Embed presentation
Download to read offline





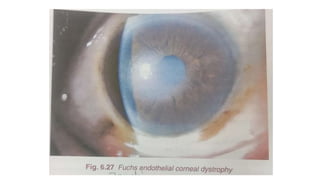




Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy is a slow progressive, bilateral eye condition that primarily affects females. It has four stages: corneal guttata, edema, bullous keratopathy, and scarring. The disease is characterized by a decrease in endothelial cell count and density over time. Early stages are asymptomatic, but later stages involve pain, decreased vision, and corneal scarring. Treatment options include lubricants, medications, and penetrating keratoplasty for advanced cases.









