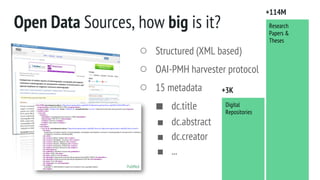
The document describes the development of a research paper recommender system utilizing metadata from various open access digital repositories, focusing on methodologies for content recommendation based on keywords and multi-thesaurus approaches. It outlines technical validation, including data harvesting with OAI-PMH, the structure of metadata, and performance metrics from a prototype analysis. Future work involves enhancements for multi-repository recommendations, scalability assessments, and user validation tests.
















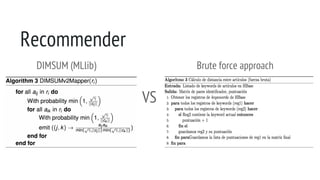

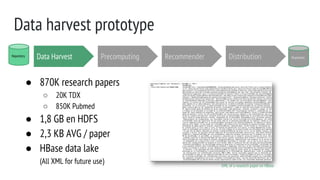
![Repository
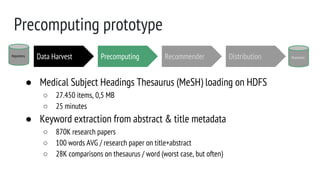
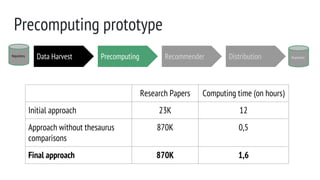
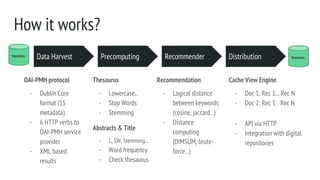
Data harvest prototype
Data Harvest
● First, XML on FS. Second approach, insert on HBase.
● Fetch XML + insert on HBase
○ Adapt (an existing) harvester module
○ To do a new harvester
● New harvester implementation, effective but not efficient
○ Connection management problems
○ [prototype] manual intervention vs improve connection management
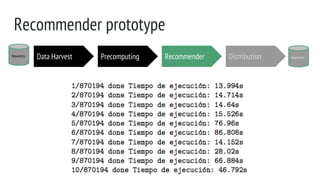
Precomputing RecommenderRepository
Distribution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scientificoutputsrecommender-150921112836-lva1-app6891/85/Research-Papers-Recommender-based-on-Digital-Repositories-Metadata-26-320.jpg)