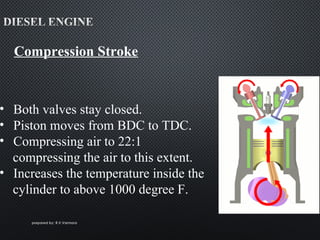
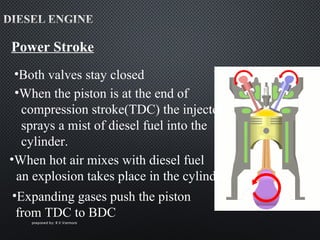
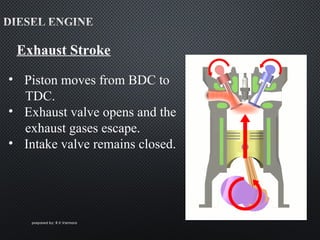
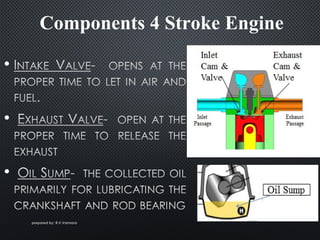
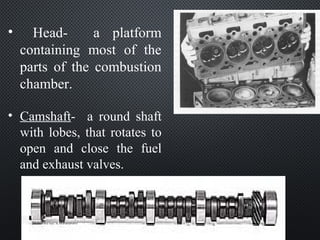
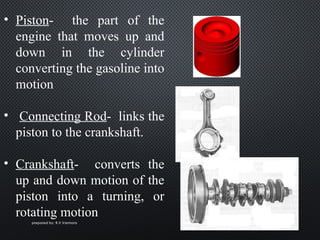
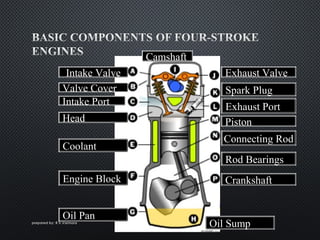
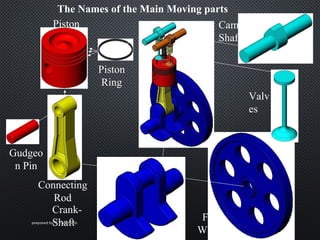
The document describes the four strokes of a diesel engine: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. In the intake stroke, air enters the cylinder as the piston moves down. In the compression stroke, both valves remain closed and the piston compresses the air. In the power stroke, fuel is injected and ignites when the piston reaches top dead center, pushing the piston back down. Finally, in the exhaust stroke, the exhaust valve opens and waste gases are expelled as the piston moves back up. The document also lists key engine components like the head, camshaft, piston, connecting rod, and crankshaft.