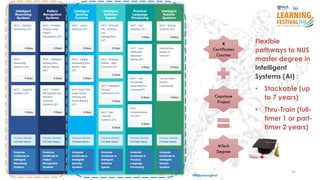
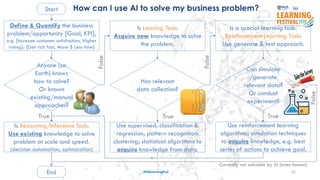
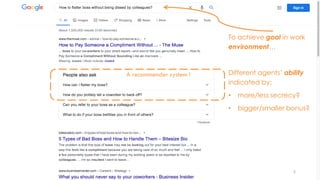
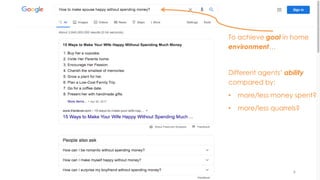
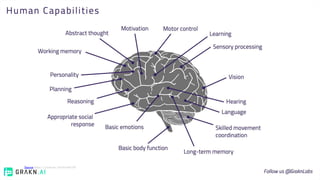
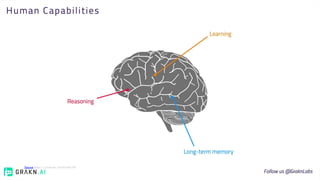
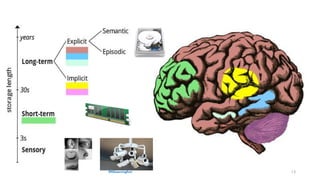
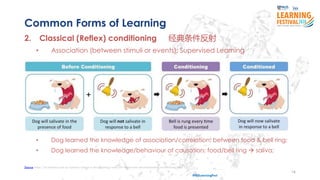
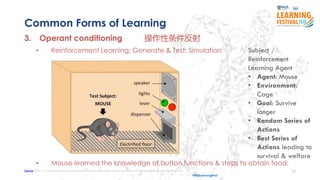
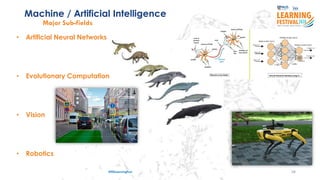
The document discusses the concept of intelligence, highlighting the distinctions between human and machine intelligence in various environments such as school, work, and home. It details different learning and reasoning processes, including habituation, classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observational learning, while paralleling these processes with artificial intelligence systems. The document also emphasizes the importance of continuous learning and development in AI technologies and encourages further exploration through educational programs.




















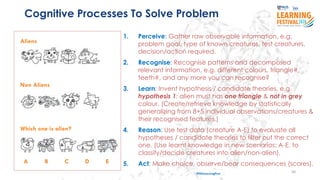
![Functions/Models: Perceive 受; Think/Reason 想; Act 行; Recognize/Learn 识;
31
#ISSLearningFest
Cognitive Processes/Functions/Models
[ Patterns & Exp ]
[ Percepts ]
[ Representations ]
[ Solutions ]Model:
Reason/Think
Model:
Learn
Model:
Recognize
Model:
Act
Model:
Perceive
[ Sensors ]
Rule based learning:
Mom told me
never to touch !
Similarity
based
recognition
Logic based reasoning
(Use/Apply knowledge
in new/SG scenario)
Act: Avoid touching !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day111-200825092544/85/From-Human-Intelligence-to-Machine-Intelligence-31-320.jpg)
![Functions/Models: Perceive 受; Think/Reason 想; Act 行; Recognize/Learn 识;
32
#ISSLearningFest
Cognitive Processes/Functions/Models
[ Patterns & Exp ]
[ Percepts ]
[ Representations ]
[ Solutions ]Model:
Reason/Think
Model:
Learn
Model:
Recognize
Model:
Act
Model:
Perceive
[ Sensors ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day111-200825092544/85/From-Human-Intelligence-to-Machine-Intelligence-32-320.jpg)