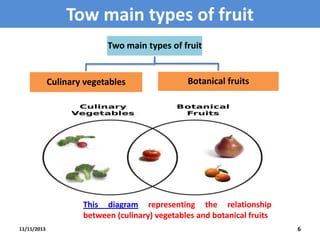
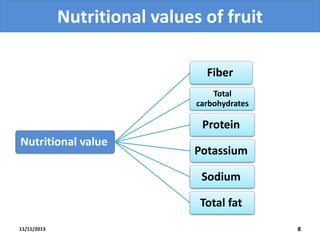
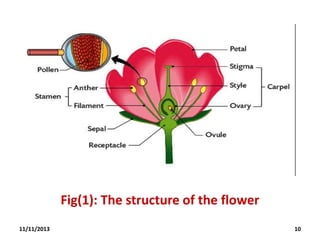
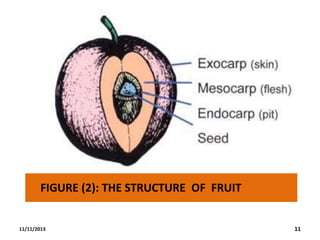
This document provides an outline and overview of a biology lecture on fruits given by Halala Rahman Qadir. The objectives are to define fruit, understand its structure, advantages, and types. Fruits are defined botanically as the seed-bearing part of a flowering plant derived from ovaries. There are two main types - culinary vegetables and botanical fruits. Fruits are nutritious and important for plant reproduction, carrying seeds. The development of fruit involves pollination, fertilization, and growth. Examples of fruit types discussed are berries, drupes, legumes, and achenes. Homework questions and references are also included.