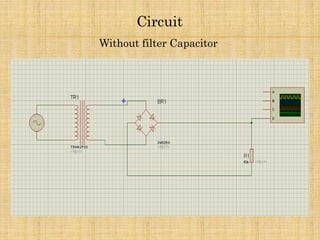
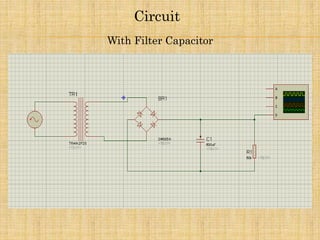
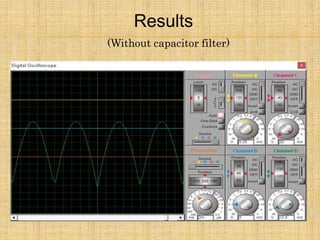
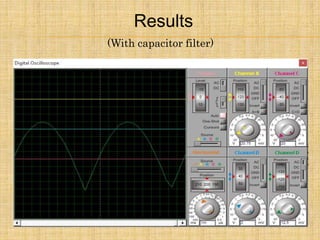
1) The document describes a full wave bridge rectifier circuit with and without a filter capacitor.
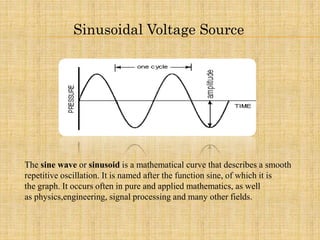
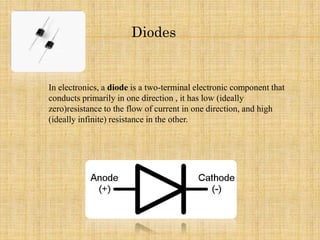
2) It explains how the circuit works by using 4 diodes to convert an AC input voltage into a DC output voltage that only contains the positive half of the sinusoidal wave.
3) The summary compares the results with and without a filter capacitor, noting that the capacitor reduces the ripple in the output when used.