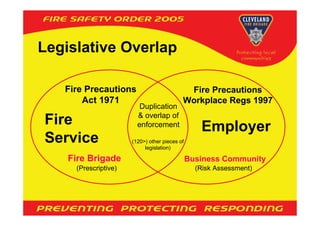
The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 establishes fire safety regulations applicable to various premises, requiring a responsible person to conduct fire risk assessments and maintain safety measures. It excludes certain locations such as domestic premises and ships, and mandates compliance through general fire precautions while delineating the role of the fire service and enforcement authorities. The document includes guidance on fire safety for different types of premises and outlines steps for risk assessment and compliance monitoring.