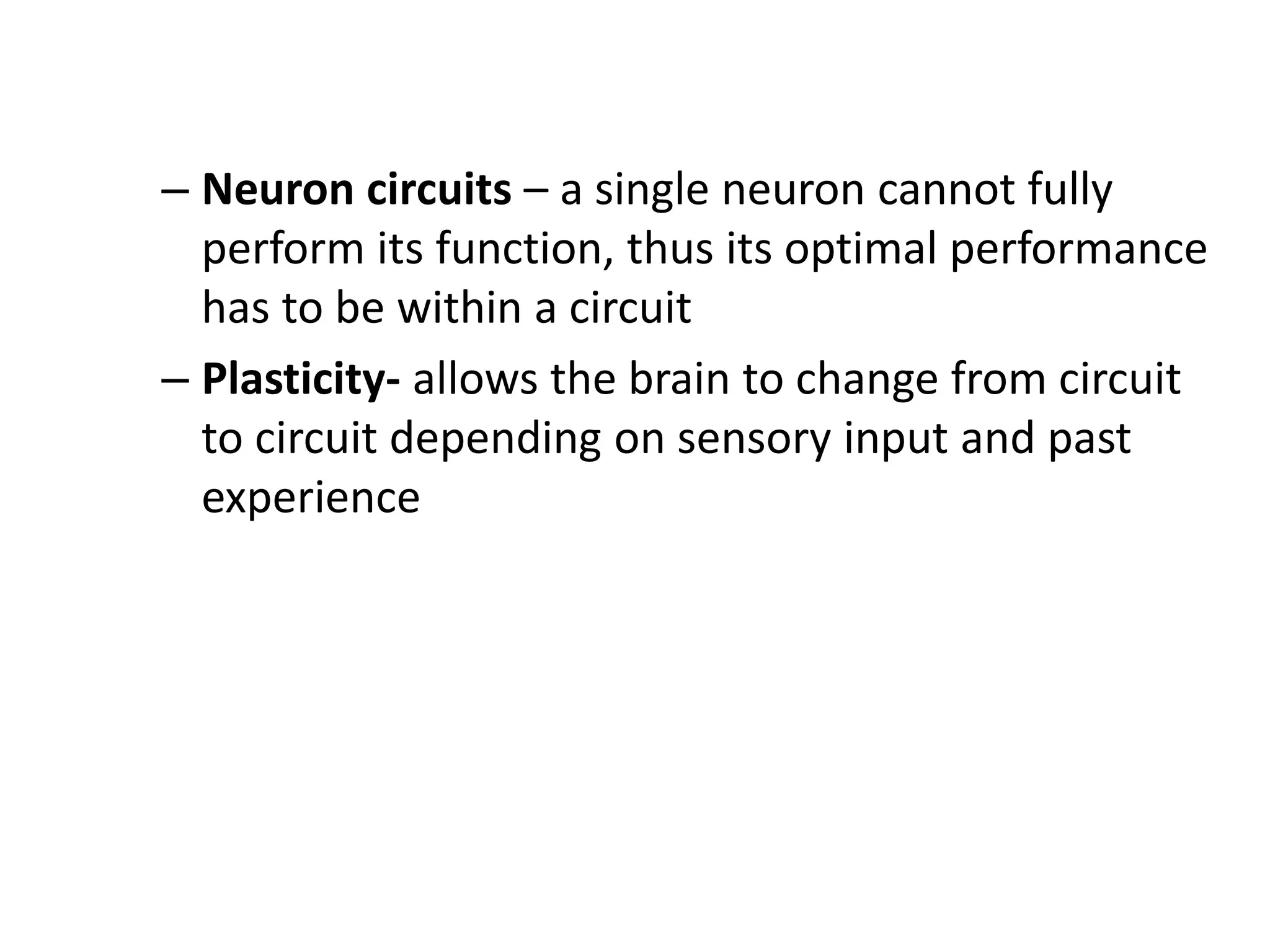
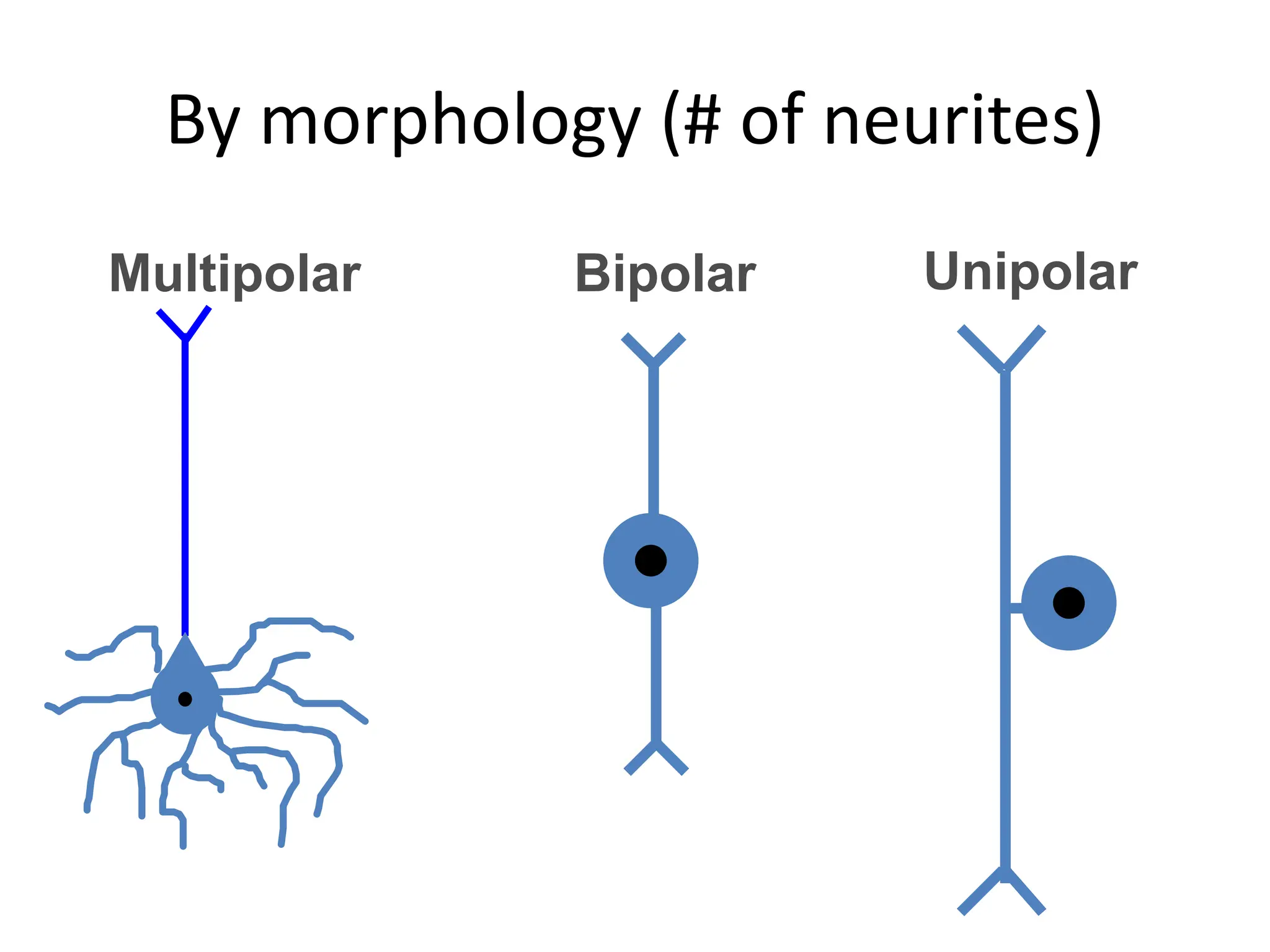
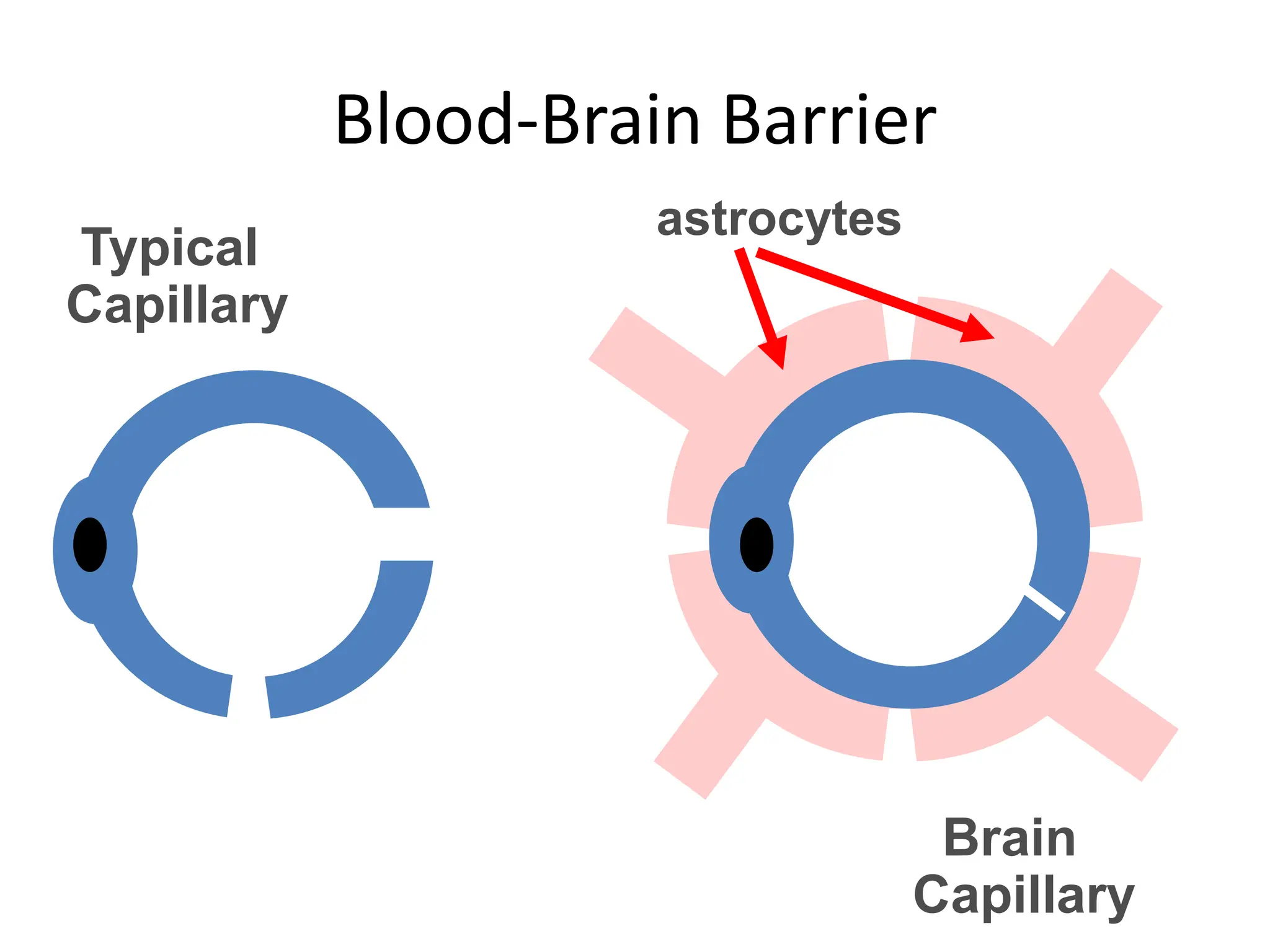
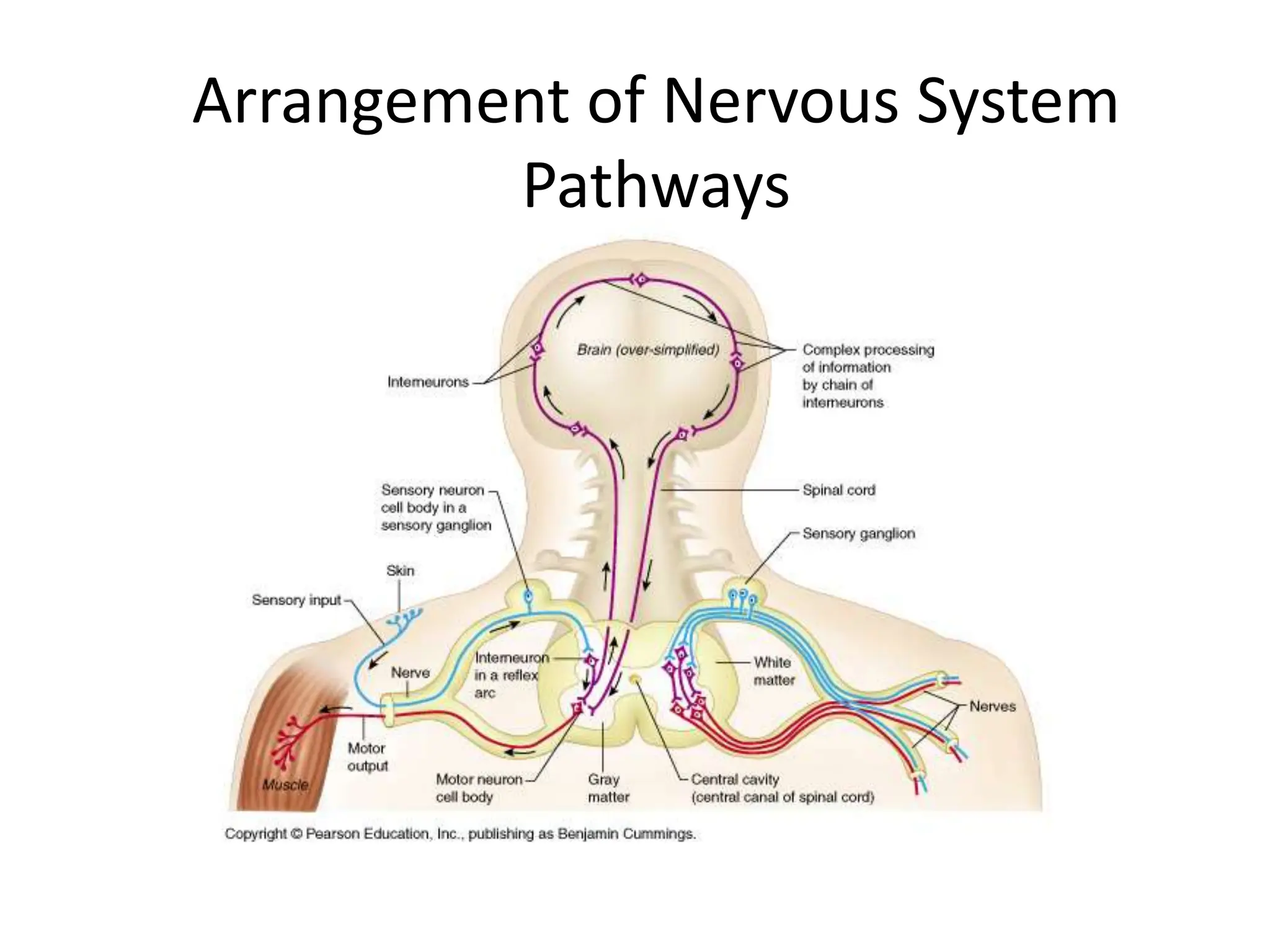
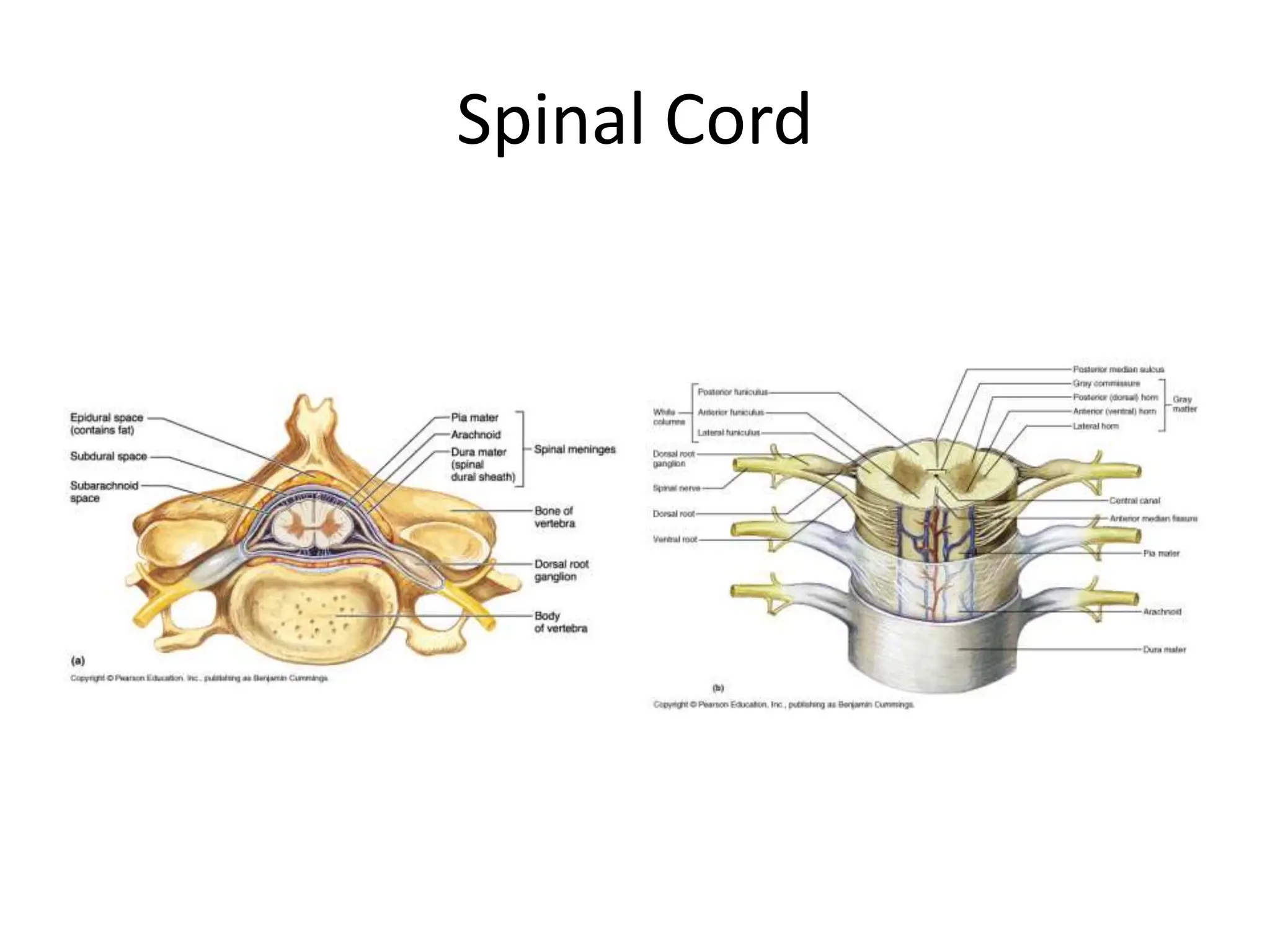
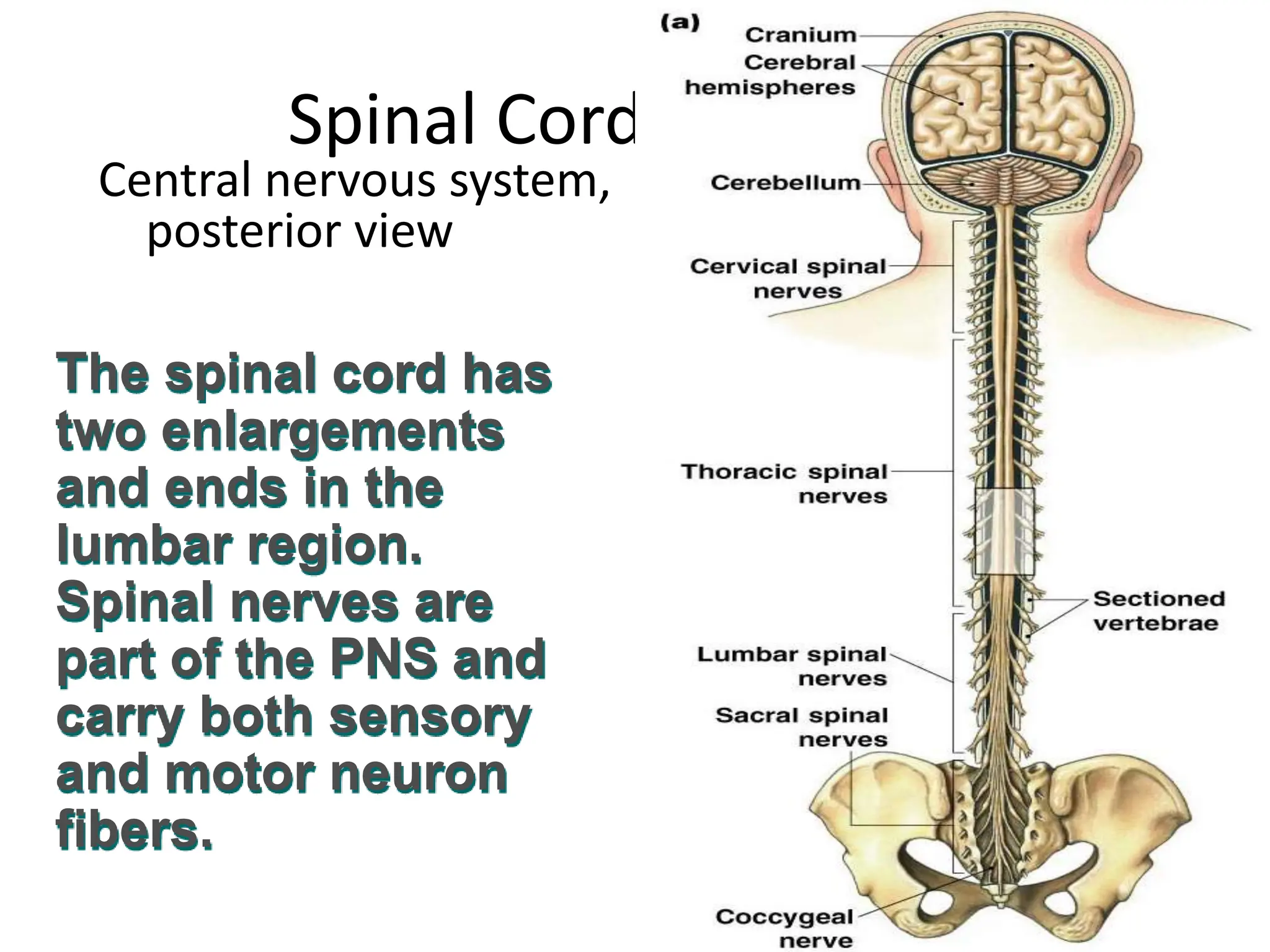
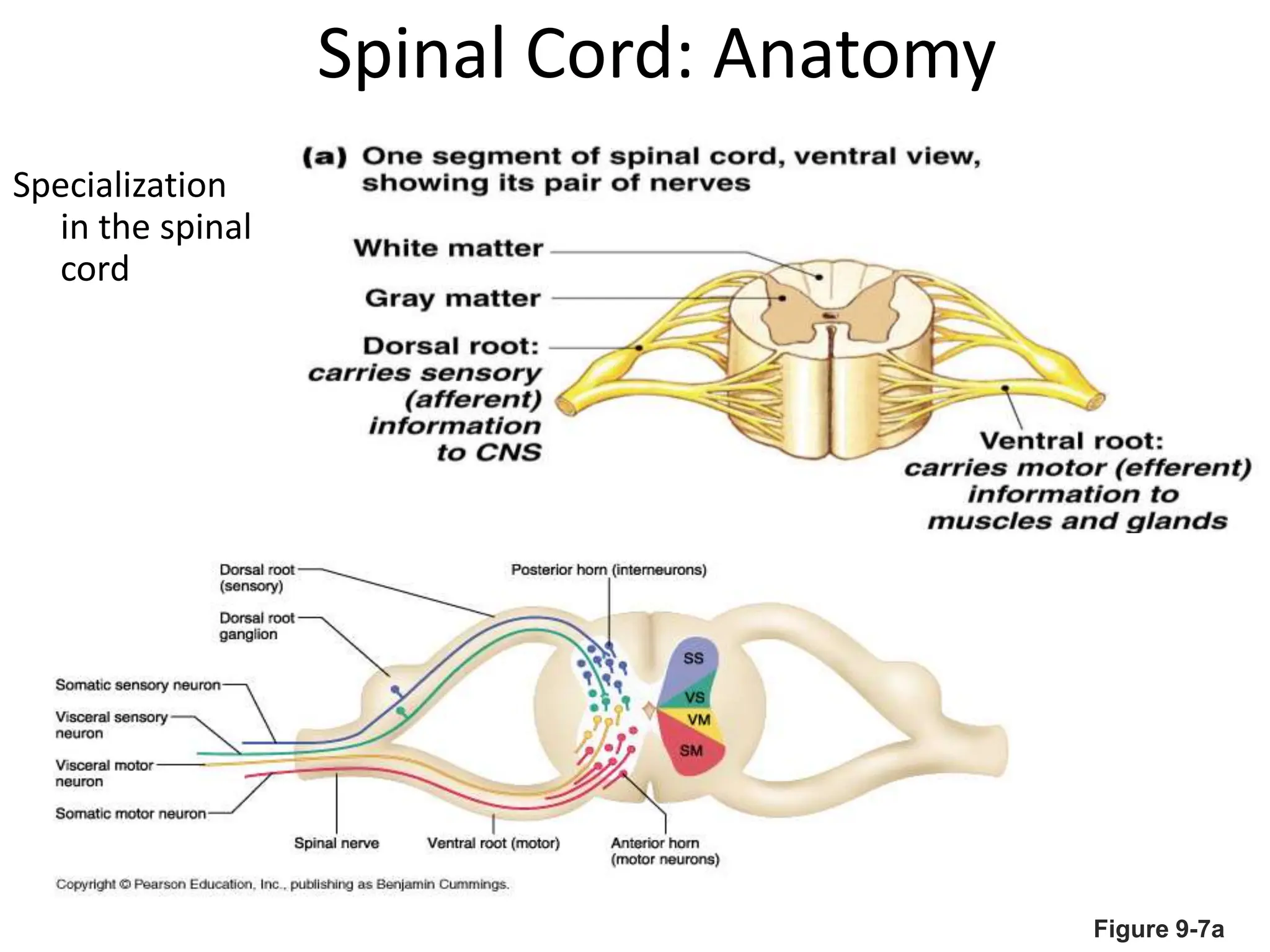
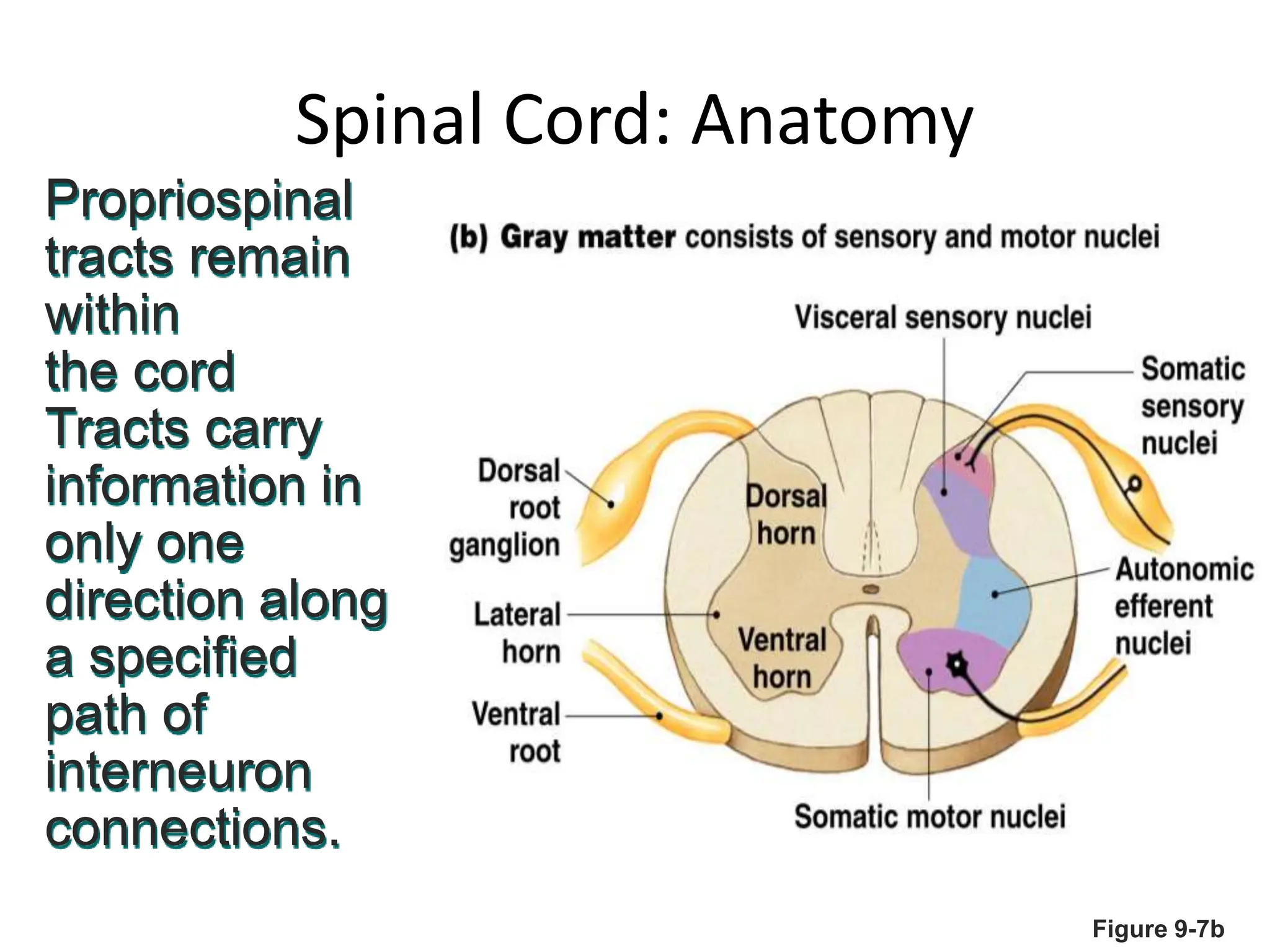
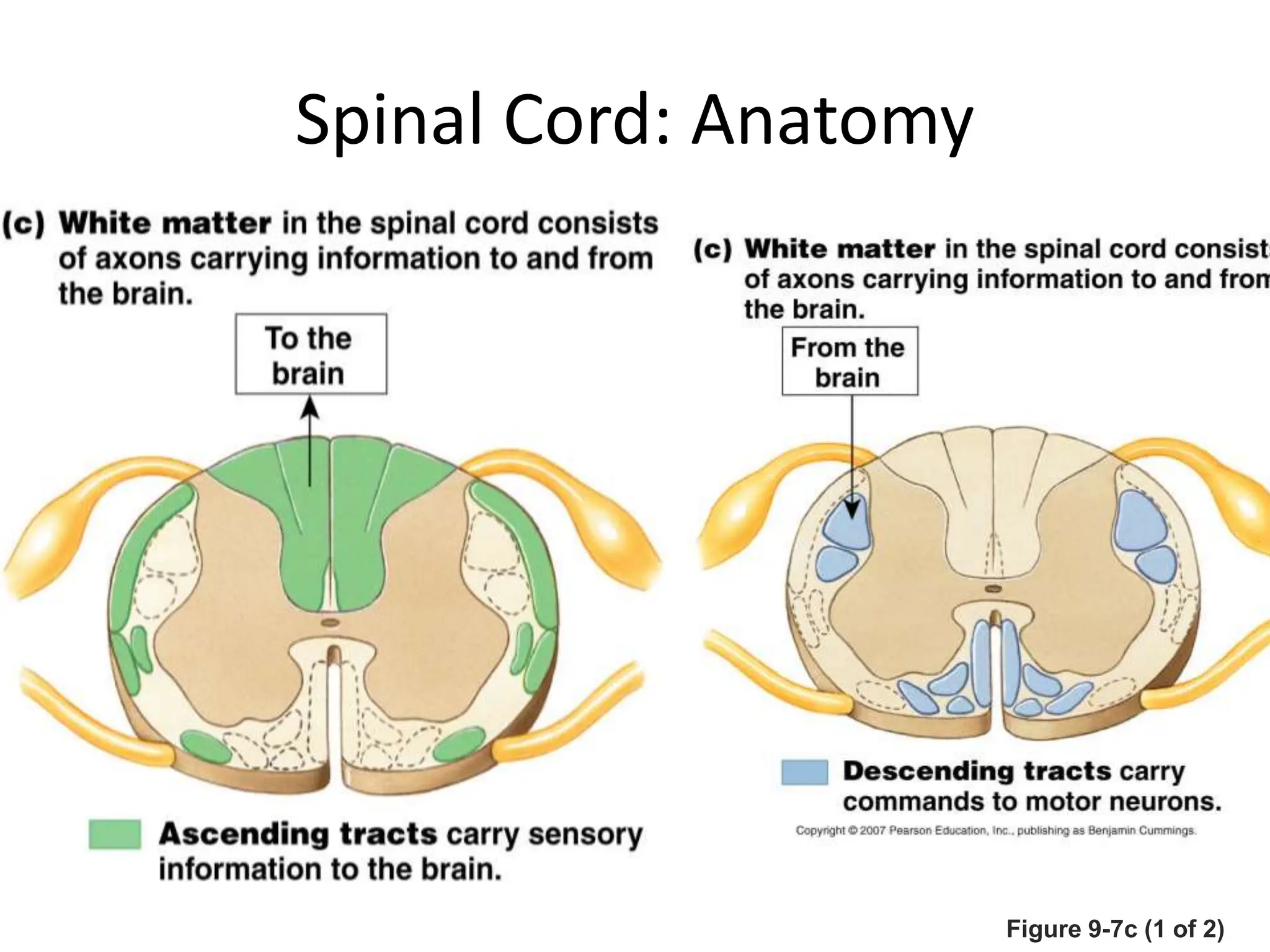
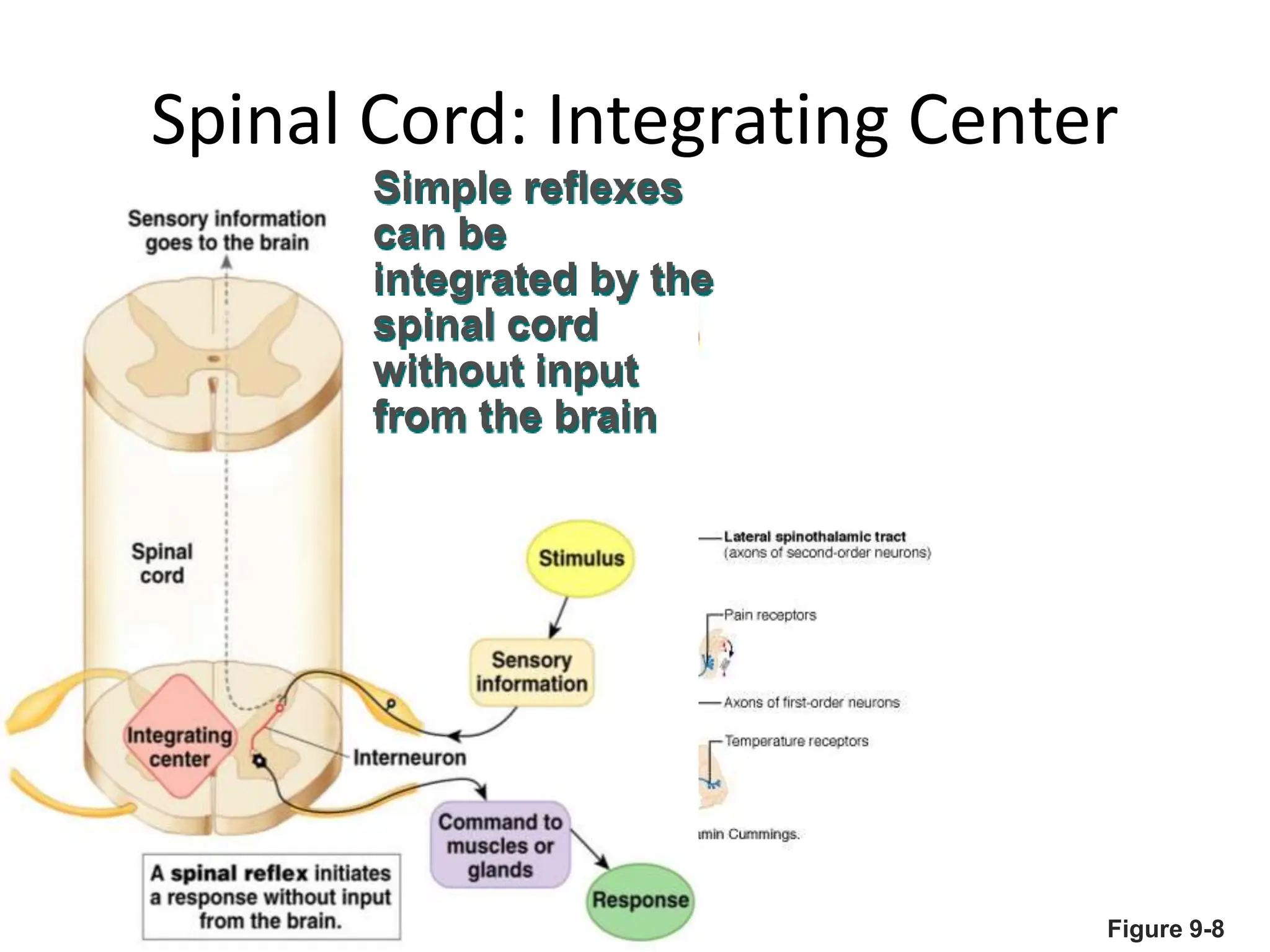
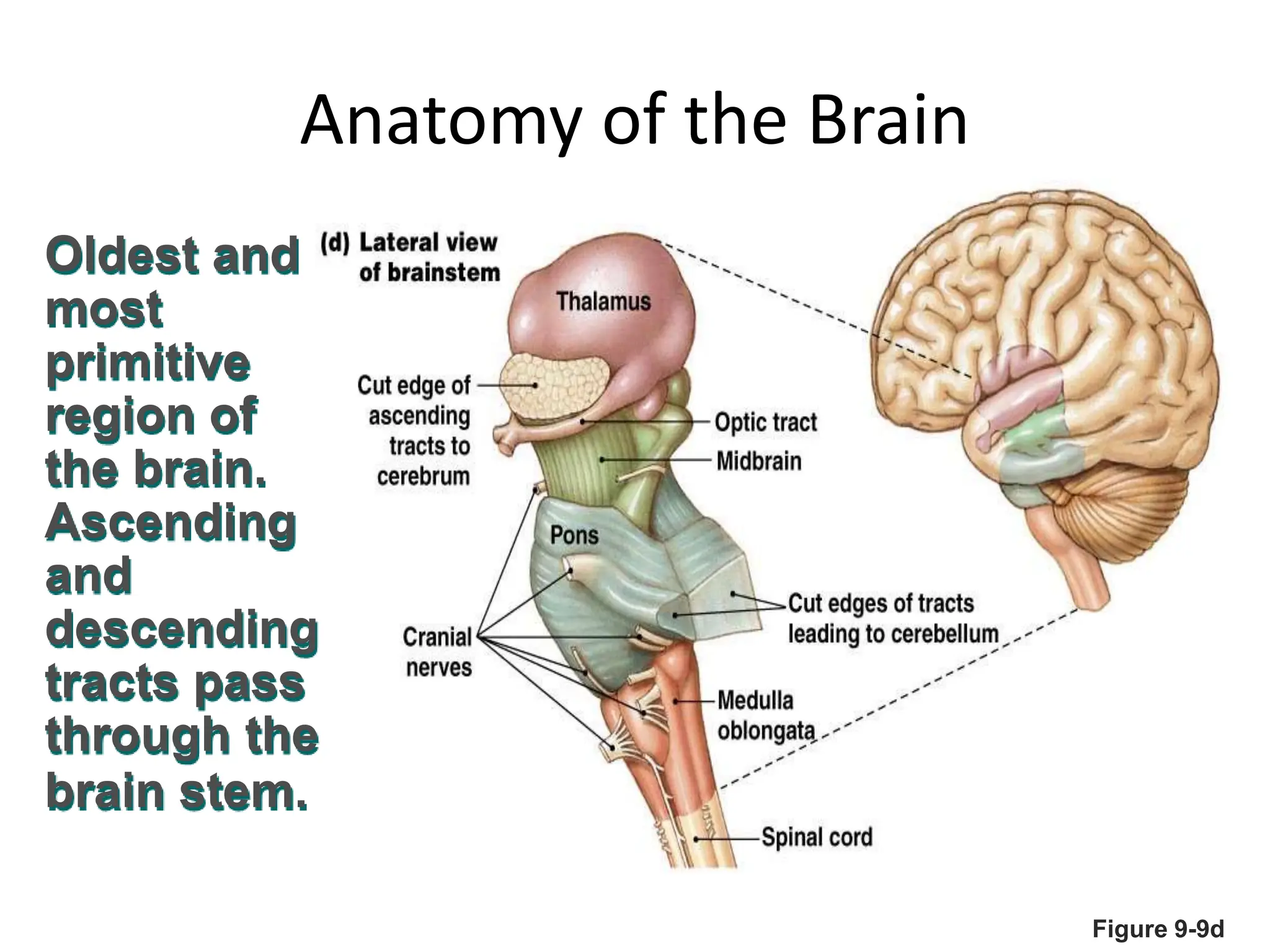
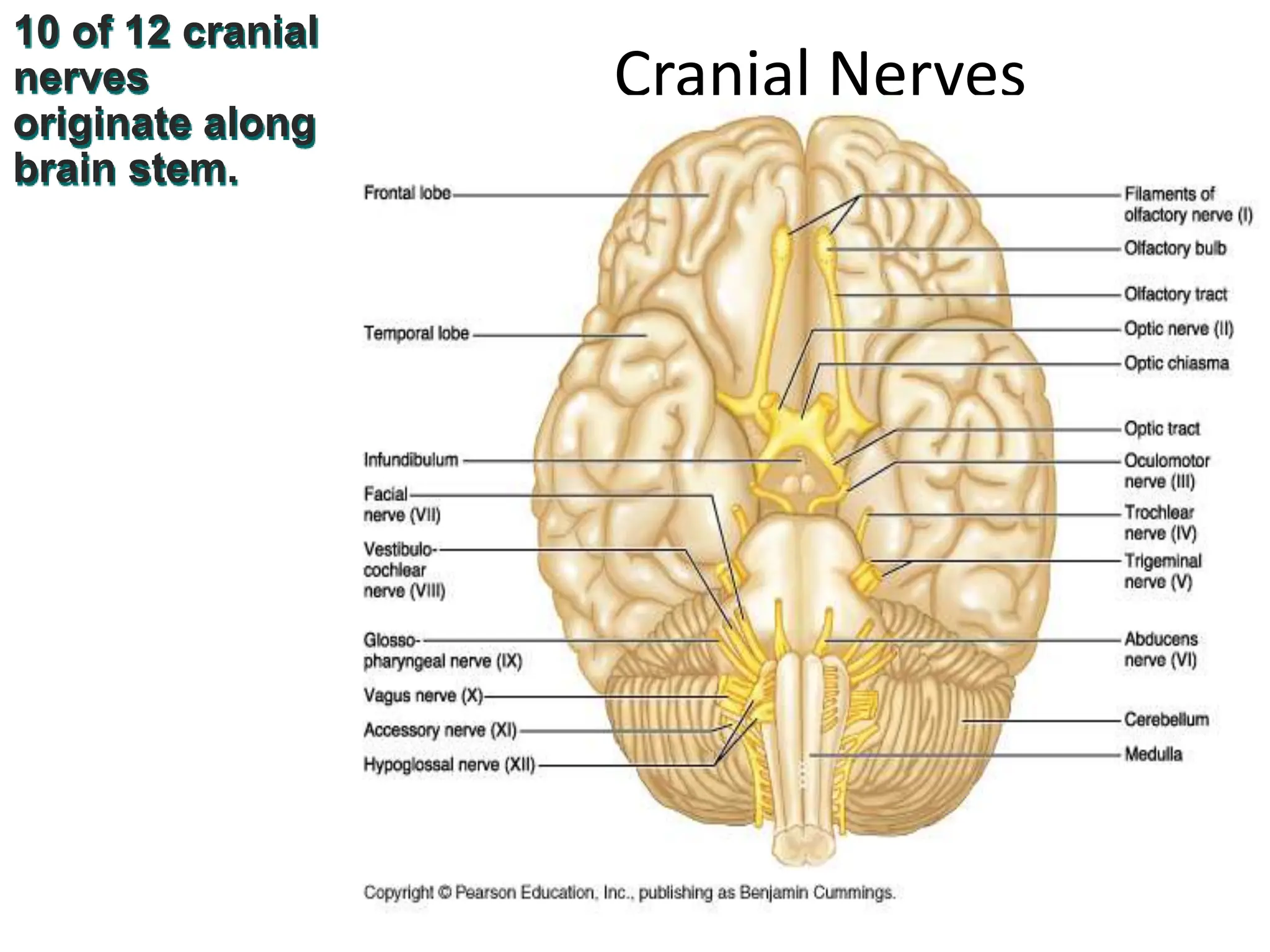
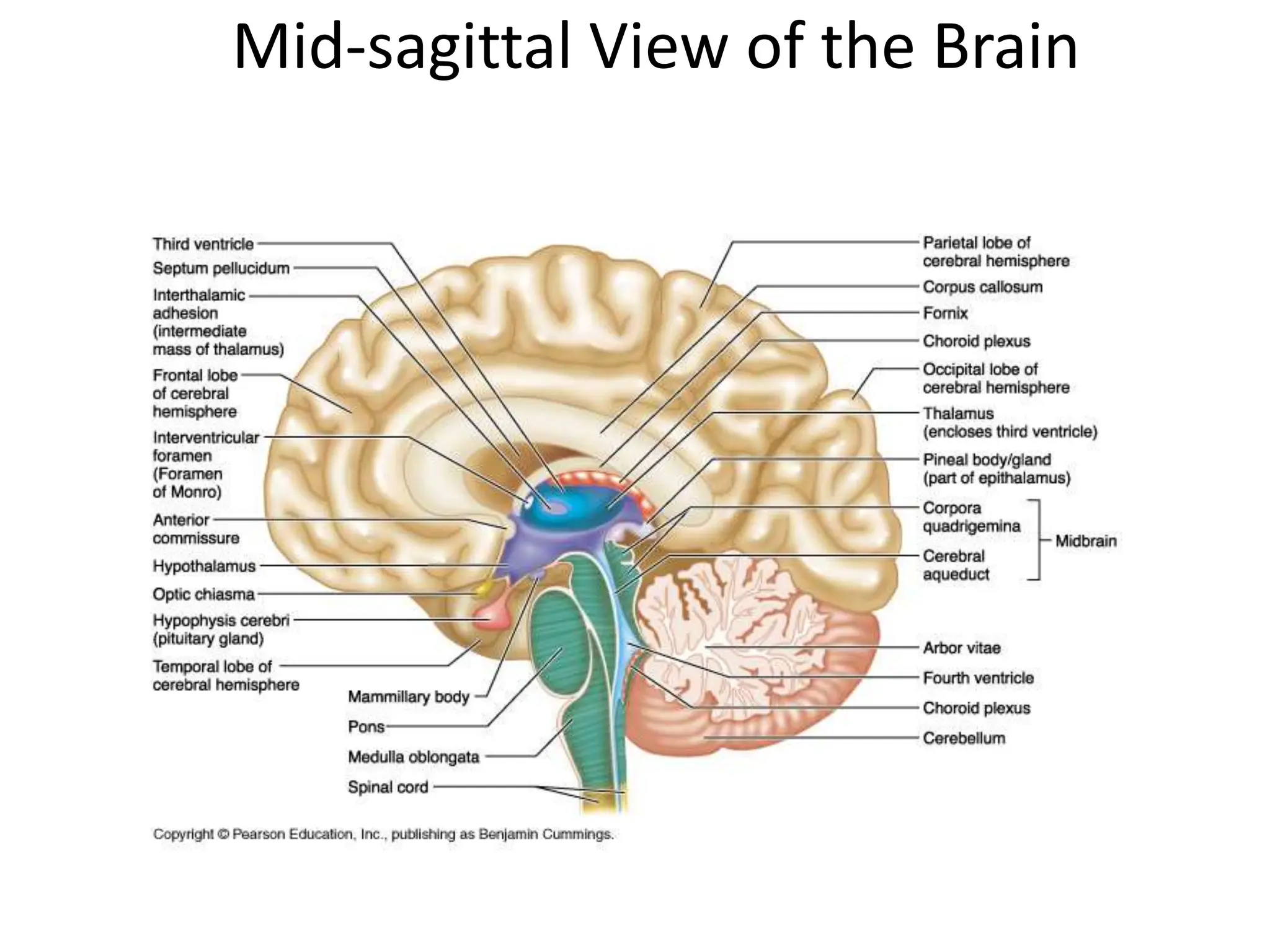
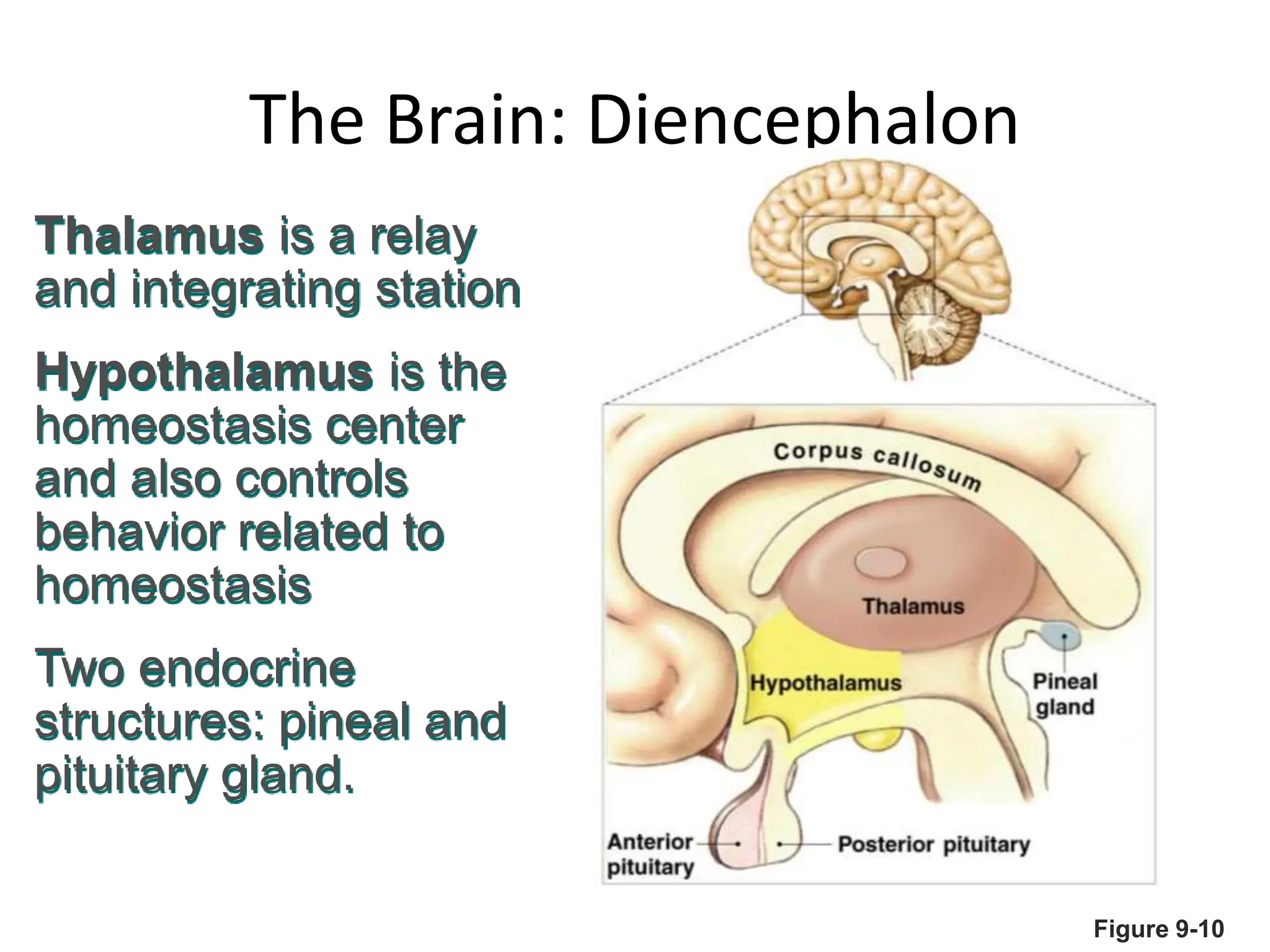
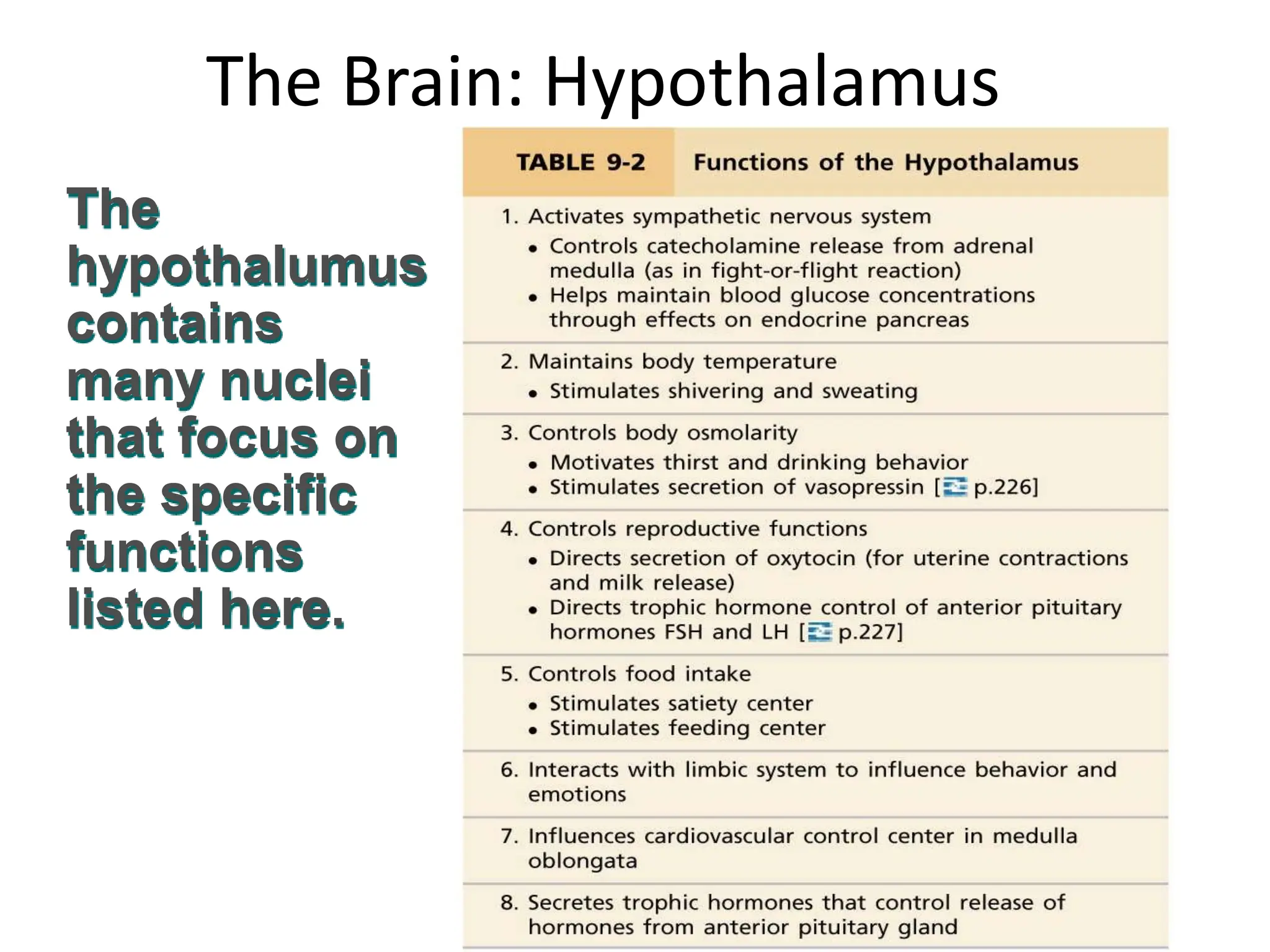
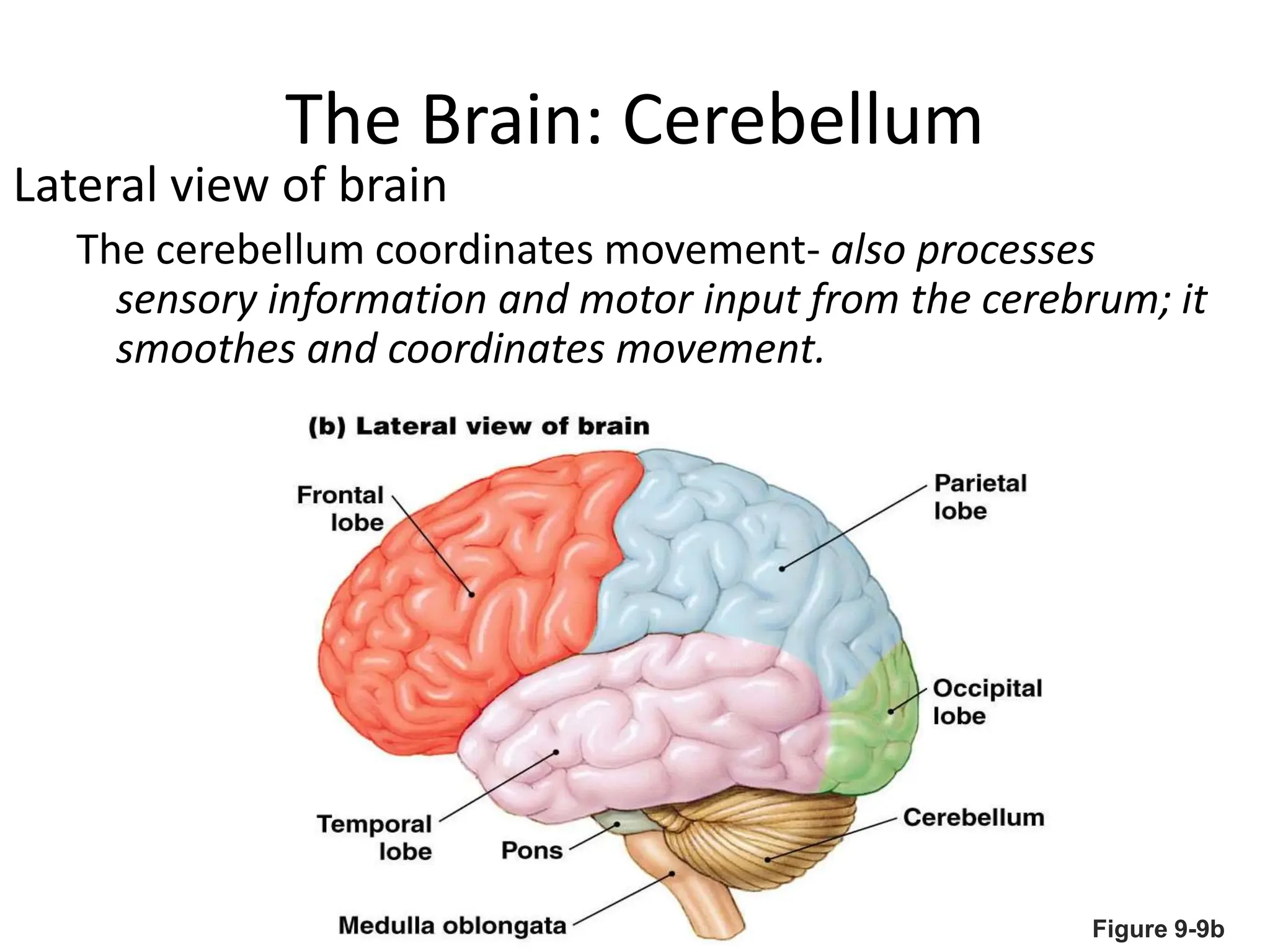
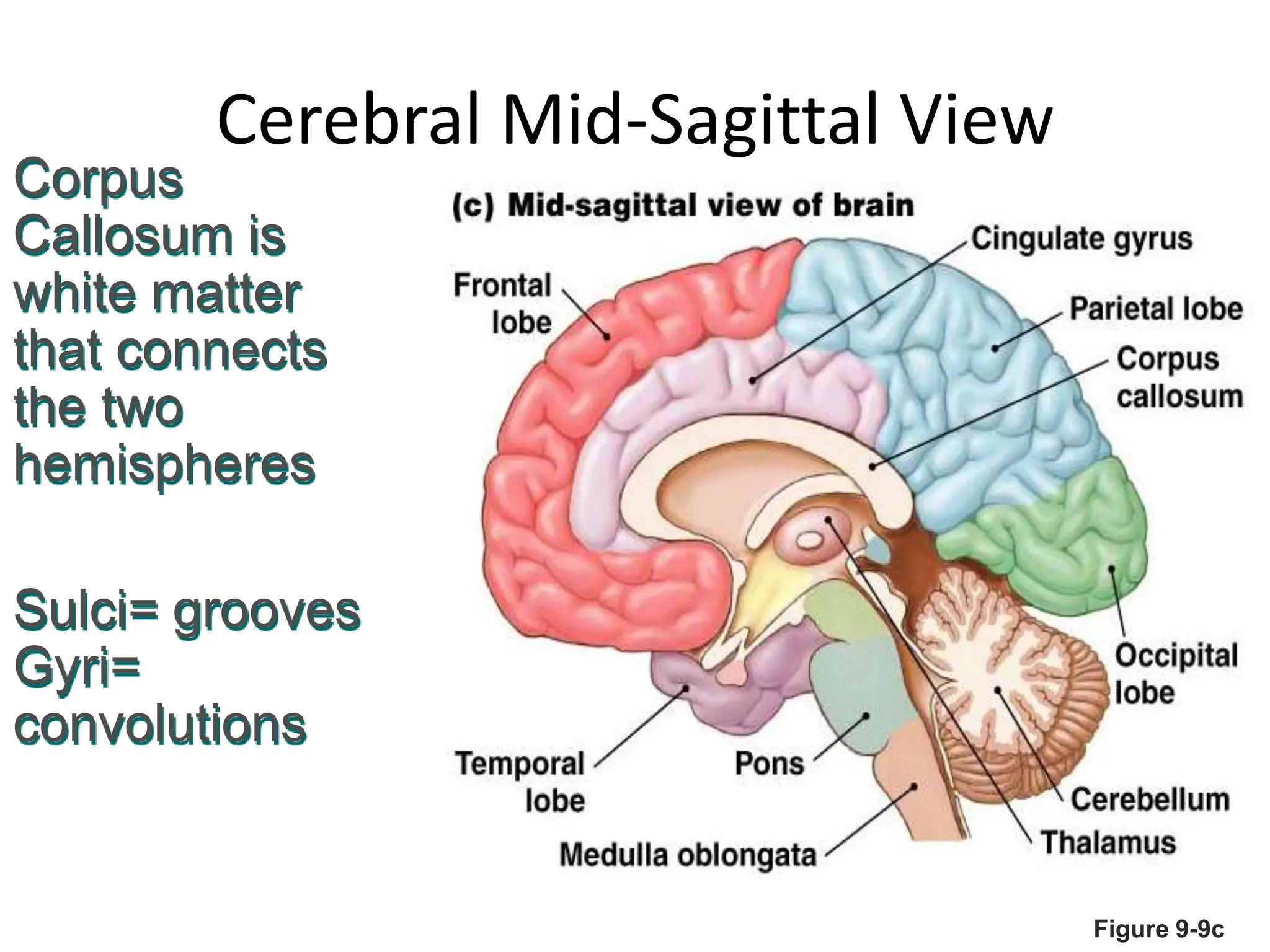
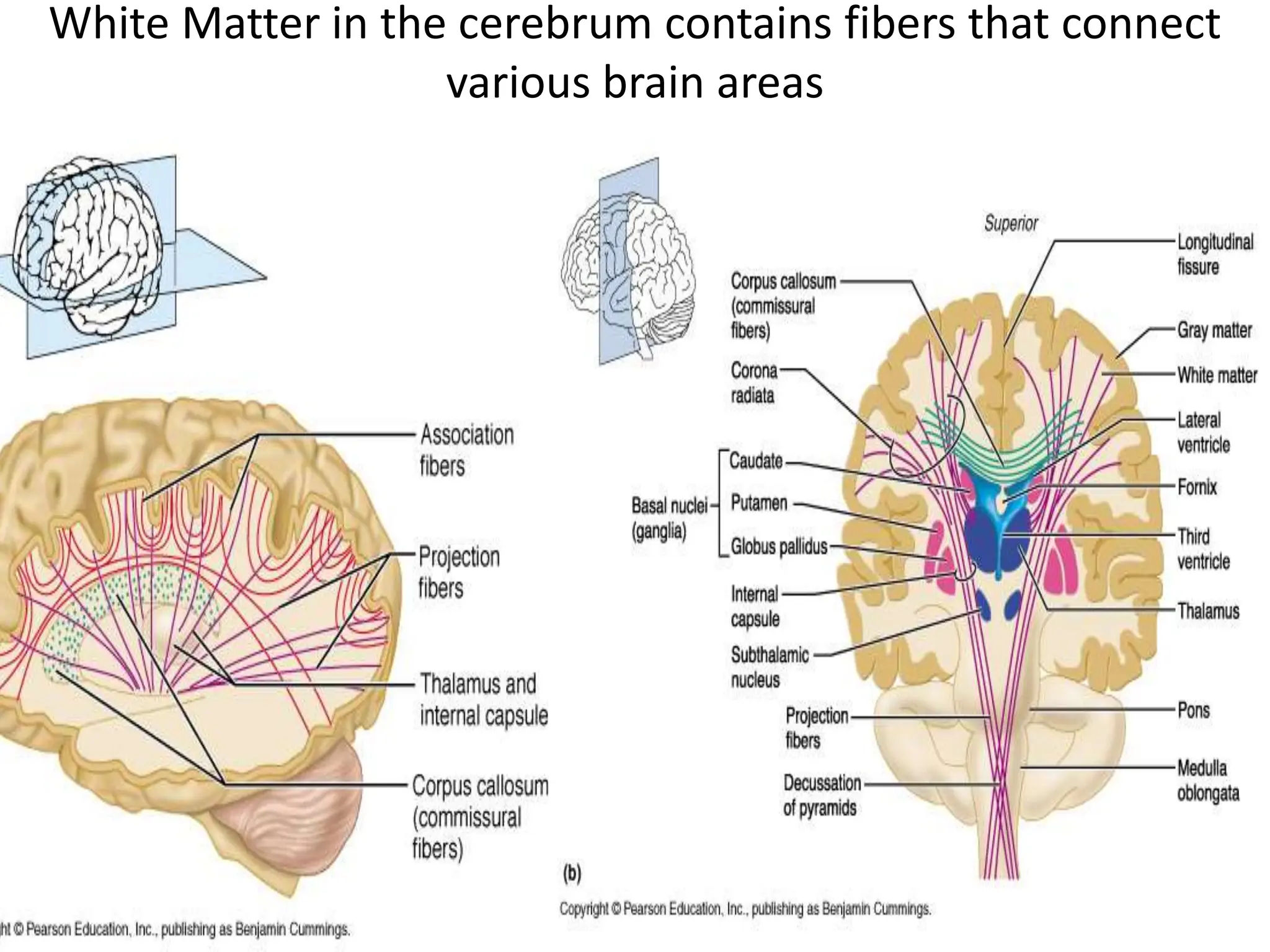
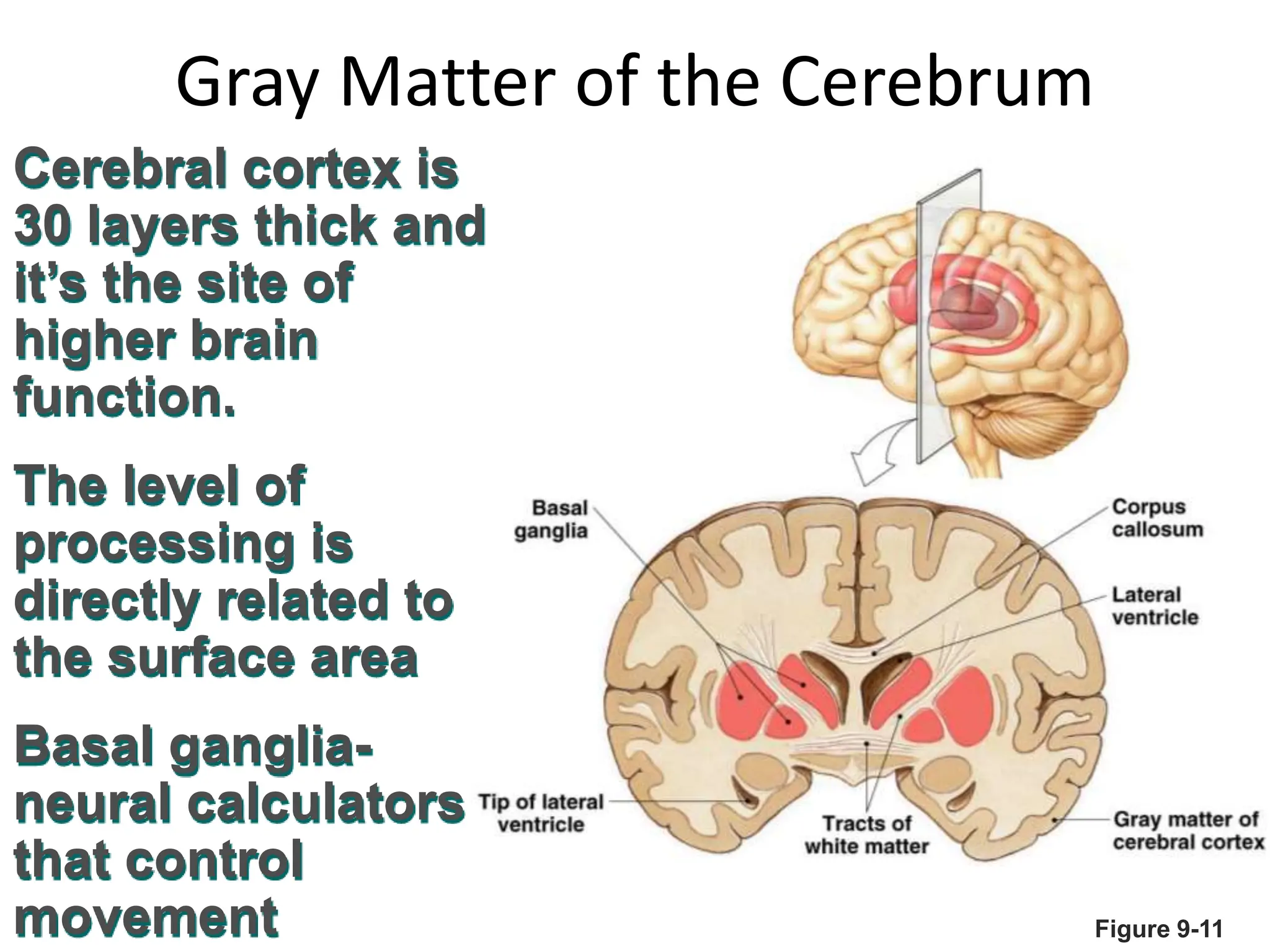
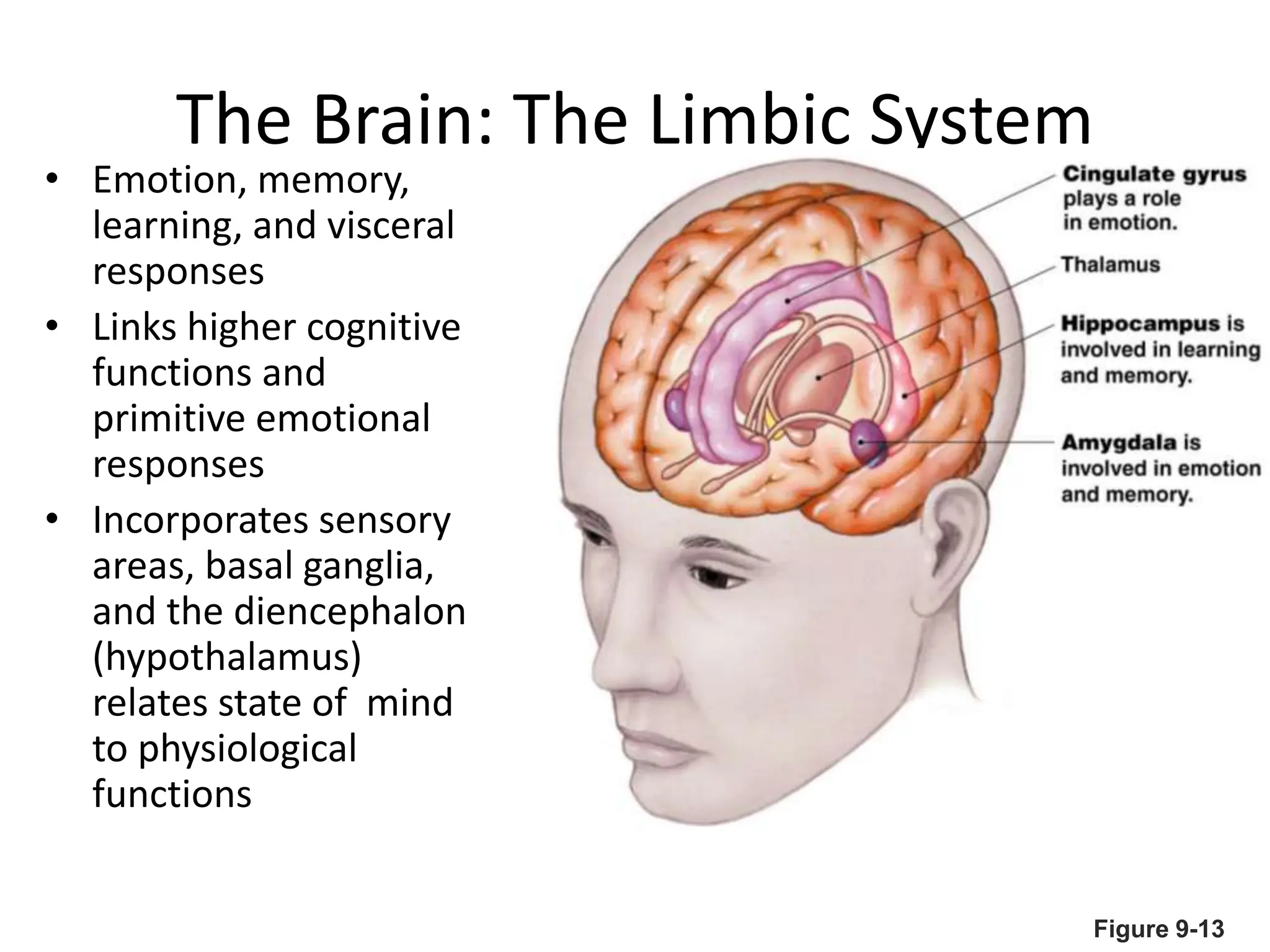
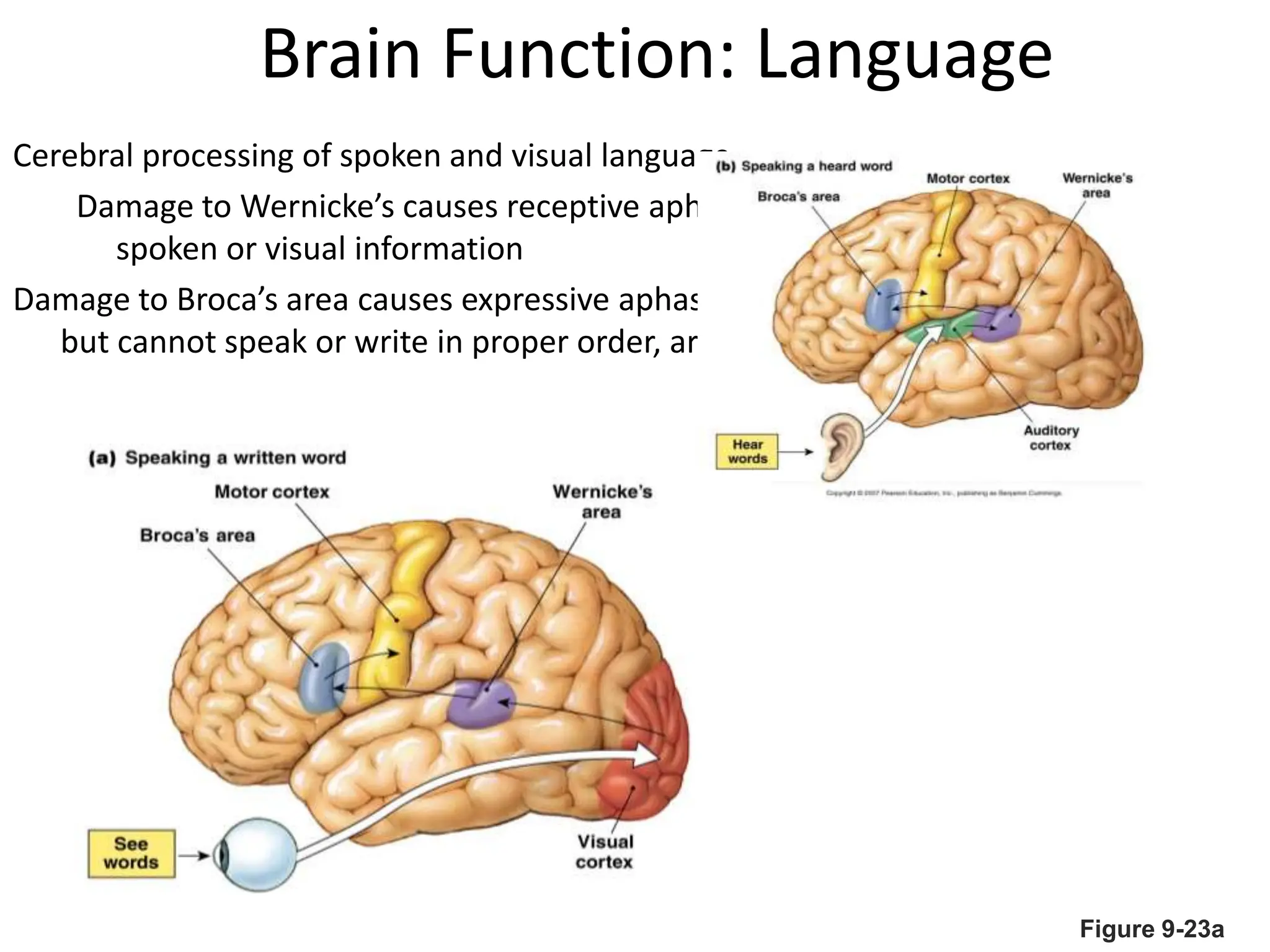
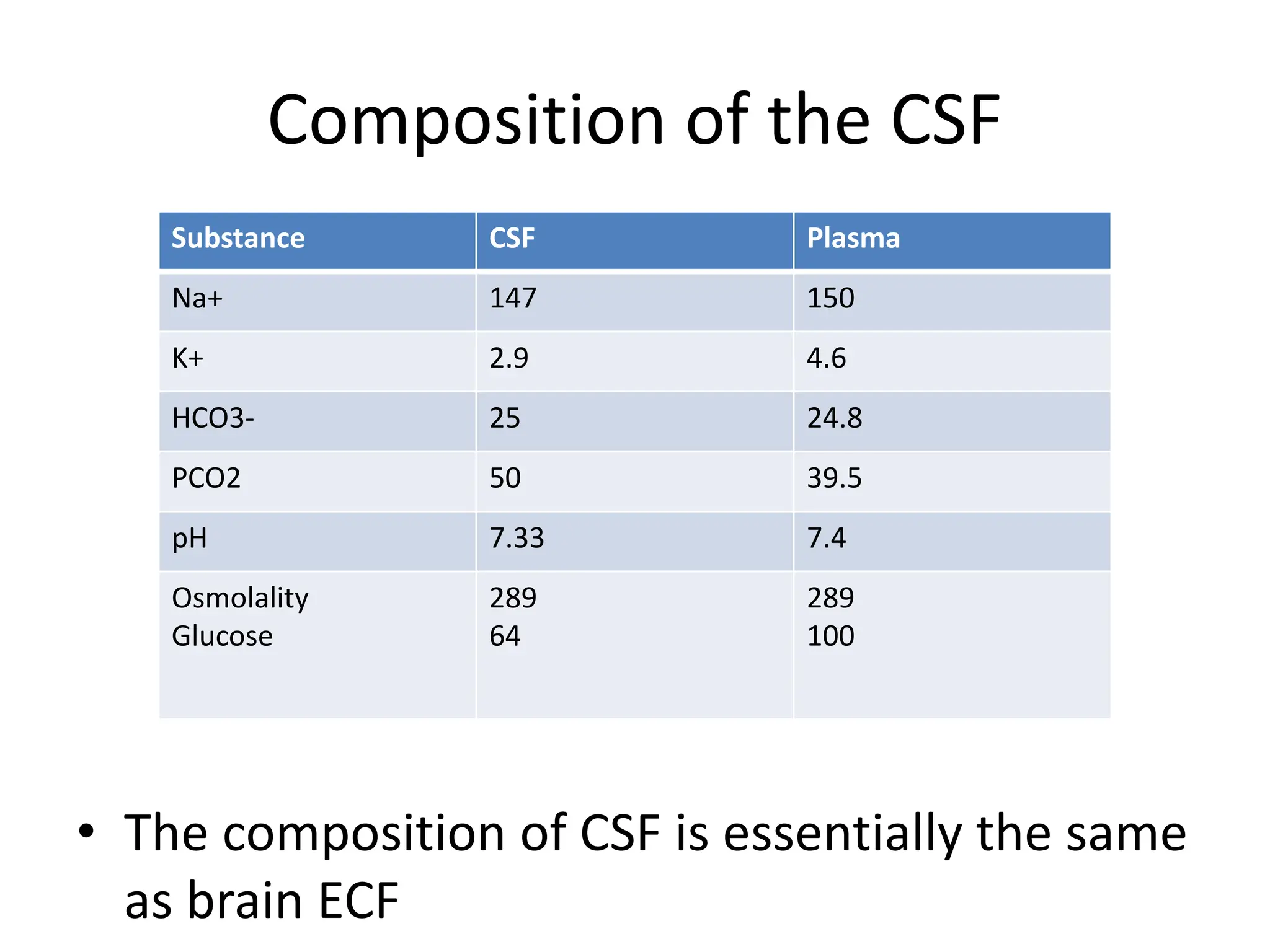
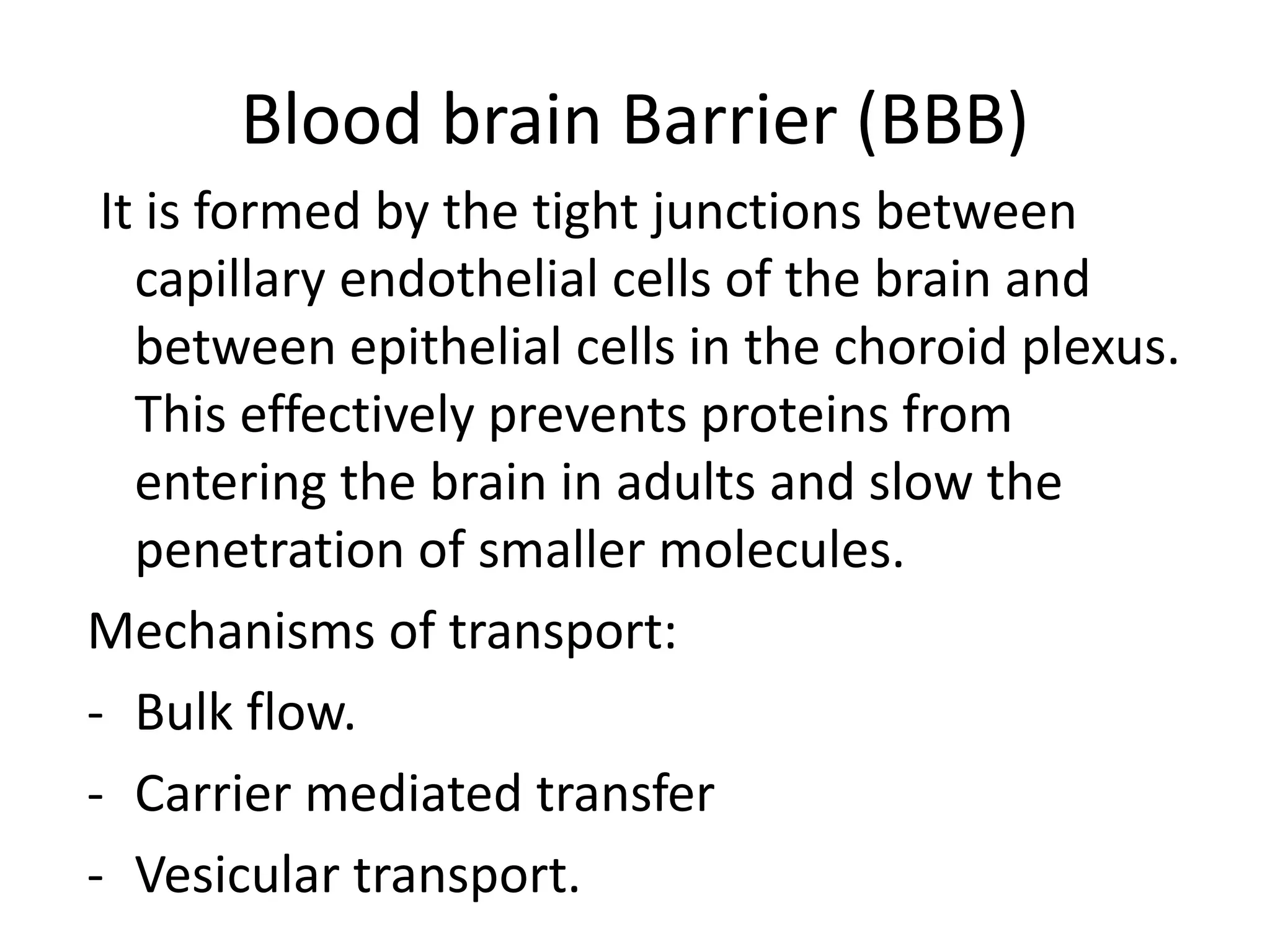
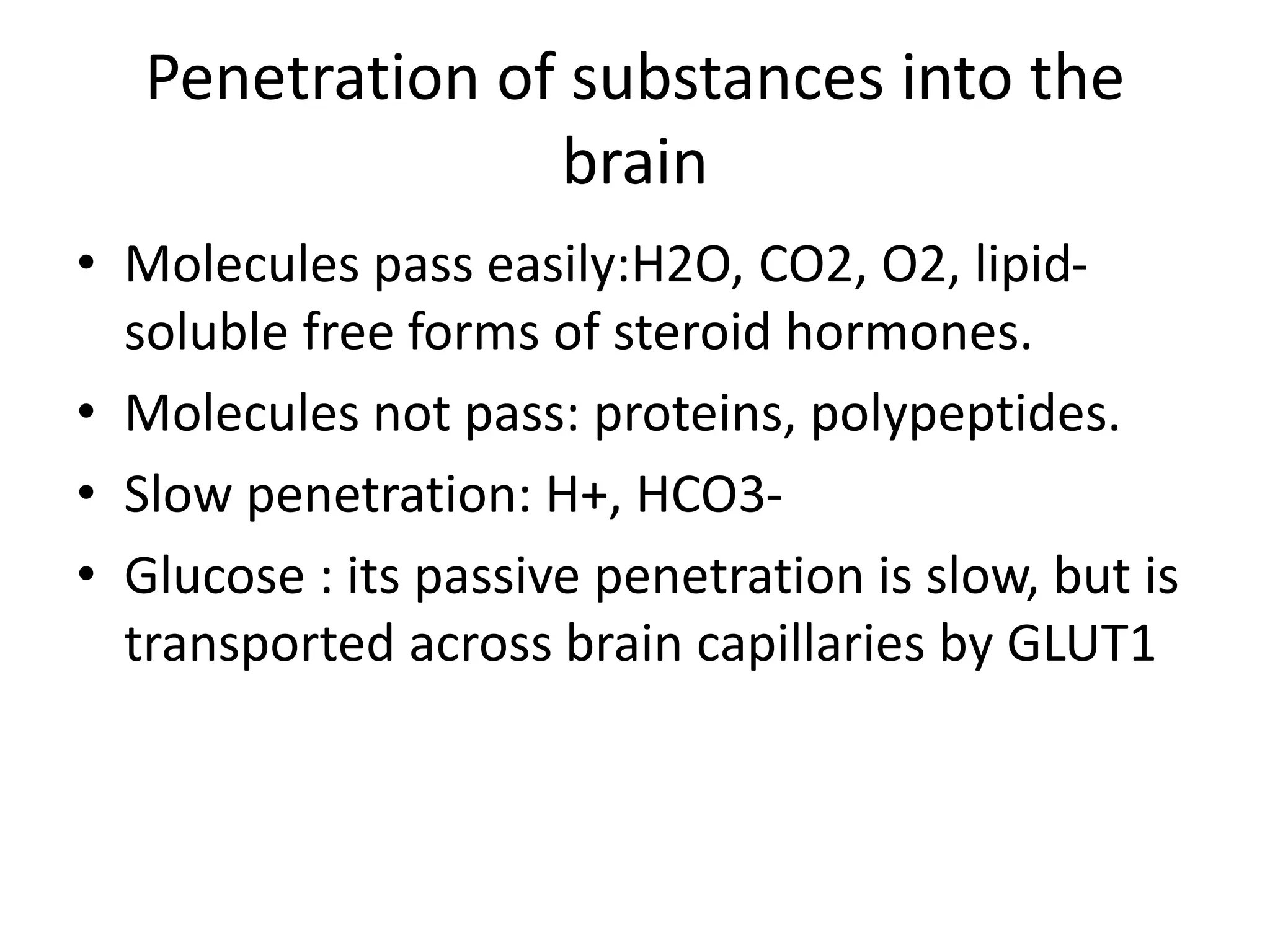
1. The document discusses the structure and function of the central nervous system, including neurons, neuroglia, the brain stem, cerebellum, diencephalon, cerebrum, and spinal cord. It describes the roles of different brain regions in functions like sensory processing, motor control, arousal, sleep, and homeostasis.
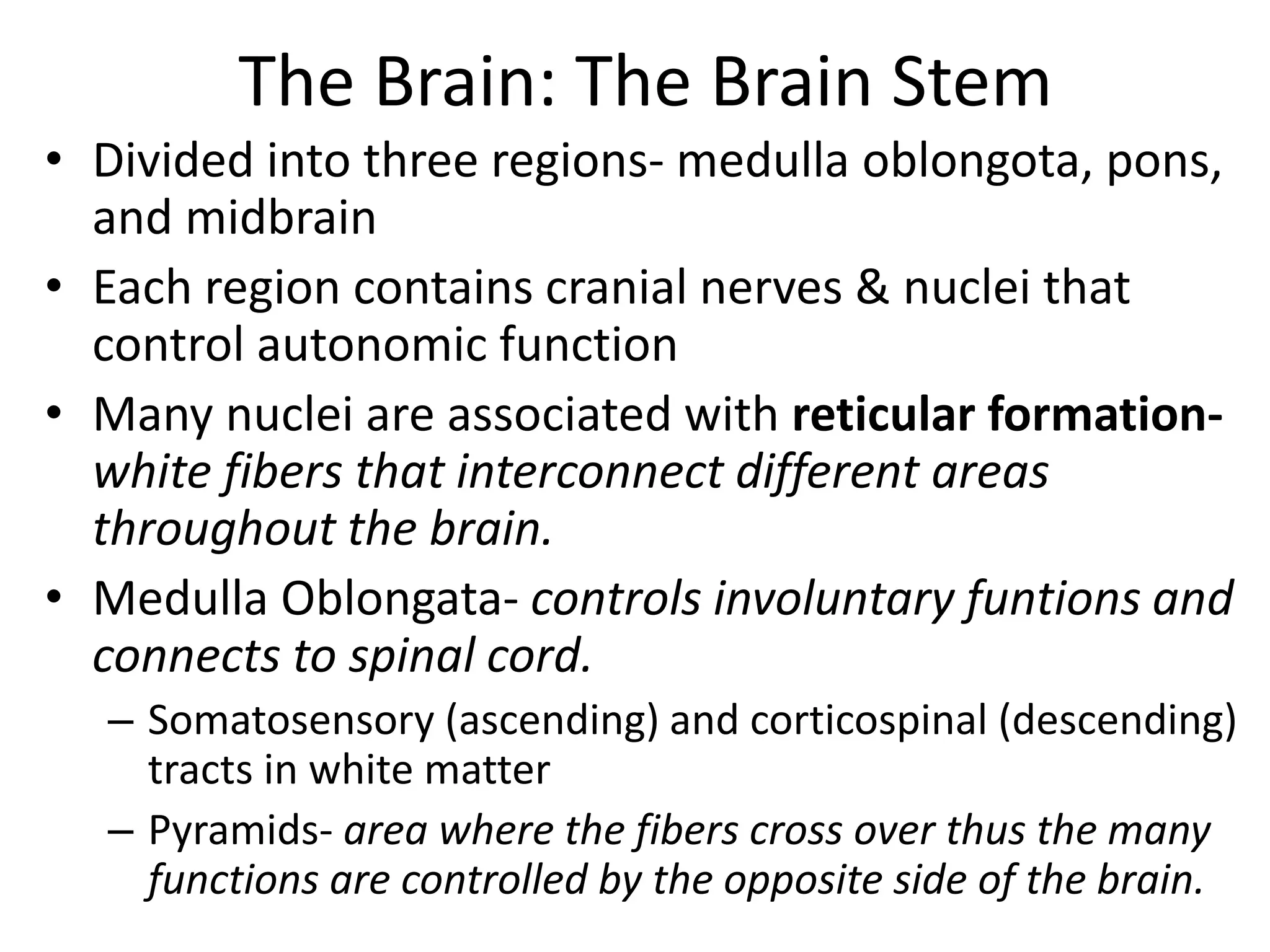
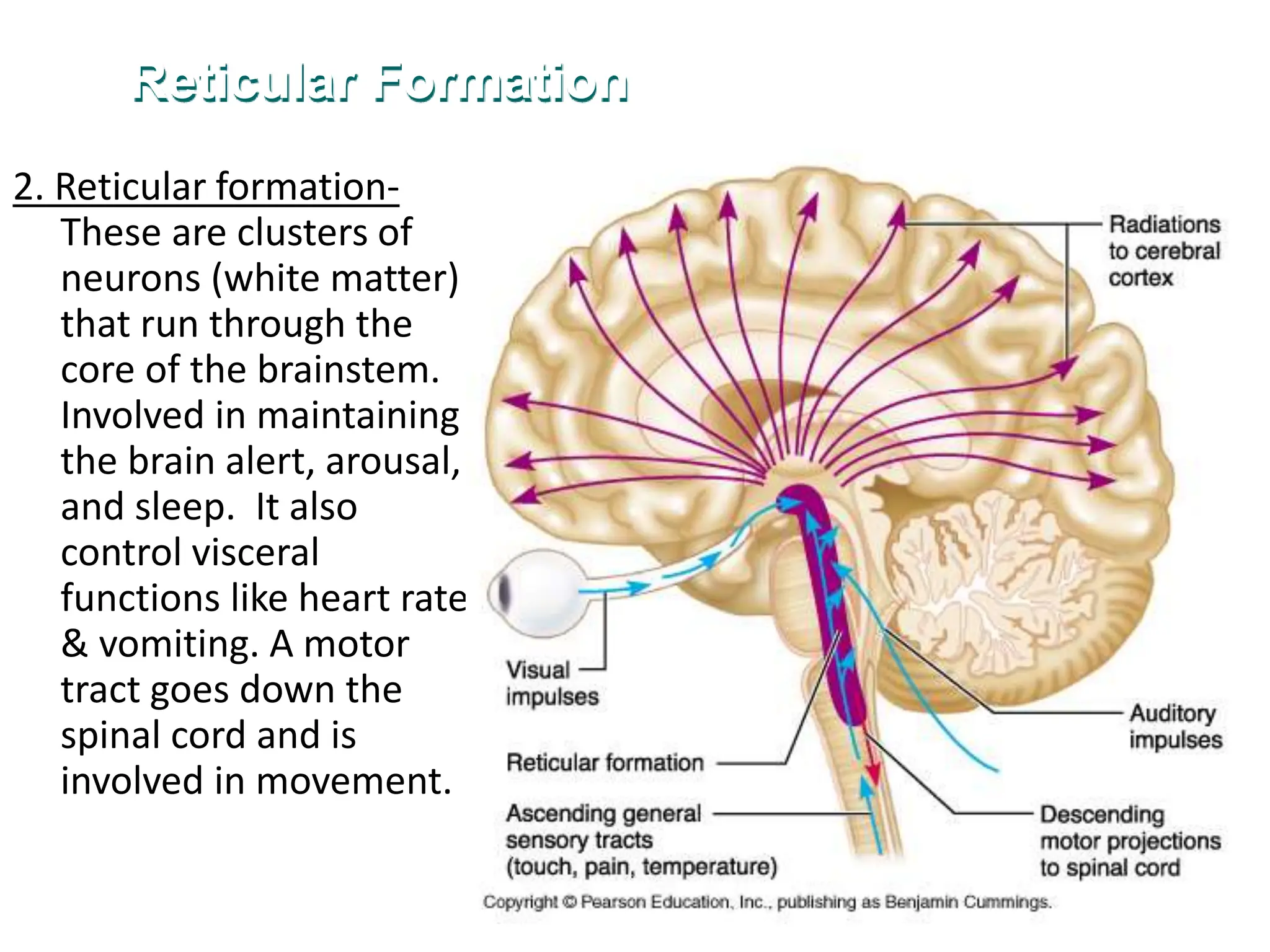
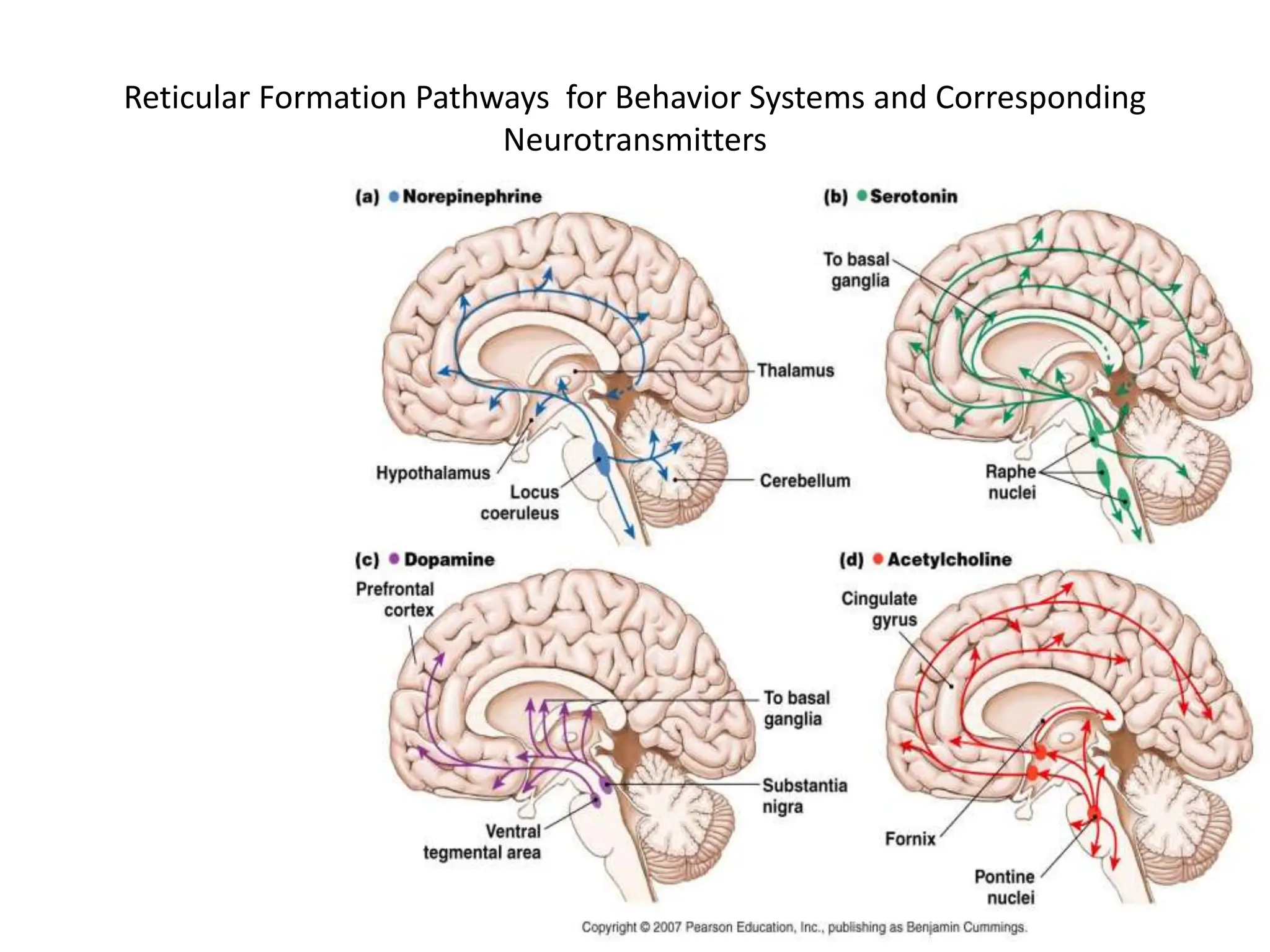
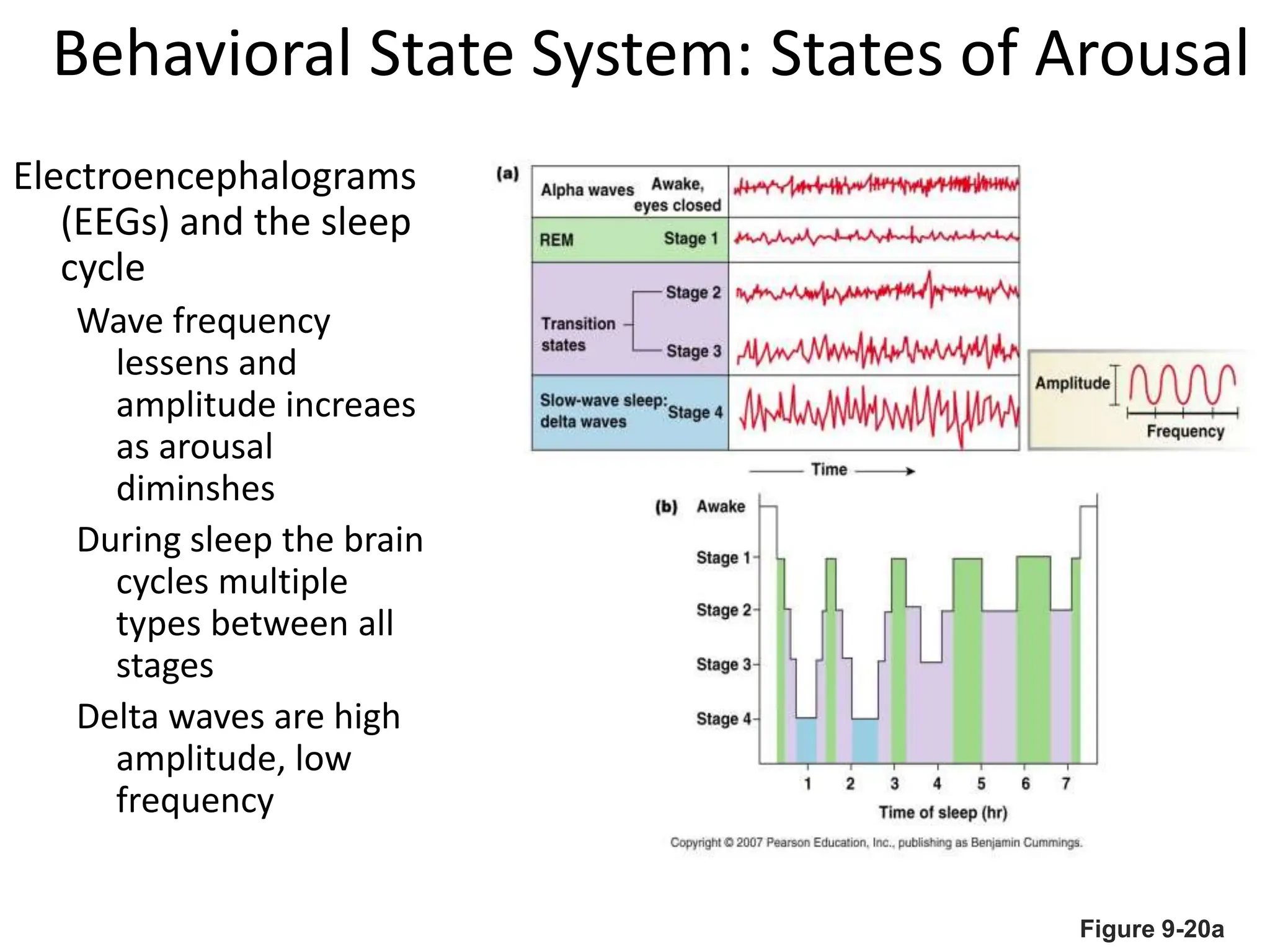
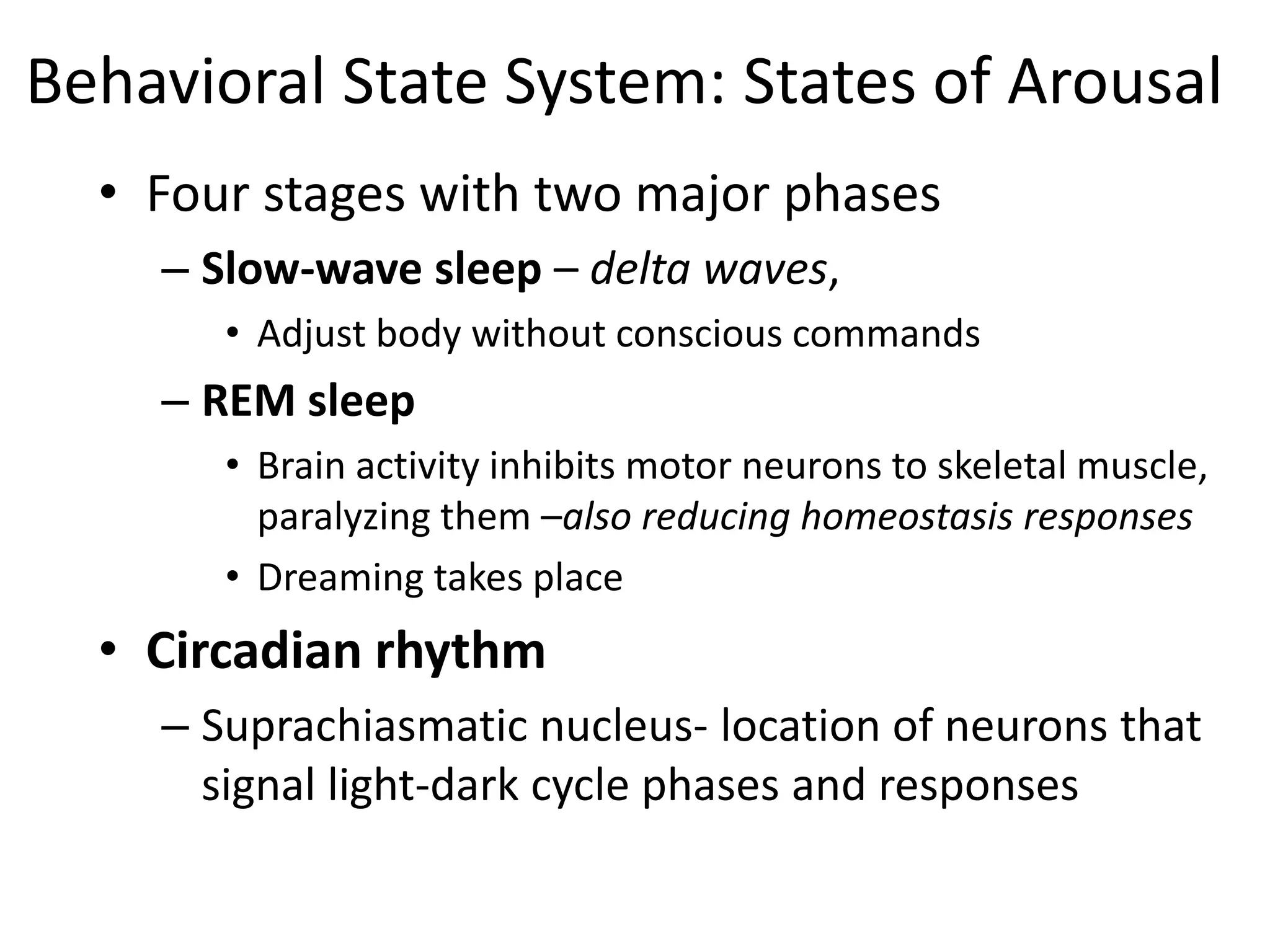
2. Key areas of the brain stem like the reticular formation are involved in maintaining arousal, sleep-wake cycles, and autonomic functions. The cerebellum coordinates movement and integrates sensory and motor information.
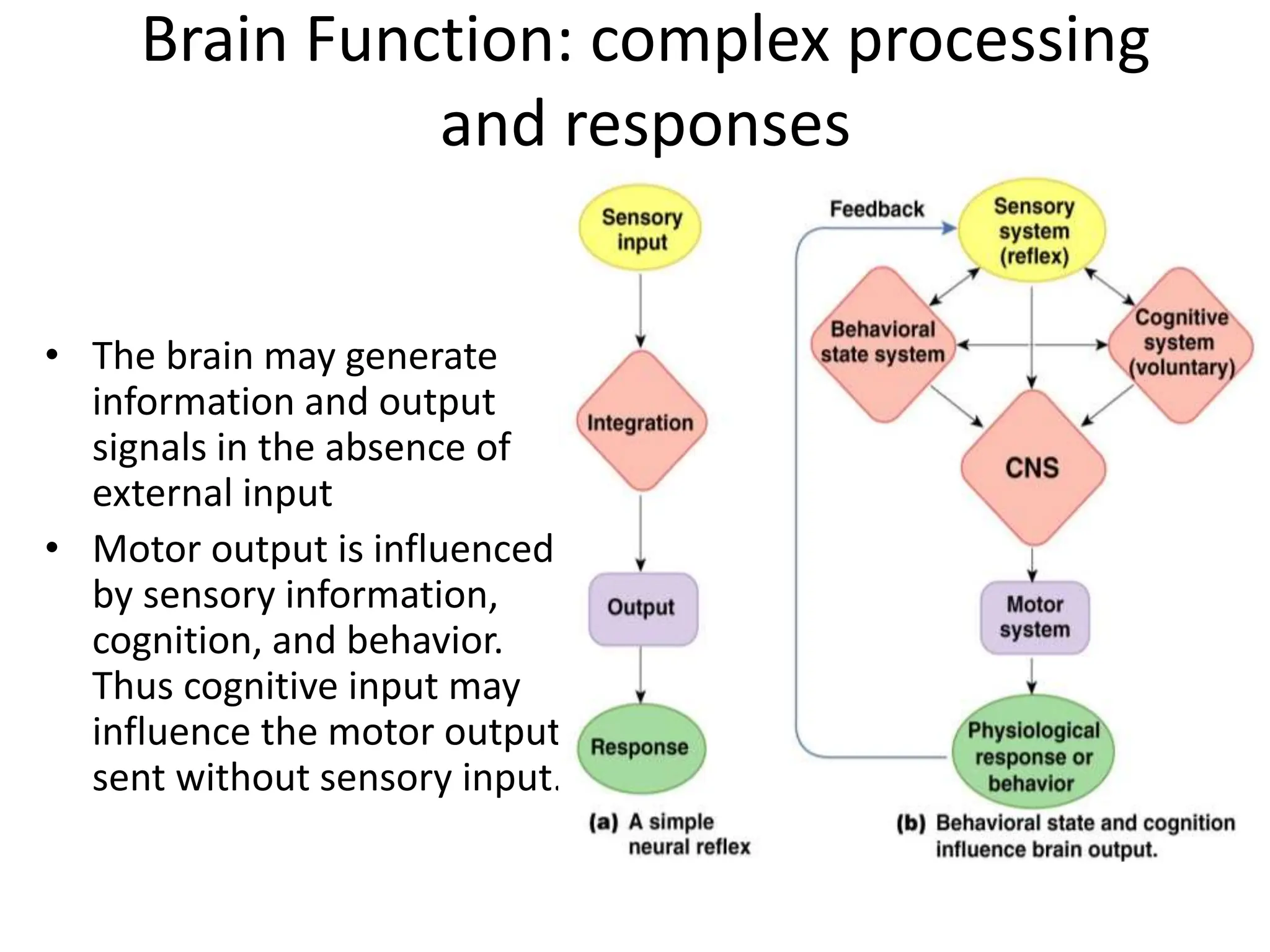
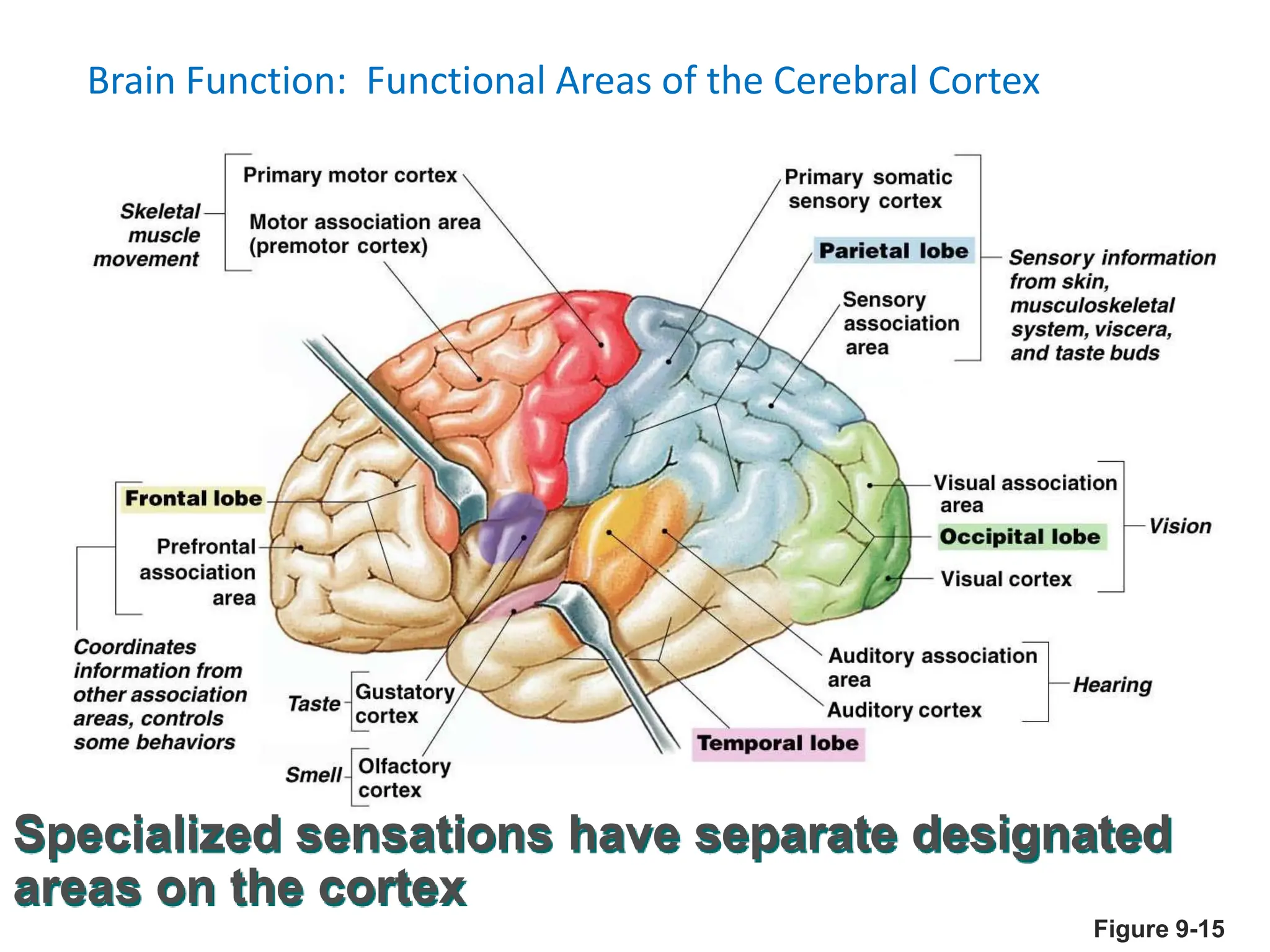
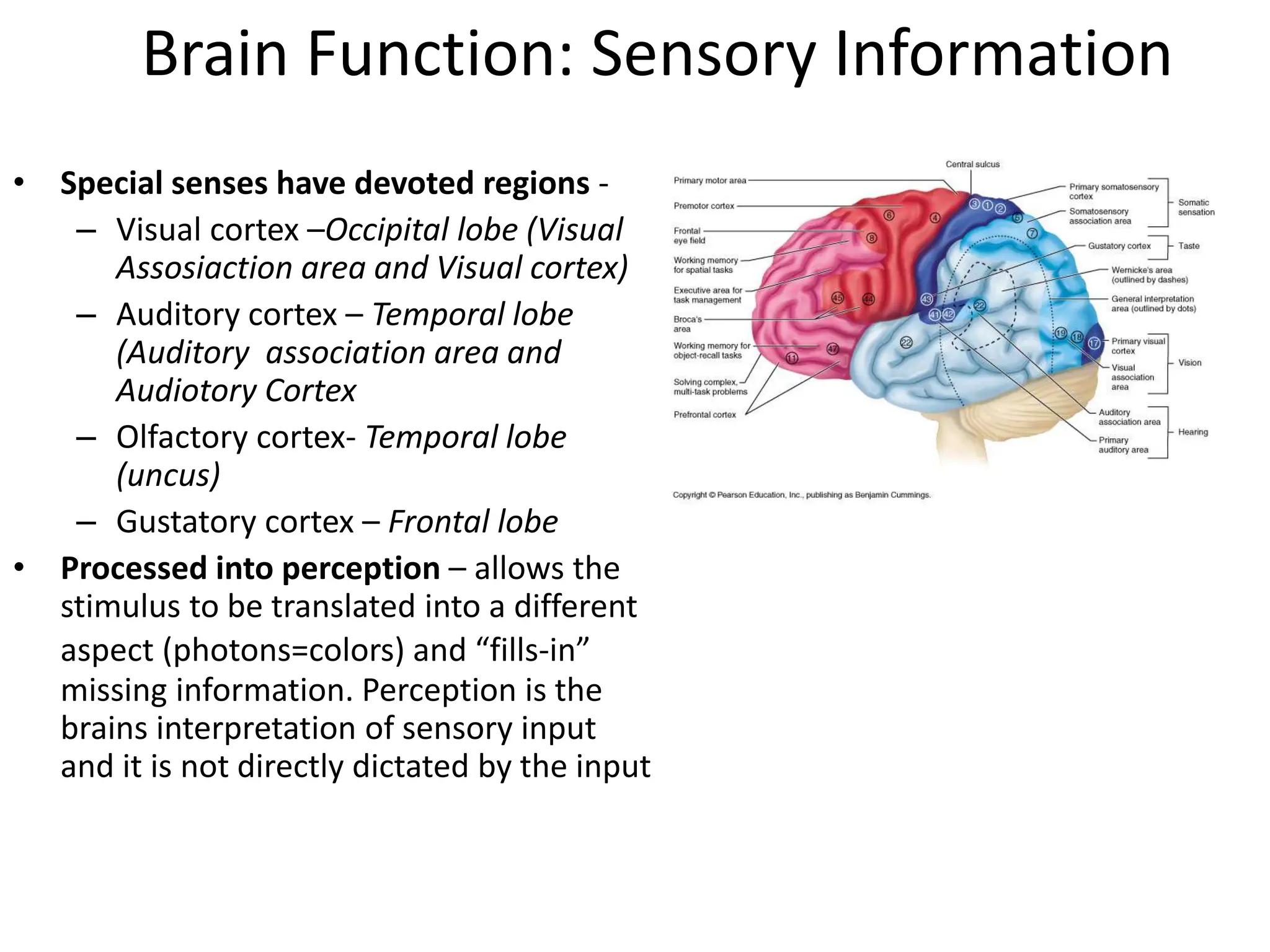
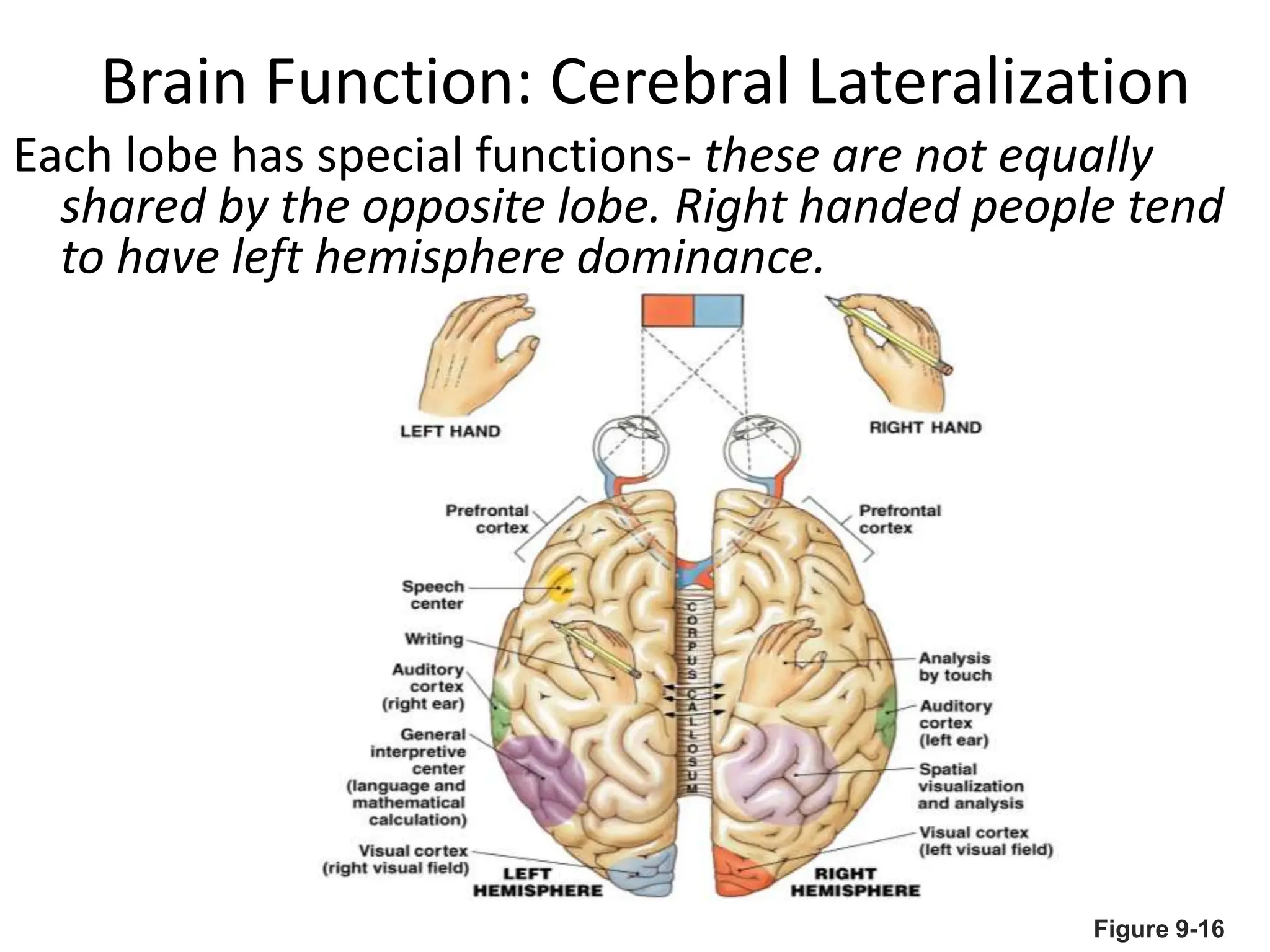
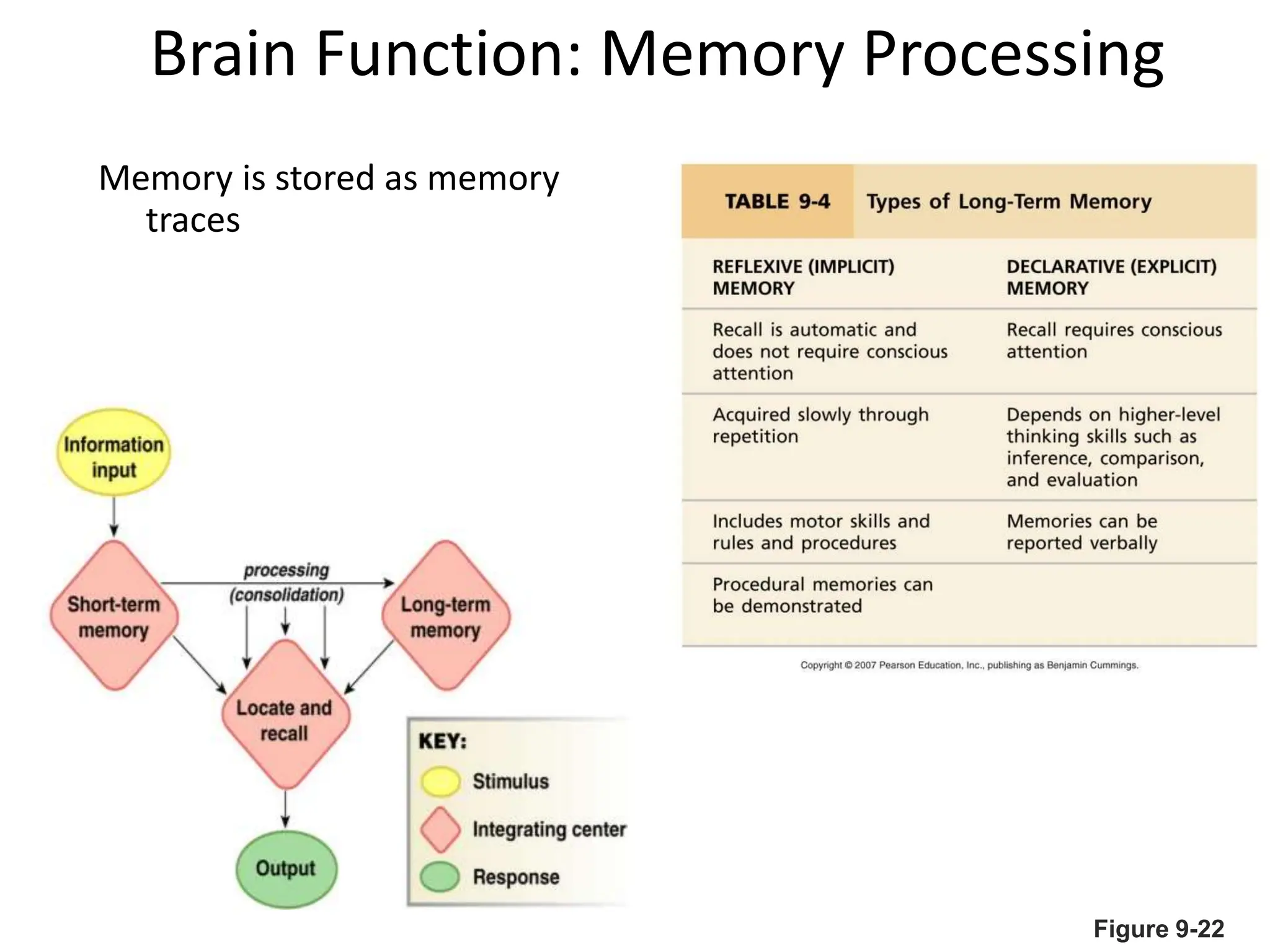
3. Sensory information is processed in specific cortical regions before being perceived. Motor output is controlled by motor areas and influenced by sensory input, cognition, and behavior