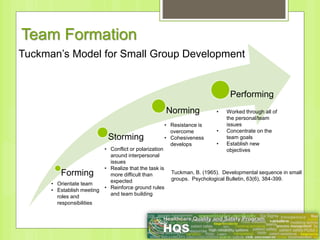
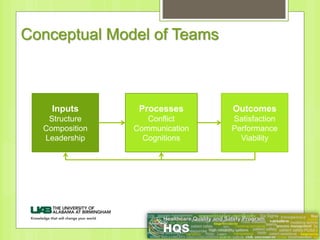
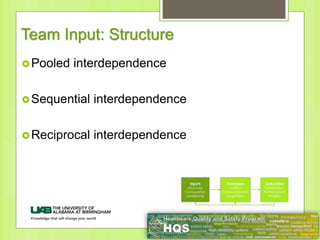
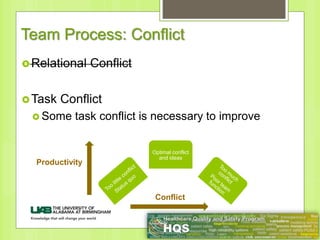
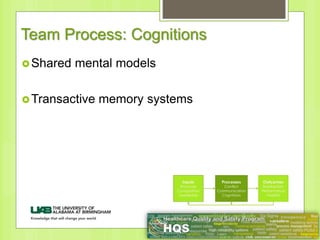
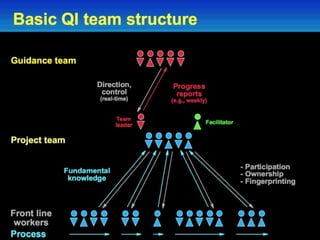
This document provides information on forming effective teams in healthcare settings. It discusses the importance of teams and defines what constitutes a team. Characteristics of effective teams include shared goals, clear roles, mutual trust, effective communication, and measurable processes and outcomes. Barriers to effective teamwork include dysfunction, mistrust, and poor communication. Facilitators include well-defined goals and objectives, selecting members based on skills, having defined roles for each member, developing mutual respect and trust, and effective management. The document also discusses team inputs like structure, composition, and leadership as well as processes like conflict management, communication, and shared mental models that influence outcomes like performance and satisfaction.