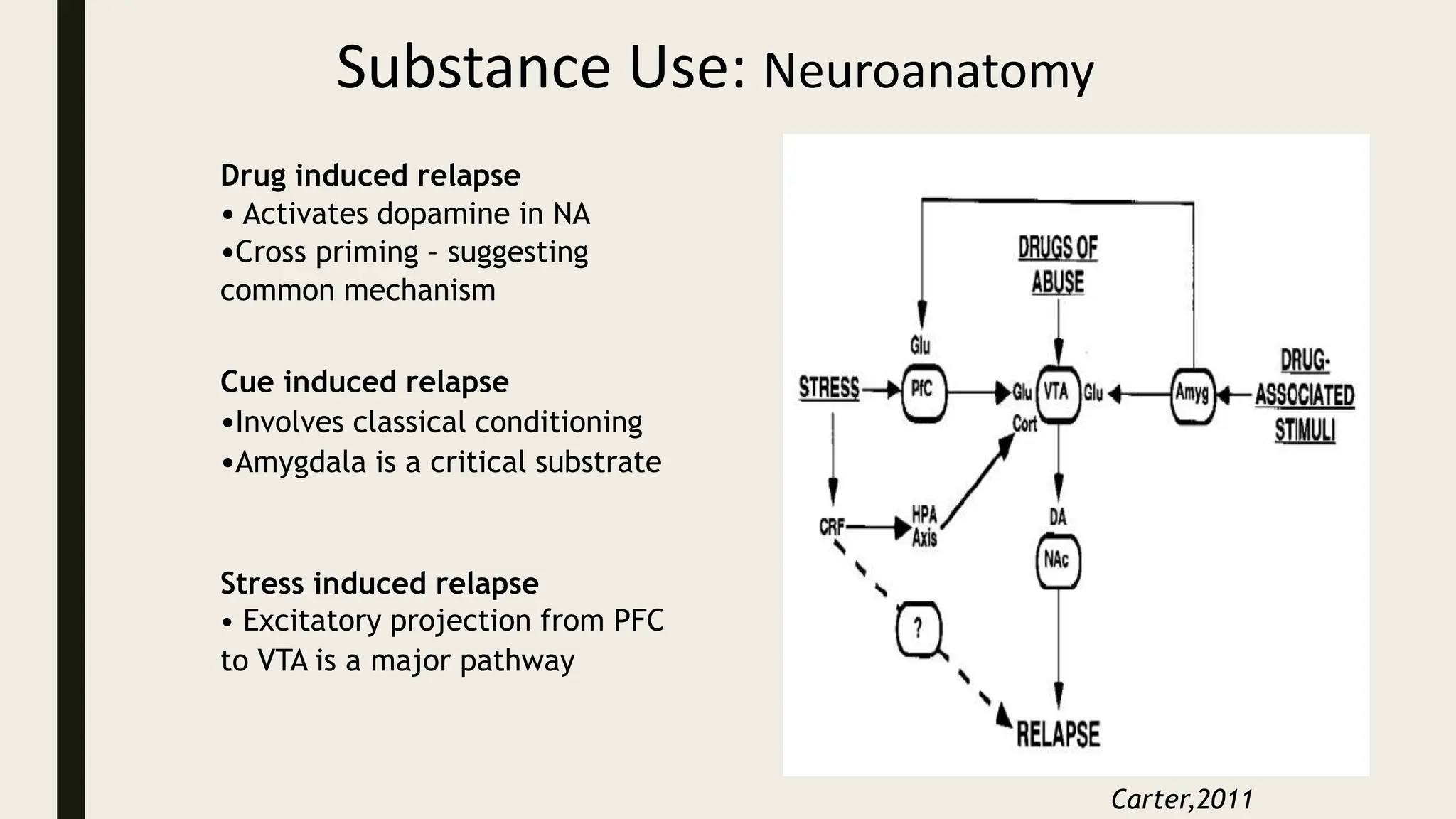
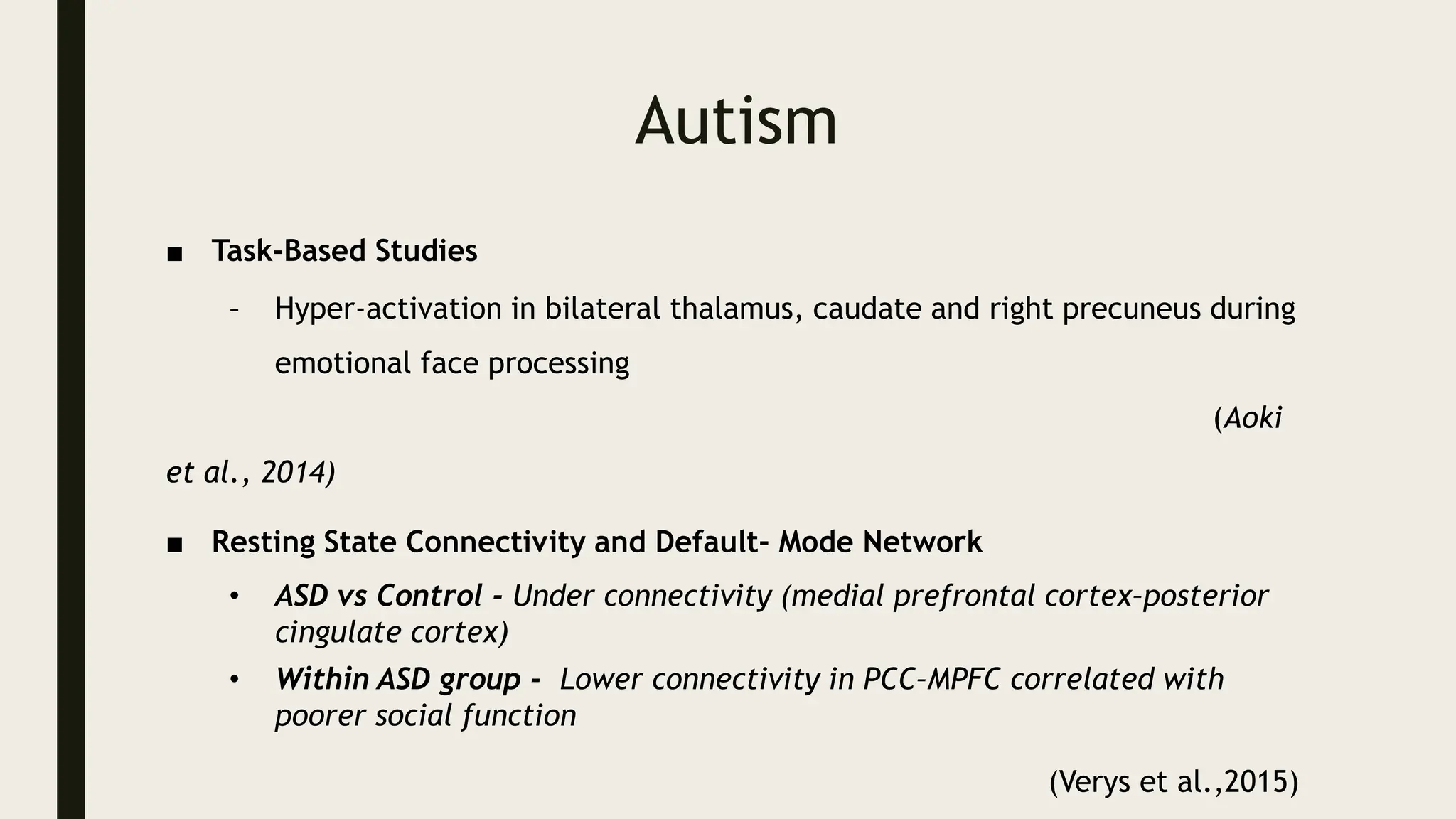
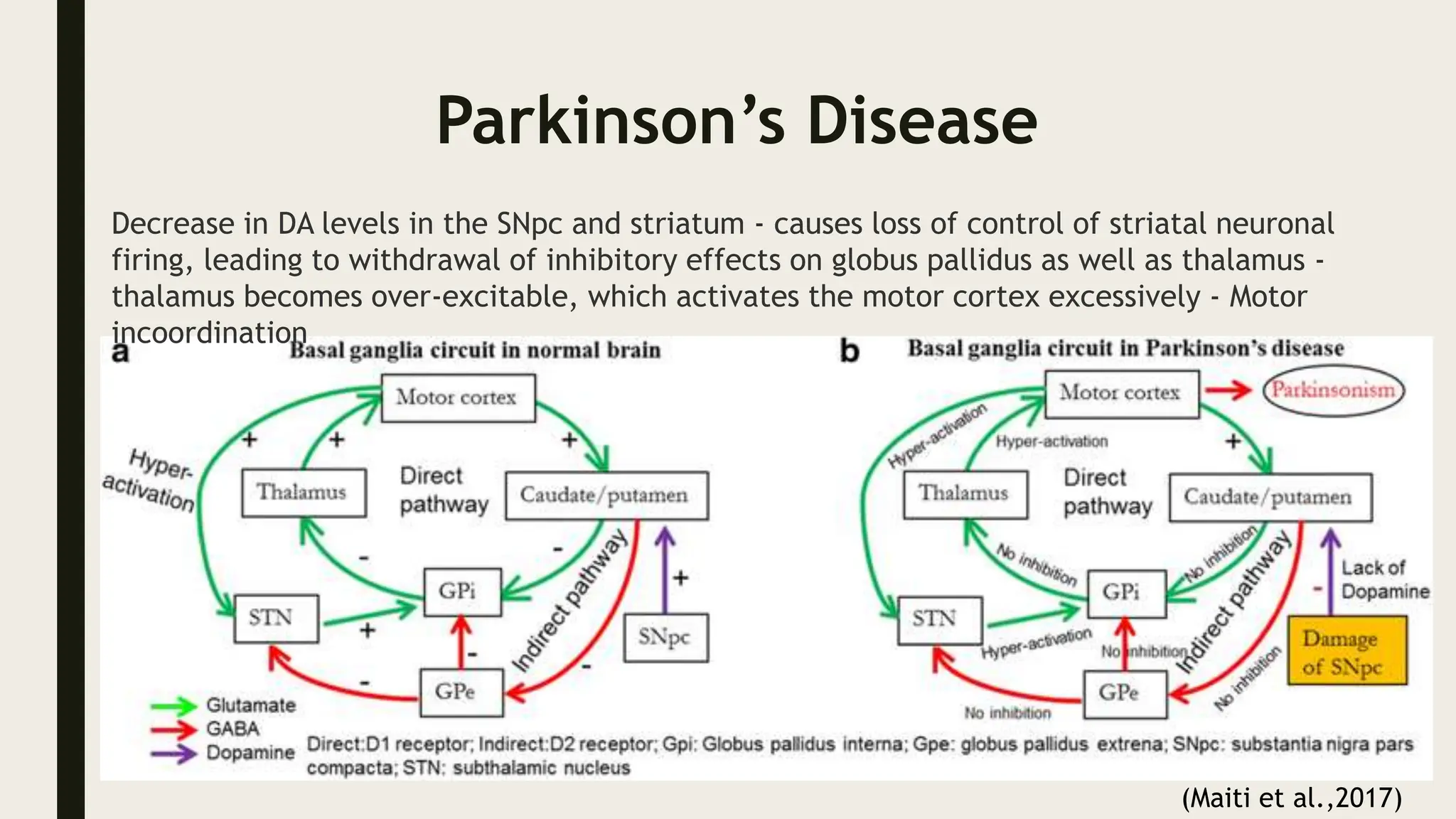
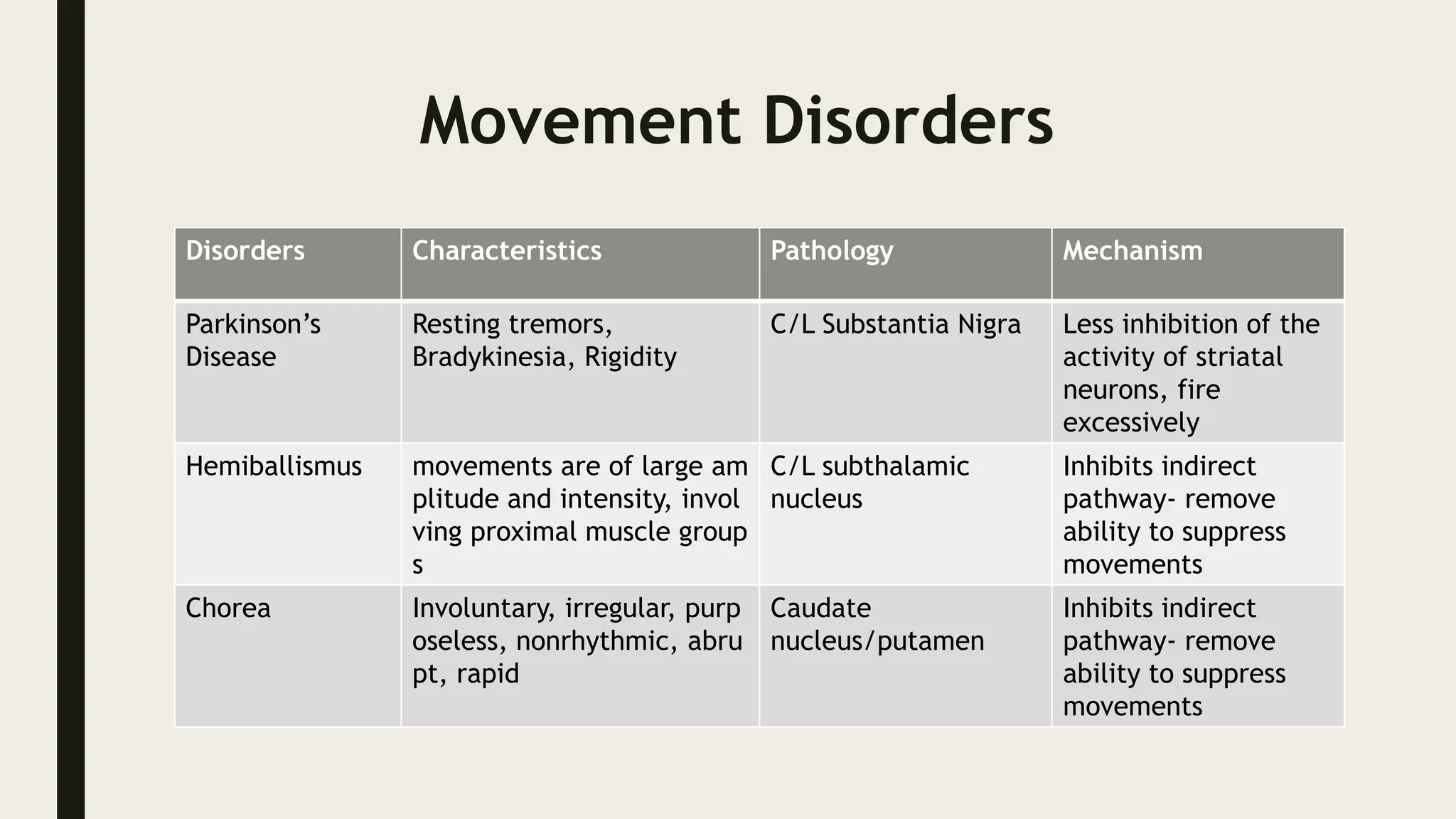
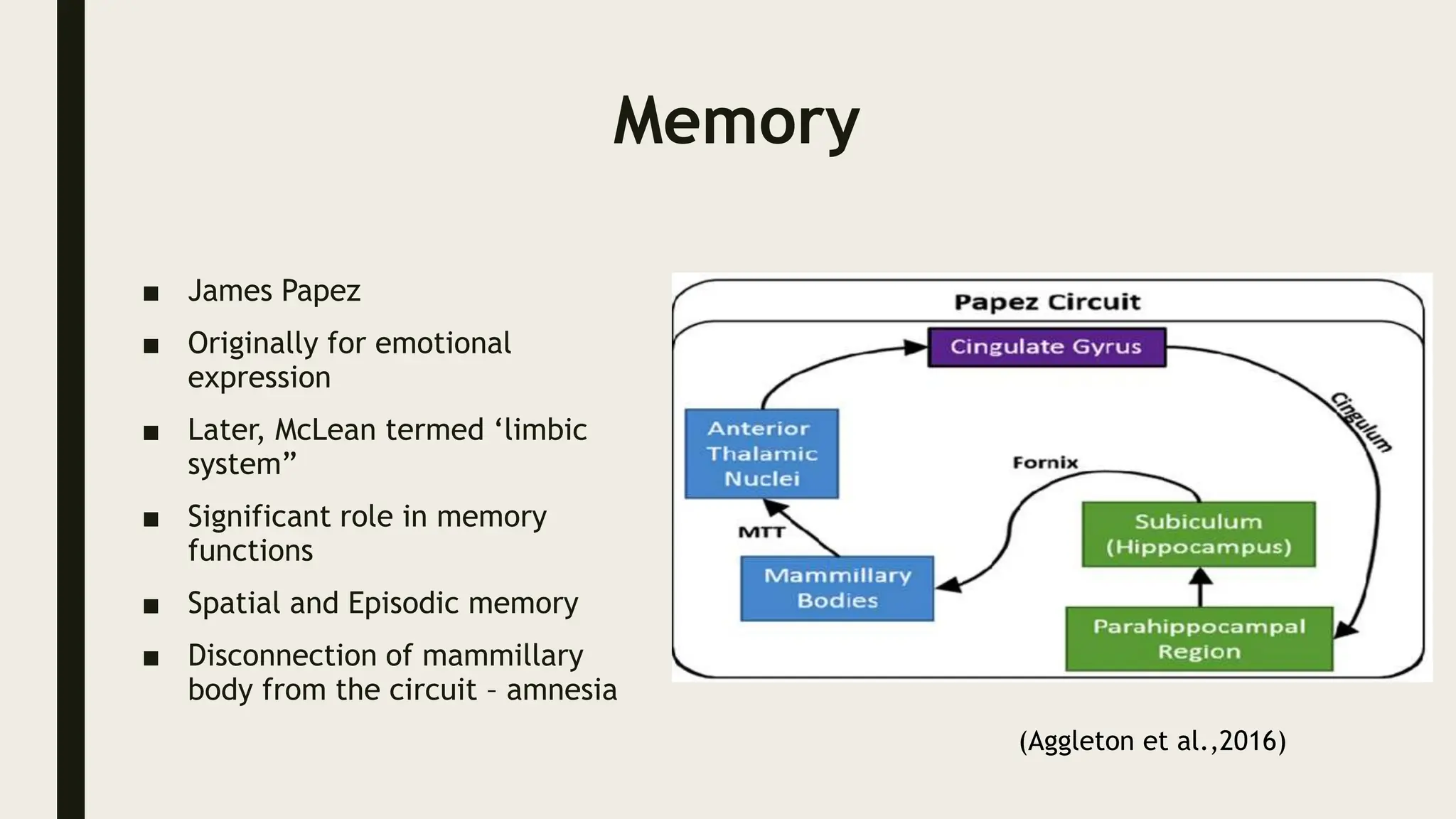
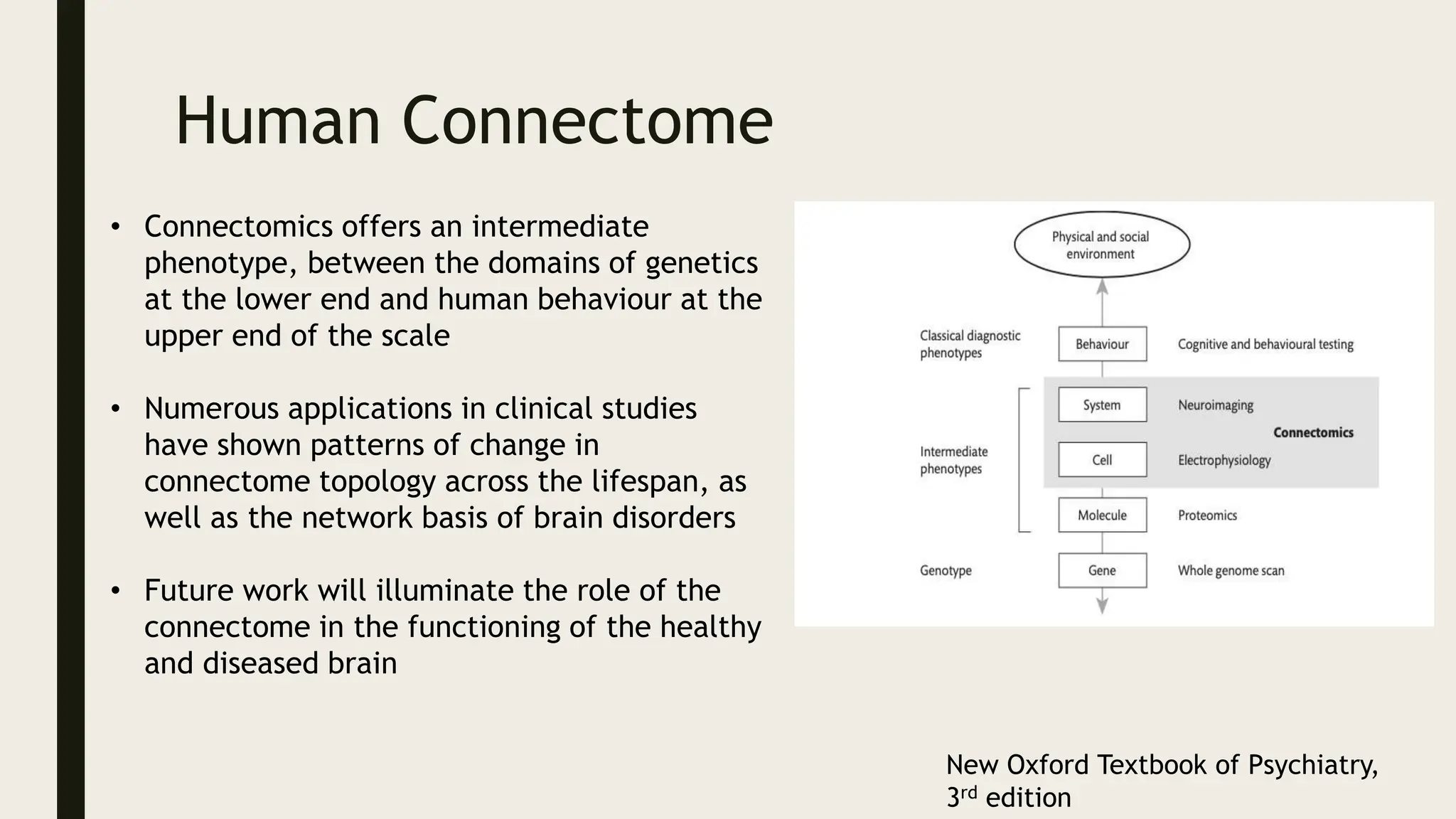
The document discusses functional neuroanatomy and its relevance to psychiatry, outlining the organization of the human brain and its various systems, including the cerebral cortex, thalamus, basal ganglia, and limbic system. It examines the neuroanatomical correlates of major psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, mood disorders, and anxiety disorders, highlighting changes in brain structures and functions associated with these conditions. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of understanding these neurobiological bases for advancements in psychiatric care and treatment.