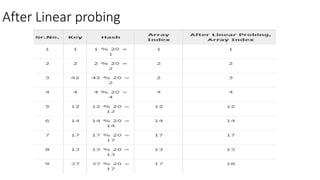
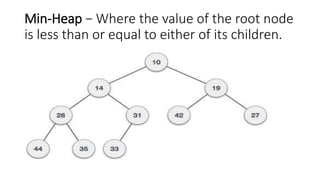
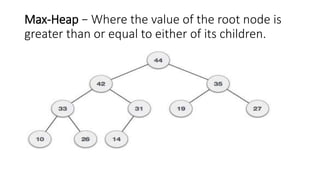
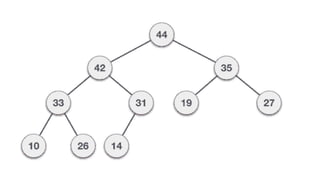
The document discusses heap data structures, detailing max heaps and min heaps, with examples of construction and deletion algorithms using C code. It also covers hash tables, providing an overview of how data is stored associatively with a focus on hashing techniques and the distribution of key-value pairs. Additionally, the document includes a practical example of implementing a hash table with specified items.





![1.#include <stdio.h>
2.#include <stdlib.h>
3.#define MAX 20
4.void maxheapify(int *, int, int);
5.int* buildmaxheap(int *, int);
6.void main()
7.{
8.int i, t, n;
9.int *a = calloc(MAX, sizeof(int));
10.int *m = calloc(MAX, sizeof(int));
11.printf("Enter no of elements in the arrayn");
12.scanf("%d", &n);
13.printf("Enter the arrayn");
14.for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
15.scanf("%d", &a[i]);
16.}
17.m = buildmaxheap(a, n);
18.printf("The heap isn");
19.for (t = 0; t < n; t++) {
20.printf("%dn", m[t]);
21.}
22.}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsconcepts-180522073846/85/DataStructure-Concepts-HEAP-HASH-Graph-9-320.jpg)
![1.int* buildmaxheap(int a[], int n)
2.{
3.int heapsize = n;
4.int j;
5.for (j = n/2; j >= 0; j--) {
6.maxheapify(a, j, heapsize);
7.}
8.return a;
9.}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsconcepts-180522073846/85/DataStructure-Concepts-HEAP-HASH-Graph-10-320.jpg)
![1.void maxheapify(int a[], int i, int heapsize)
2.{
3.int temp, largest, left, right, k;
4.left = (2*i+1);
5.right = ((2*i)+2);
6.if (left >= heapsize)
7.return;
8.else {
9.if (left < (heapsize) && a[left] > a[i])
10.largest = left;
11.else
12.largest = i;
13.if (right < (heapsize) && a[right] > a[largest])
14.largest = right;
15.if (largest != i) {
16.temp = a[i];
17.a[i] = a[largest];
18.a[largest] = temp;
19.maxheapify(a, largest, heapsize);
20.}
21.}
22.}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsconcepts-180522073846/85/DataStructure-Concepts-HEAP-HASH-Graph-11-320.jpg)