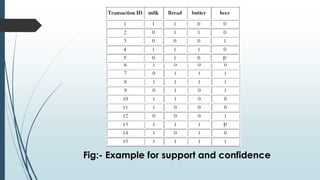
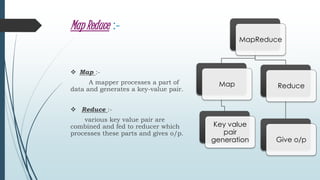
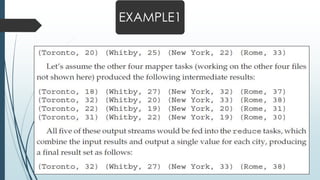
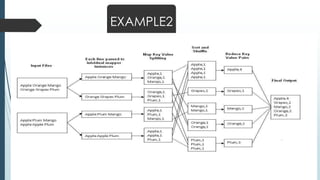
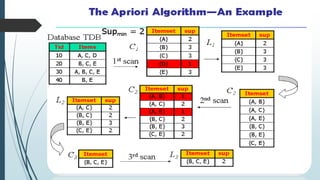
Frequent itemset mining on big data involves finding frequently occurring patterns in large datasets. Hadoop is an open-source framework for distributed storage and processing of big data using MapReduce. MapReduce allows distributed frequent itemset mining algorithms to scale to large datasets by partitioning the search space across nodes. Common approaches include single-pass counting, fixed and dynamic pass combined counting, and parallel FP-Growth algorithms. Distribution of the prefix tree search space and balanced partitioning are important for adapting algorithms to the MapReduce framework.