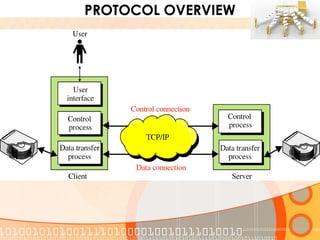
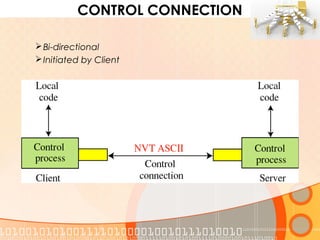
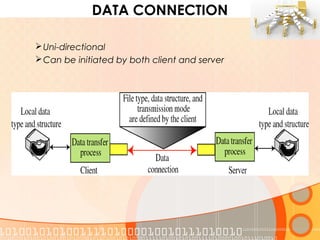
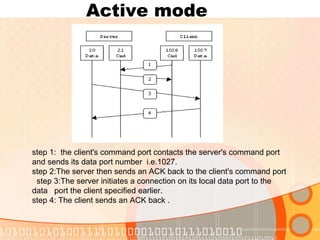
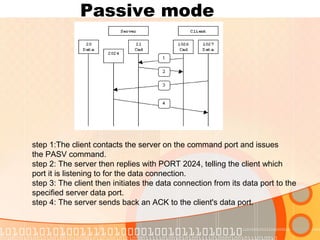
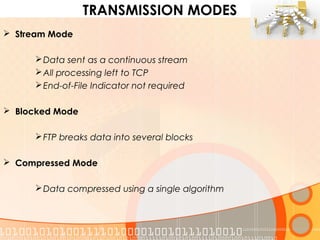
The document provides an overview of the File Transfer Protocol (FTP), detailing its network architecture, control and data connections, and authentication methods. It also describes the two connection modes (active and passive), file structures, and transmission modes used in FTP. The main function of FTP is to facilitate the exchange of files over TCP/IP networks.